Abstract
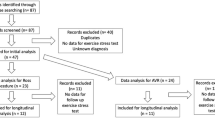
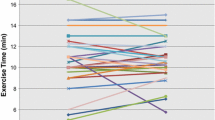
Adult studies suggest a better functional outcome after aortic valve replacement with a pulmonary autograft compared with mechanical or homograft valves. Little is known about functional results after Ross surgery in growing children. This study reports formal exercise stress echocardiographic data from 26 pediatric Ross patients. A retrospective cohort study analyzed stress echocardiographic data of patients who underwent Ross surgery as a child (<17 years old). All patients were operated by a single surgeon and underwent a Bruce protocol stress echocardiogram on the treadmill. Twenty-six patients (4 girls) were 9.3 ± 5.0 years at surgery and 14.9 ± 3.5 years (range 6.6–19.7 years) at follow-up. Mean follow-up was 5.4 ± 3.7 years (median 4.2). All were asymptomatic. The exercise time was normal in 87% of cases at 12.8 ± 2.5 min. On stress echocardiography, the mean right-ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) gradient increased from 38 ± 22 mmHg at rest to 82 ± 33 mmHg after exercise, but this did not correlate with exercise times. Stress echocardiography is useful in evaluating patients after childhood Ross surgery for aortic valve disease. In this pediatric cohort, most patients achieved normal exercise capacity. The presence of mild or moderate RVOT obstruction had no significant impact on exercise capacity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohm JO, Botha CA, Horke A, Hemmer W, Roser D, Blumenstock G et al (2006) Is the Ross operation still an acceptable option in children and adolescents? Ann Thorac Surg 82:940–947
Bruce RA, Kusumi, Hosmer FD (1973) Maximal oxygen intake and nomographic assessment of functional aerobic impairment in cardiovascular disease. Am Heart J 85:546–562
Da Costa F, Haggi H, Pinton R, Lenke W, Adam E, Costa IS (1998) Rest and exercise hemodynamics after the Ross procedure: an echocardiographic study. J Card Surg 13:177–185
Elkins RC, Lane MM, McCue C (2001) Ross operation in children: Late results. J Heart Valve Dis 10:736–741
Hazekamp MG, Grotenhuis HB, Schoof PH, Rijlaarsdam ME, Ottenkamp J, Dion RA (2005) Results of the Ross operation in a pediatric population. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 27:975–979
Hörer J, Hanke T, Stierle U, Takkenberg JJ, Bogers AJ, Hemmer W et al (2009) Homograft performance in children after the Ross operation. Ann Thorac Surg 88:609–615
Hraska V, Krajci M, Haun C, Ntalakoura K, Razek V, Lacour-Gayet F et al (2004) Ross and Ross-Konno procedure in children and adolescents: Mid-term results. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 25:742–747
Kadner A, Raisky O, Degandt A et al (2008) The Ross procedure in infants and young children. Ann Thorac Surg 85:803–809
Kalavrouziotis G, Raja S, Ciotti G, Karunaratne A, Corno AF, Pozzi M (2006) Medium-term results from pulmonary autografts after the Ross procedure in children and adolescents. Hellenic J Cardiol 47:337–343
Kampmann C, Wiethoff C, Wenzel A, Stolz G, Betancor M, Wippermann C et al (2000) Normal values of M mode echocardiographic measurements of more than 2000 healthy infants and children in central Europe. Heart 83:667–672
Khwaja S, Nigro JJ, Starnes VA (2005) The Ross procedure is an ideal aortic valve replacement operation for the teen patient. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu 8(1):173–175
Laforest I, Dumesnil JG, Briand M et al (2002) Hemodynamic performance at rest and during exercise after aortic valve replacement: Comparison of pulmonary autografts versus aortic homografts. Circulation 106:57–62
Luciani GB, Favaro A, Casali G, Santini F, Mazzucco A (2005) Ross operation in the young: A ten-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg 80:2271–2277
Marino BS, Pasquali SK, Wernovsky G, Bockoven JR, McBride M, Cho CJ et al (2006) Exercise performance in children and adolescents after the Ross procedure. Cardiol Young 16:40–47
Pasquali SK, Shera D, Wernovsky G, Cohen MS, Tabbutt S, Nicolson S et al (2007) Midterm outcomes and predictors of reintervention after the Ross procedure in infants, children, and young adults. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 133:893–899
Pibarot P, Dumesnil JG, Briand M, Laforest I, Cartier P (2000) Hemodynamic performance during maximum exercise in adult patients with the Ross operation and comparison with normal controls and patients with aortic bioprostheses. Am J Cardiol 86:982–988
Puranik R, Tsang VT, Broadley A, Nordmeyer J, Lurz P, Muthialu N et al (2010) Functional outcomes after the Ross (pulmonary autograft) procedure assessed with magnetic resonance imaging and cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Heart 96:304–308
Ross DN (1967) Replacement of aortic and mitral valves with a pulmonary autograft. Lancet 2:956
Ruzmetov M, Vijay P, Rodefeld MD, Turrentine MW, Brown JW (2006) Evolution of aortic valve replacement in children: A single center experience. Int J Cardiol 113:194–200
Stewart RD, Backer CL, Hillman ND, Lundt C, Mavroudis C (2007) The Ross operation in children: Effects of aortic annuloplasty. Ann Thorac Surg 84:1326–1330
Takkenberg JJ, Kappetein AP, van Herwerden LA, Witsenburg M, Van Osch-Gevers L et al (2005) Pediatric autograft aortic root replacement: A prospective follow-up study. Ann Thorac Surg 80:1628–1633
Takkenberg JJ, Klieverik LM, Schoof PH, van Suylen RJ, van Herwerden LA, Zondervan PE et al (2009) The Ross procedure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 119:222–228
Wang A, Jaggers J, Ungerleider RM, Lim CS, Ryan T (2003) Exercise echocardiographic comparison of pulmonary autograft and aortic homograft replacements for aortic valve disease in adults. J Heart Valve Dis 12:202–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pauliks, L.B., Brian Clark, J., Rogerson, A. et al. Exercise Stress Echocardiography After Childhood Ross Surgery: Functional Outcome in 26 Patients From a Single Institution. Pediatr Cardiol 33, 797–801 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-012-0218-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-012-0218-7