Abstract
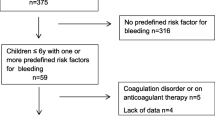
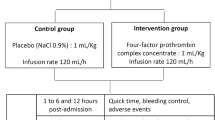
Bleeding during and after cardiac surgery is a major issue in pediatric patients. A prospective cohort study was conducted to evaluate the effect of a commercially available prothrombin complex (Confidex) administered in cardiac surgery after weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass of infants with nonsurgical bleeding. In this study, 14 patients younger than 1 year received a Confidex bolus and were matched with 11 patients of a similar age who did not receive the drug. The preoperative coagulation profile was similar in the two groups. No side effects, including anaphylaxis or thrombotic events, were observed. The numbers of units of packed red blood cells and fresh frozen plasma administered both intra- and postoperatively were similar. The postoperative coagulation examination results and thromboelastographic parameters did not differ significantly between the two groups. However, the Confidex patients bled significantly less than the control subjects during the first 24 postoperative hours. The median volume of drained blood was 0.0 ml/kg h (range 0–1.9 ml/kg h) compared with 1.9 ml/kg h (range 1–3 ml/kg h) (p = 0.009). At least one unit of packed red blood cells in the postoperative phase was required by 2 patients (14 %) in the Confidex group and six patients (54 %) in the control group (odds ratio [OR], 0.13; 95 % confidence interval [CI], 0.02–0.9; p = 0.03). The median duration of mechanical ventilation was 3 days (range 2–4 days) in the Confidex group and 4 days (range 0–8 days) in the control group (p = 0.66). The median stay in the intensive care unit was 6 days (range 5–9 days) in the Confidex group and 7 days (range 4–12 days) in the control group (p = 0.88). The use of Confidex for infants undergoing cardiac surgery was safe and effective. It reduced postoperative bleeding and allowed fewer units of packed red blood cells to be infused in the postoperative phase without major side effects.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander DC, Butt WW, Best JD, Donath SM, Monagle PT, Shekerdemian LS (2010) Correlation of thromboelastography with standard tests of anticoagulation in paediatric patients receiving extracorporeal life support. Thromb Res 125:387–392
Bruce D, Nokes TJ (2008) Prothrombin complex concentrate (Beriplex P/N) in severe bleeding: experience in a large tertiary hospital. Crit Care 12:R105
Chaiwat O, Lang JD, Vavilala MS, Wang J, MacKenzie EJ, Jurkovich GJ, Rivara FP (2009) Early packed red blood cell transfusion and acute respiratory distress syndrome after trauma. Anesthesiology 110:351–360
Evans G, Luddington R, Baglin T (2001) Beriplex P/N reverses severe warfarin-induced overanticoagulation immediately and completely in patients presenting with major bleeding. Br J Haematol 115:998–1001
Guzzetta NA, Miller BE, Todd K, Szlam F, Moore RH, Tosone SR (2005) An evaluation of the effects of a standard heparin dose on thrombin inhibition during cardiopulmonary bypass in neonates. Anesth Analg 100:1276–1282
Harker LA, Malpass TW, Branson HE, Hessel EA II, Slichter SJ (1998) Mechanism of abnormal bleeding in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: acquired transient platelet dysfunction associated with selective a-granule release. Blood 56:824–834
Holland L, Warkentin TE, Refaai M, Crowther MA, Johnston MA, Sarode R (2009) Suboptimal effect of a three-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (Profilnine-SD) in correcting supratherapeutic international normalized ratio due to warfarin overdose. Trasfusion 49:1171–1177
Ignjatovic V, Furmedge J, Newall F, Chan A, Berry L, Fong C, Cheng K, Monagle P (2006) Age-related differences in heparin response. Thromb Res 118:741–745
Khan H, Belsher J, Yilmaz M, Afessa B, Winters JL, Moore SB, Hubmayr RD, Gajic O (2007) Fresh-frozen plasma and platelet transfusions are associated with development of acute lung injury in critically ill medical patients. Chest 131:1308–1314
Levy JH, Tanaka KA, Dietrich W (2008) Perioperative hemostatic management of patients treated with vitamin K antagonists. Anesthesiology 109:918–926
Miller BE, William GD (2010) Bleeding and coagulation: monitoring and management. In: Andropoulos DB, Stayer SA, Russell IA, Mossad EB (eds) Anesthesia for congenital heart disease, 2nd edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, p 207–219
Oliver WC (2009) Anticoagulation and coagulation management for ECMO. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 13:154–175
Owings JT, Pollock ME, Gosselin RC, Ireland K, Jahr JS, Larkin EC (2000) Anticoagulation of children undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass is overestimated by current monitoring techniques. Arch Surg 135:1042–1047
Preston FE, Laidlaw ST, Sampson B, Kitchen S (2002) Rapid reversal of oral anticoagulation with warfarin by a prothrombin complex concentrate (Beriplex): efficacy and safety in 42 patients. Br J Haematol 116:619–624
http://www.who.int/bloodproducts/catalogue/BlooJan10.pdf. Accessed 5 July 2013
Riess HB, Meier-Hellmann A, Motsch J, Elias M, Kursten FW, Dempfle CE (2007) Prothrombin complex concentrate (Octaplex) in patients requiring immediate reversal of oral anticoagulation. Thromb Res 121:9–16
Rinder CS, Gaal D, Student LA, Smith BR (1994) Platelet-leukocyte activation and modulation of adhesions receptors in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 107:280–288
Schick KS, Fertmann JM, Jauch KW, Hoffmann JN (2009) Prothrombin complex concentrate in surgical patients: retrospective evaluation of vitamin K antagonist reversal and treatment of severe bleeding. Crit Care 13:R191
Sørensen B, Spahn DR, Innerhofer P, Spannagl M, Rossaint R (2011) Clinical review: prothrombin complex concentrates: evaluation of safety and thrombogenicity. Crit Care 15:201
Warren O, Simon B (2009) Massive, fatal, intracardiac thrombosis associated with prothrombin complex concentrate. Ann Emerg Med 53:758–761
White R, Rushbrook J, McGoldrick J (2008) The dangers of prothrombin complex concentrate administration after heart surgery. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 19:609–610
Yeh T Jr, Kavarana MN (2005) Cardiopulmonary bypass and the coagulation system. Progr Pediatr Cardiol 21:87–115
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giorni, C., Ricci, Z., Iodice, F. et al. Use of Confidex to Control Perioperative Bleeding in Pediatric Heart Surgery: Prospective Cohort Study. Pediatr Cardiol 35, 208–214 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-013-0760-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-013-0760-y