Abstract
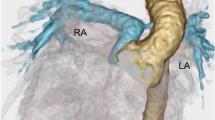
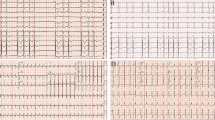
Ventricular pre-excitation causing reversible left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction has been reported in adults and children. We describe severe heart failure secondary to ventricular pre-excitation in a 3-month-old girl who presented with echocardiographic evidence of marked intraventricular dyssynchrony. The patient was initially considered for transplantation, but dual chamber left atrioventricular epicardial pacing initiated at 4.5 months of age resulted in a marked clinical and echocardiographic improvement. Five years later, successful radiofrequency ablation resulted in loss of pre-excitation and reversal of LV dyssynchrony, thus allowing pacemaker explantation. To our knowledge, this is one of very few reported cases of pre-excitation–induced cardiomyopathy affecting a young infant and the only case palliated with resynchronization pacing.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cadrin-Tourigny J, Fournier A, Andelfinger D, Khairy P (2008) Severe left ventricular dysfunction in infants with ventricular preexitation. Heart Rhythm 5:1320–1322
Emmel M, Balaji S, Sreeram N (2004) Ventricular preexitation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy: a casual relationship? Cardiol Young 14:594–599
Iwasaku T, Hirooka K, Taniguchi T, Hamano G, Utsunomitya Y, Nakagawa A et al (2009) Successful catheter ablation to accessory atrioventricular pathway as cardiac resynchronization therapy in a patient with dilated cardiomyopathy. Europace 11:121–123
Suffoletto MS, Dohi K, Cannnesso M, Saba S, Gorcsan J (2006) Novel speckle-tracking radial strain from routine black and white echocardiographic images to quantify dyssynchrony and predict response to cardiac resynchronization therapy. Circulation 113:960–968
Mele D, Pasanisi G, Capasso F, De Simone A, Morales MA, Poggio D et al (2006) Left intraventricular myocardial deformation dyssynchrony identifies responders to cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with heart failure. Eur Heart J 27:1070–1078
Pitzalis MV, Iacoviello M, Romito R, Massari F, Rizzon B, Luzzi G et al (2002) Cardiac resynchronization therapy tailored by echocardiographic evaluation of ventricular asynchrony. J Am Coll Cardiol 40:1615–1622
DeMaria A, Vera Z, Neumann A, Mason D (1976) Alterations in ventricular contraction pattern in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation 53:250–257
Tomaske M, Janousek J, Rázek V, Gebauer RA, Tomek V, Hindricks G et al (2008) Adverse effects of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with right septal or posteroseptal accessory pathways on cardiac function. Europace 10:181–189
Yamanaka S, Shirayama T, Inoue K, Kawata K, Yagi T, Azuma A et al (1998) Improved cardiac function after catheter ablation in a patient with type B Wolff-Parkingon-White syndrome with an old myocardial infarction. Jpn Circ J 62:860–862
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilina, M.V., Abrams, D.J., Lowe, M.D. et al. Resolution of Dyssynchronous Left Ventricular Failure via Cardiac Resynchronization and Subsequent Radiofrequency Ablation in an Infant With Pre-excitation. Pediatr Cardiol 31, 897–900 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-010-9733-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-010-9733-6