Abstract
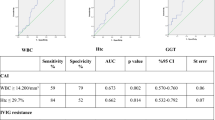
Kawasaki disease (KD) is characterized by myocarditis and left ventricular dysfunction during the acute phase of the illness. Despite treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), a significant number of patients are IVIG resistant. We evaluated KD patients in the acute phase of illness using tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) to assess whether myocardial dysfunction may predict IVIG resistance. All patients with acute KD presenting to Children’s Hospital Colorado from February 2007 through March 2014 were included in this study and underwent echocardiograms with TDI evaluation at diagnosis. Patients were divided into two groups: IVIG resistant and IVIG responder. Group differences were assessed using Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney and Chi-square testing. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was utilized to determine threshold values of TDI measurements associated with IVIG resistance. Fifty-one age-matched IVIG resistant patients were compared to 51 IVIG responder patients [median age, IQR 44.57 (20.13–77.07) vs. 33.49 (17.30–62.89) months, p < 0.44]. There were significant differences in the septal and mitral early diastolic velocities (E′) (p < 0.001 and p < 0.01), respectively. ROC analysis demonstrated that tricuspid E′ <0.15 cm/s, septal E′ <0.12 cm/s, and mitral E′ <0.16 cm/s were good predictors of IVIG unresponsiveness (AUC = 0.66, 0.66, and 0.70, respectively). There were no differences between the systolic velocities and late diastolic velocities (A′). IVIG resistant KD patients present with significantly greater diastolic dysfunction compared to responders in patients with KD. TDI may be a useful tool to differentiate KD patients at higher risk of IVIG resistance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoozgar H, Mehdizadeh S, Ajami G, Alyasin S, Borzoee M, Abtahi S, Cheriki S (2009) Evaluation of myocardial function by pulsed tissue Doppler in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 30(7):936–940
Anderson TM, Meyer RA, Kaplan S (1985) Long-term echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac size and function in patients with Kawasaki disease. Am Heart J 110(1 Pt 1):107–115
Ashouri N, Takahashi M, Dorey F, Mason W (2008) Risk factors for nonresponse to therapy in Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 153(3):365–368
Daniels LB, Gordon JB, Burns JC (2012) Kawasaki disease: late cardiovascular sequelae. Curr Opin Cardiol 27(6):572–577
Daniels LB, Tjajadi MS, Walford HH, Jimenez-Fernandez S, Trofimenko V, Fick DB Jr, Phan HA, Linz PE, Nayak K, Kahn AM, Burns JC, Gordon JB (2012) Prevalence of Kawasaki disease in young adults with suspected myocardial ischemia. Circulation 125(20):2447–2453
Egami K, Muta H, Ishii M, Suda K, Sugahara Y, Iemura M, Matsuishi T (2006) Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 149(2):237–240
Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Takeuchi K, Okada Y, Tamura K, Tomomasa T, Morikawa A (2006) Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 113(22):2606–2612
Kobayashi T, Saji T, Otani T, Takeuchi K, Nakamura T, Arakawa H, Kato T, Hara T, Hamaoka K, Ogawa S, Miura M, Nomura Y, Fuse S, Ichida F, Seki M, Fukazawa R, Ogawa C, Furuno K, Tokunaga H, Takatsuki S, Hara S, Morikawa A (2012) Efficacy of immunoglobulin plus prednisolone for prevention of coronary artery abnormalities in severe Kawasaki disease (RAISE study): a randomised, open-label, blinded-endpoints trial. Lancet 379(9826):1613–1620
Koteda Y, Suda K, Kishimoto S, Ito S, Kudo Y, Nishino H, Ishii H, Iemura M, Matuishi T (2009) Impact of intravenous immunoglobulin infusion on longitudinal left ventricular performance in patients with acute Kawasaki disease of usual course. J Cardiol 54(1):45–51
Kurotobi S, Kawakami N, Shimizu K, Aoki H, Nasuno S, Takahashi K, Kogaki S, Ozono K (2005) Brain natriuretic peptide as a hormonal marker of ventricular diastolic dysfunction in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 26(4):425–430
