Abstract
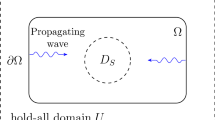
We are interested in shape sensitivity analysis for an optimization problem arising in medical applications of high intensity focused ultrasound. The goal is to find the optimal shape of a focusing acoustic lens so that the desired acoustic pressure at a kidney stone is achieved. Coupling of the silicone acoustic lens and nonlinearly acoustic fluid region is modeled by the Westervelt equation with nonlinear strong damping and piecewise constant coefficients. We follow the variational approach to calculating the shape derivative of the cost functional which does not require computing the shape derivative of the state variable; however assumptions of certain spatial regularity of the primal and the adjoint state are needed to obtain the derivative, in particular for its strong form according to the Delfour–Hadamard–Zolésio structure theorem.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamberger, A., Glowinski, R., Tran, Q.H.: A domain decomposition method for the acoustic wave equation with discontinuous coefficients and grid change. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 34, 603–639 (1997)
Berggren, M.: A Unified Discrete-continuous Sensitivity Analysis Method for Shape Optimization. Lecture at the Radon Institut, Linz, Austria (2005)
Brunnhuber, R., Kaltenbacher, B., Radu, P.: Relaxation of regularity for the Westervelt equation by nonlinear damping with application in acoustic-acoustic and elastic-acoustic coupling. Evolut. Equ. Control Theory 3(4), 595–626 (2014)
Delfour, M.C., Zolesio, J.P.: Shapes and Geometries, 2nd edn. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA (2001)
Demengel, F., Demengel, G., Erné, R.: Functional Spaces for the Theorey of Elliptic Partial Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Evans, L.C.: Partial Differential Equations, 2nd edn. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1998)
Gangl, P., Langer, U., Laurain, A., Meftahi, H., Sturm, K.: Shape optimization of an electric motor subject to nonlinear magnetostatics. arXiv:1501.04752
Hamilton, M.F., Blackstock, D.T.: Nonlinear Acoustics. Academic Press, New York (1997)
Hiptmair, R., Paganini, A., Sargheini, S.: Comparison of Approximate Shape Gradients. BIT Numerical Mathematics. Springer, Netherlands (2014)
Hofmannm, S., Mitrea, M., Taylor, M.: Geometric and transformational properties of Lipschitz domains, Semmes-Kenig-Toro Domains, and other classes of finite perimeter domains. J. Geom. Analy. 17, 593–647 (2007)
Ito, K., Kunisch, K., Peichl, G.: Variational approach to shape derivatives for a class of Bernoulli problems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 314, 126–149 (2006)
Ito, K., Kunisch, K., Peichl, G.: Variational approach to shape derivatives. ESAIM Control Optim. Calc. Var. 14, 517–539 (2008)
Kaltenbacher, B., Lasiecka, I.: Global existence and exponential decay rates for the Westervelt equation. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. S 2, 503–525 (2009)
Kaltenbacher, B., Lasiecka I., Veljović, S.: Well-posedness and exponential decay for the Westervelt equation with inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary data. In: Escher, J. (eds.), Progress in Nonlinear Differential Equations and Their Applications, vol. 60, pp. 357–387 (2011)
Kaltenbacher, B., Peichl, G.: Sensitivity Analysis for a Shape Optimization Problem in Lithotripsy (submitted)
Kaltenbacher, B., Veljović, S.: Sensitivity analysis of linear and nonlinear lithotripter models. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 22, 21–43 (2010)
Kaltenbacher, M.: Numerical Simulations of Mechatronic Sensors and Actuators. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Kaltenbacher, M., Landes, H., Hoffelner, J., Simkovics, R.: Use of modern simulation for industrial applications of high power ultrasonics. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, CD-ROM Proceedings, pp. 673–678. IEEE (2002)
Kasumba, H., Kunisch, K.: Vortex control in channel flows using translational invariant cost functionals. Comput. Optim. Appl. 52, 691–727 (2012)
Laurain, A., Sturm, K.: Domain expression of the shape gradient and application to electrical impedance tomography. Technical Report 1863, Weierstrass Institute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics (2013)
Leoni, G.: A First Course in Sobolev Spaces. American Mathematical Society, Providence (2009)
Lindqvist, P.: Notes on the p-Laplace Equation. Lecture Notes. University of Jyväskylä (2006)
Liu, W., Yan, N.: Qasi-norm local error estimators for \(p\)-Laplacian. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39, 100–127 (2002)
Murat, F., Simon, J.: Sur le contrôle par un domaine géometrique, Rapport 76015. Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris (1976)
Nikolić, V.: Local existence results for the Westervelt equation with nonlinear damping and Neumann as well as absorbing boundary conditions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jmaa.2015.02.076
Nikolić, V., Kaltenbacher, B.: On higher regularity for the Westervelt equation with strong nonlinear damping. Appl. Anal. doi:10.1080/00036811.2015.1114607
Sokolowski, J., Zolesio, J.P.: Introduction to Shape Optimization. Springer, Berlin (1991)
Tröltzsch, F.: Optimal Control of Partial Differential Equations: Theory, Methods and Applications. AMS 2010 Graduate Studies in Mathematics (2010)
Veljović, S.: Shape Optimization and Optimal Boundary Control for High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU). PhD thesis, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (2009)
Westervelt, P.J.: Parametric acoustic array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 35, 535–537 (1963)
Acknowledgments
The financial support by the FWF (Austrian Science Fund) under grant P24970 is gratefully acknowledged as well as the support of the Karl Popper Kolleg “Modeling-Simulation-Optimization”, which is funded by the Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt and by the Carinthian Economic Promotion Fund (KWF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolić, V., Kaltenbacher, B. Sensitivity Analysis for Shape Optimization of a Focusing Acoustic Lens in Lithotripsy. Appl Math Optim 76, 261–301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-016-9340-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-016-9340-x