Abstract
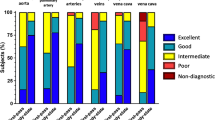
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of a high-resolution 3D dark-blood turbo spin echo sequence with variable flip angles (3D-SPACE) in evaluation of congenital heart disease. SPACE sequence was performed in 20 patients (mean age, 17.6 ± 12.6 years, range 9 months–57 years, M: 13) with either unrepaired (N = 3) or post-repair (n = 17) congenital heart disease. All scans were performed on 1.5 T Aera scanners (Siemens). Two separate observers with expertise in cardiovascular imaging scored the quality of the images for blood suppression and definition of key anatomical structures in a blinded fashion using a 5 grade scoring system. Mean of average overall quality scores for two observers was 4 ± 0.62. All overall quality scores were greater than 3. None of the studies were deemed nondiagnostic. Mean length of the SPACE acquisition time was 12.7 min (4–21 min). There was no significant correlation between image quality and duration of scans. Lack of blood suppression was the limiting factor in image quality with the most common place being ascending aorta in nine patients. However, overall blood suppression score was very good with score of 3.9 ± 0.43. There was very good overall agreement between observers in rating the image quality (85.6 % agreement, kappa 0.5, standard error 0.04, p < 0.0001). The 3D-SPACE dark-blood sequence with near-isotropic spatial resolution coupled with respiratory and cardiac gating can be feasibly performed in all age groups with diagnostic image quality in all cases in this study.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Driessen MM, Breur JM, Budde RP, van Oorschot JW, van Kimmenade RR, Sieswerda GT et al (2015) Advances in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of congenital heart disease. Pediatr Radiol 45(1):5–19
Fan Z, Zhang Z, Chung YC, Weale P, Zuehlsdorff S, Carr J et al (2010) Carotid arterial wall MRI at 3T using 3D variable-flip-angle turbo spin-echo (TSE) with flow-sensitive dephasing (FSD). J Magn Reson Imaging 31(3):645–654
Fratz S, Chung T, Greil GF, Samyn MM, Taylor AM, Valsangiacomo Buechel ER et al (2013) Guidelines and protocols for cardiovascular magnetic resonance in children and adults with congenital heart disease: SCMR expert consensus group on congenital heart disease. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 15:51
Morita S, Ueno E, Masukawa A, Suzuki K, Machida H, Fujimura M et al (2009) Comparison of SPACE and 3D TSE MRCP at 1.5T focusing on difference in echo spacing. Magn Reson Med Sci 8(3):101–105
Rogers L, Li J, Liu L, Balluz R, Rychik J, Ge S (2013) Advances in fetal echocardiography: early imaging, three/four dimensional imaging, and role of fetal echocardiography in guiding early postnatal management of congenital heart disease. Echocardiography 30(4):428–438
Siripornpitak S, Pornkul R, Khowsathit P, Layangool T, Promphan W, Pongpanich B (2013) Cardiac CT angiography in children with congenital heart disease. Eur J Radiol 82(7):1067–1082
Wong SK, Mobolaji-Iawal M, Arama L, Cambe J, Biso S, Alie N et al (2014) Atherosclerosis imaging using 3D black blood TSE SPACE vs 2D TSE. World J Radiol 6(5):192–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malayeri, A.A., Spevak, P.J. & Zimmerman, S.L. Utility of a High-Resolution 3D MRI Sequence (3D-SPACE) for Evaluation of Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 36, 1510–1514 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1194-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1194-5