Marcella JJ, Ursell PC, Goldberger M, Lovejoy W, Fenoglio JJ Jr, Weiss MB (1983) Kawasaki syndrome in an adult: endomyocardial histology and ventricular function during acute and recovery phases of illness. J Am Coll Cardiol 2(2):374–378
Matsuura H, Ishikita T, Yamamoto S, Umezawa T, Ito R, Hashiguchi R, Saji T, Matsuo N, Takano M (1987) Gallium-67 myocardial imaging for the detection of myocarditis in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome): the usefulness of single photon emission computed tomography. Br Heart J 58(4):385–392
Moffett BS, Syblik D, Denfield S, Altman C, Tejtel-Sexson K (2015) Epidemiology of immunoglobulin resistant Kawasaki disease: results from a large, national database. Pediatr Cardiol 36(2):374–378
Moran AM, Newburger JW, Sanders SP, Parness IA, Spevak PJ, Burns JC, Colan SD (2000) Abnormal myocardial mechanics in Kawasaki disease: rapid response to gamma-globulin. Am Heart J 139(2 Pt 1):217–223
Muta H, Ishii M, Furui J, Nakamura Y, Matsuishi T (2006) Risk factors associated with the need for additional intravenous gamma-globulin therapy for Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr 95(2):189–193
Nakano H, Ueda K, Saito A, Nojima K (1985) Left ventricular systolic function in children with coronary arterial lesion following Kawasaki disease. Heart Vessels 1(2):89–93
Newburger JW, Fulton DR (2004) Kawasaki disease. Curr Opin Pediatr 16(5):508–514
Newburger JW, Sanders SP, Burns JC, Parness IA, Beiser AS, Colan SD (1989) Left ventricular contractility and function in Kawasaki syndrome. Effect of intravenous gamma-globulin. Circulation 79(6):1237–1246
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, Colan SD, Duffy CE, Fulton DR, Glode MP et al (1991) A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N Engl J Med 324(23):1633–1639
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 110(17):2747–2771
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114(6):1708–1733
Sano T, Kurotobi S, Matsuzaki K, Yamamoto T, Maki I, Miki K, Kogaki S, Hara J (2007) Prediction of non-responsiveness to standard high-dose gamma-globulin therapy in patients with acute Kawasaki disease before starting initial treatment. Eur J Pediatr 166(2):131–137
Selamet Tierney ES, Newburger JW, Graham D, Baker A, Fulton DR, Colan SD (2011) Diastolic function in children with Kawasaki disease. Int J Cardiol 148(3):309–312
Sleeper LA, Minich LL, McCrindle BM, Li JS, Mason W, Colan SD, Atz AM, Printz BF, Baker A, Vetter VL, Newburger JW (2011) Evaluation of Kawasaki disease risk-scoring systems for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance. J Pediatr 158(5):831–835 e833
Takeuchi D, Saji T, Takatsuki S, Fujiwara M (2007) Abnormal tissue doppler images are associated with elevated plasma brain natriuretic peptide and increased oxidative stress in acute Kawasaki disease. Circ J Off J Jpn Circ Soc 71(3):357–362
Tremoulet AH, Best BM, Song S, Wang S, Corinaldesi E, Eichenfield JR, Martin DD, Newburger JW, Burns JC (2008) Resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 153(1):117–121
Vogel M, Smallhorn JF, Freedom RM (1992) Serial analysis of regional left ventricular wall motion by two-dimensional echocardiography in patients with coronary artery enlargement after Kawasaki disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 20(4):915–919
Yanagawa H, Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Oki I, Kayaba K (2006) Incidence of Kawasaki disease in Japan: the nationwide surveys of 1999–2002. Pediatr Int Off J Jpn Pediatr Soc 48(4):356–361
Yutani C, Go S, Kamiya T, Hirose O, Misawa H, Maeda H, Kozuka T, Onishi S (1981) Cardiac biopsy of Kawasaki disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med 105(9):470–473
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phadke, D., Patel, S.S., Dominguez, S.R. et al. Tissue Doppler Imaging as a Predictor of Immunoglobulin Resistance in Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 36, 1618–1623 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1206-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1206-5