Abstract
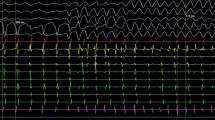
In patients with congenital heart disease (CHD), the association between supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), type of pathophysiology, and therapeutic interventions in a population-based cohort warrants further examination. A retrospective, longitudinal 15-year data set (1996–2010) was analyzed. Inclusion criteria included age ≤17 years, enrolled in South Carolina State Medicaid, and diagnosed as having one or more CHDs as well as SVT. SVT was diagnosed in 6.5 % of CHD patients (N = 1,169) during the 15-year epoch investigated. SVT was less likely to occur in African-American (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.76) or male patients (HR = 0.88), but it was significantly more likely to occur in patients age ≤12 months or in adolescents ≥13 years in those undergoing multiple surgeries/medical interventions for their CHD (HR = 1.14), those receiving antiarrhythmic/diuretic/preload-/afterload-reducing medications (HR = 5.46), and those with severe/cyanotic CHDs (HR = 1.52) or chromosomal abnormalities (HR = 1.64). Children who had an atrial septal defect secundum (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 3.03) and those treated with diuretic or antiarrhythmic medication (aOR = 1.80) were significantly more likely to undergo SVT ablation, whereas those with late-onset pulmonary hypertension (ages 6–12 years old) were significantly less likely to undergo SVT ablation. SVT recurred in only 14 of 166 patients who underwent SVT ablation. Multiple medical interventions at an early age may increase the risk of SVT occurrence in young CHD patients regardless of the severity/complexity of the CHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand RG, Rosenthal GL, Van Hare GF, Snyder CS (2009) Is the mechanism of supraventricular tachycardia in pediatrics influenced by age, gender or ethnicity? Congenit Heart Dis 4(6):464–468
Bernstein D (2011). Epidemiology and genetic basis of congenital heart disease. In: RM Kliegman et al. (eds.), Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, Available at: http://www.mdconsult.com/books/page.do?eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4377-0755-7.00418-8-s0015&isbn=978-1-4377-0755-7&sid=1430184210&uniqId=408661955-3#4-u1.0-B978-1-4377-0755-7.00418-8-s0015. Accessed 23 Jan 2013
Botto LD, Correa A, Erickson JD (2001) Racial and temporal variations in the prevalence of heart defects. Pediatrics 107(3):E32
Buddhe S, Singh H, Du W, Karpawich PP (2012) Radiofrequency and cryoablation therapies for supraventricular arrhythmias in the young: five-year review of efficacies. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 35(6):711–717
Calabrò MP, Cerrito M, Luzza F, Oreto G (2008) Supraventricular tachycardia in infants: Epidemiology and clinical management. Curr Pharm Des 14(8):723–728
Census 2010, summary file 2, demographic profile 1 by state. Available at http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=DEC_10_SF2_SF2DP1&prodType=table. Accessed 4 Feb 2013
Chang PM, Silka MJ, Moromisato DY, Bar-Cohen Y (2010) Amiodarone versus procainamide for the acute treatment of recurrent supraventricular tachycardia in pediatric patients. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 3(2):134–140
Children under 18 [Table D1] and their designated parents and children under 18 and their designated parents [Table D2]—Characteristics of families (including region). Available at http://www.census.gov/hhes/socdemo/children/data/sipp/well2009/tables.html. Accessed 30 Jan 2013
Chiu SN, Lu CW, Chang CW, Chang CC, Lin MT, Lin JL et al (2009) Radiofrequency catheter ablation of supraventricular tachycardia in infants and toddlers. Circ J 73(9):1717–1721
De Santis A, Fazio G, Silvetti MS, Drago F (2008) Transcatheter ablation of supraventricular tachycardias in pediatric patients. Curr Pharm Des 14(8):788–793
Dilber E, Mutlu M, Dilber B, Aslan Y, Gedik Y, Celiker A (2010) Intravenous amiodarone used alone or in combination with digoxin for life-threatening supraventricular tachyarrhythmia in neonates and small infants. Pediatr Emerg Care 26(2):82–84
Hafez M, Abu-Elkheir M, Shokier M, Al-Marsafawy H, Abo-Haded H, El-Maaty MA (2012) Radiofrequency catheter ablation in children with supraventricular tachycardias: intermediate term follow up results. Clin Med Insights Cardiol 6:7–16
Health insurance coverage for children under 19 years of age, at or below 200 % of poverty by state, 2006–2008 and 2009–2011. Available at http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/hlthins/data/children/low-income.html. Accessed 30 Jan 2013
Hoffman JI, Kaplan S (2002) The incidence of congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 39(12):1890–1900
Inaba AS, Horeczko T (2009) Cardiac disorders. In: Marx JA, Hockberger RS, Walls RM, et al (eds.) Rosen’s Emergency Medicine. 7th ed. Pa: Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia chap 166 Available at: http://www.mdconsult.com/books/page.do?eid=4-u1.0-B978-0-323-05472-0.00169-9-s0110&isbn=978-0-323-05472-0&sid=1423407102&uniqId=406675227-4#4-u1.0-B978-0-323-05472-0.00169-9-s0295. Accessed 30 Jan 2013
Kanter RJ (2010) Pearls for ablation in congenital heart disease. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 21:223–230
Karpawich PP, Pettersen MD, Gupta P, Shah N (2008) Infants and children with tachycardia: Natural history and drug administration. Curr Pharm Des 14(8):743–752
Knudson JD, Cannon BC, Kim JJ, Moffett BS (2011) High-dose sotalol is safe and effective in neonates and infants with refractory supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Pediatr Cardiol 32(7):896–903
Salerno JC, Garrison MM, Larison C, Seslar SP (2011) Case fatality in children with supraventricular tachycardia in the United States. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 34(7):832–836
Sanatani S, Potts JE, Reed JH, Saul JP, Stephenson EA, Gibbs KA et al (2012) The study of antiarrhythmic medications in infancy (SAMIS): a multicenter, randomized controlled trial comparing the efficacy and safety of digoxin versus propranolol for prophylaxis of supraventricular tachycardia in infants. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 5(5):984–991
Sulafa Ali KM (2008) Collateral effects of antiarrhythmics in pediatric age. Curr Pharm Des 14(8):782–787
Vignati G, Annoni G (2008) Characterization of supraventricular tachycardia in infants: Clinical and instrumental diagnosis. Curr Pharm Des 14(8):729–735
Acknowledgments
Funding for this study was provided through a Clinical Incentive Research Grant from the University of South Carolina, Office of the Provost. No external funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, A., Black, G.B., Park, YM.M. et al. Factors Associated With the Occurrence and Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia in a Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease Cohort. Pediatr Cardiol 35, 368–373 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-013-0784-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-013-0784-3