Abstract
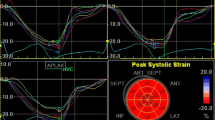
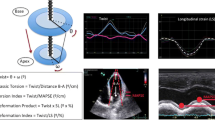
This study aimed to investigate left ventricular myocardial deformation in children with Kawasaki disease during the acute phase of their illness. A total of 50 patients and 35 normal control subjects were assessed. Data were obtained from the patients during the acute and convalescent phases of Kawasaki disease. Analyses of myocardial deformation [strain (ε), strain rate (SR)] was performed using two-dimensional speckle-tracking imaging in three directions (longitudinal, circumferential, and radial) at the basal and mid levels of the left ventricular myocardium. Basal longitudinal ε (P < 0.001) and midlongitudinal ε (P < 0.0001) were lower during the acute phase of the disease than in the control subjects and associated with serum albumin level and left ventricular mass index (LVMI). Midlongitudinal SR (P < 0.0001) was lower during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease than in the control subjects and associated with LVMI. Decreased systolic SR was not detected in any direction. In conclusion, left ventricular longitudinal systolic ε was significantly decreased during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. This may be a result of myocardial swelling from myocarditis during the acute phase of the disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleton CP, Jensen JL, Hatle LK, Oh JK (1997) Doppler evaluation of left and right ventricular diastolic function: a technical guide for obtaining optimal flow velocity recordings. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 10:271–291
Dandel M, Hetzer R (2009) Echocardiographic strain and strain rate imaging: clinical applications. Int J Cardiol 132:11–24
Devereux R, Reichek N (1977) Echocardiographic determination of left ventricular mass in man: anatomic validation of the method. Circulation 55:613–618
Dokainish H, Sengupta R, Pillai M, Bobek J, Lakkis N (2009) Correlation of tissue Doppler and two-dimensional speckle myocardial velocities and comparison of derived ratios with invasively measured left ventricular filling pressures. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 22:284–289
Galderisi M, Benjamin EJ, Evans JC, D’Agostino RB, Fuller DL, Lehman B, Wolf PA, Levy D (1992) Intra- and interobserver reproducibility of Doppler-assessed indexes of left ventricular diastolic function in a population-based study (the Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol 70:1341–1346
Greenberg NL, Firstenberg MS, Castro PL, Main M, Travaglini A, Odabashian JA, Drinko JK, Rodriguez LL, Thomas JD, Garcia MJ (2002) Doppler-derived myocardial systolic strain rate is a strong index of left ventricular contractility. Circulation 105:99–105
Hiraish S, Yashiro K, Oguchi K, Kusano S, Ishii K, Nakazawa K (1981) Clinical course of cardiovascular involvement in the mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. Am J Cardiol 47:323–330
Newburger JW, Sanders SP, Burns JC, Parness IA, Beiser AS, Colan SD (1989) Left ventricular contractility and function in Kawasaki syndrome. Circulation 79:1237–1246
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114:1708–1733
Sahn DJ, DeMaria A, Kisslo J, Weyman A (1978) Recommendations regarding quantitation in M-mode echocardiography: results of a survey of echocardiographic measurements. Circulation 58:1072–1083
Terai M, Honda T, Yasukawa K, Higashi K, Hamada H, Kohno Y (2003) Prognostic impact of vascular leakage in acute Kawasaki disease. Circulation 108:325–330
Weidemann F, Eyskens B, Sutherland GR (2002) New ultrasound methods to quantify regional myocardial function in children with heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol 23:292–306
Weidemann F, Jamal F, Sutherland GR, Claus P, Kowalski M, Hatle L, De Scheerder I, Bijnens B, Rademakers FE (2002) Myocardial function defined by strain rate and strain during alterations in inotropic states and heart rate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H792–H799
Yu JJ, Kwak BO, Jeon YH, Park YM, Lee R, Chung S, Bae SH, Pyun BY (2009) Elevation of the index of left ventricular mass during the acute and subacute phase of Kawasaki disease, and its association with indexes of diastolic function. Cardiol Young 19:64–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J.J., Choi, H.S., Kim, Y.B. et al. Analyses of Left Ventricular Myocardial Deformation by Speckle-Tracking Imaging During the Acute Phase of Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 31, 807–812 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-010-9708-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-010-9708-7