Abstract.
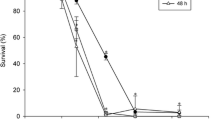
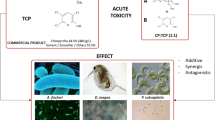
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are used or developed as substitutes for fully halogenated chlorofluorocarbons. Based on the results of closed-bottle tests, the biodegradation of HFC-32, HCFC-123, HCFC-124, HFC-125, HFC-134a, HCFC-141b, HCFC-225ca, and HCFC-225cb was less than 60% after 28 days and therefore these compounds are considered not readily biodegradable. Standard acute toxicity tests with HCFC-123, HCFC-141b, and HCFC-225ca using algae, water fleas, and fish revealed EC50 values in the range of 17–126 mg/L. EC50 values of HFC-134a ranged between 450–980 mg/L. Fish studies with HCFC-141b and HCFC-225ca revealed bioaccumulation factors of <3 and 15–64, respectively. A study with plants revealed no effect of HCFC-141b on seed germination and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum), radish (Raphanus sativus), and cress (Lepidium sativum). In conclusion, HFCs and HCFCs are not very toxic to aquatic organisms and terrestrial plants. No evidence for any aerobic biodegradation for most of the HFCs and HCFCs was found.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 May 1998/Accepted: 30 September 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berends, A., de Rooij, C., Shin-ya, S. et al. Biodegradation and Ecotoxicity of HFCs and HCFCs. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 36, 146–151 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900454
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900454