Abstract
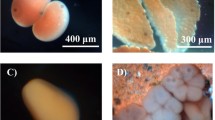
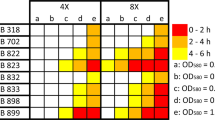
Marine sponges (Microciona prolifera) collected in St. Joseph Bay, Florida panhandle, were exposed for 2 h to pH/salinity unit combinations of 7.4/30, 6.3/30, 7.4/11, and 6.3/11. Cell suspensions from these were aggregated with 24 μM of either CaCl2 or CdCl2. Cells exposed to the low/low (11/6.3) combination aggregated spontaneously (no added stimulus) in 8/11 experiments, suggesting a significant disturbance of normal function, possibly involving disrupted ion uptake. In all other combinations aggregation proceeded normally and there were no statistically significant differences among the groups. CdCl2 was as effective an aggregation stimulus as CaCl2. The calcium channel blocker verapamil (100 μM) reduced calcium-induced aggregation by 15% but had no effect on cadmium (Cd)-induced aggregation, indicating that L-type calcium channels do not play a major role in aggregation induced by these divalent cations. Sponge tissue was exposed for 48 h to the same pH/salinity combinations but containing Cd (15 or 150 μg/ml) and then dried and analyzed for Cd. All sponges concentrated Cd but those exposed to low salinity concentrated it most (in one case ×13). Low pH alone had no appreciable effect but appeared to increase the effect of low salinity. One sponge with a native Cd content of 47.2 μg/g dry weight had the highest acquired Cd content. The results of this study indicate that low levels of salinity and pH, similar to those we recorded in the study area, facilitate the accumulation of Cd, but not via L-type calcium channels, and disrupt normal aggregation responses of the cell. These results may help explain a previous observation that cells from M. prolifera from this area, with high native levels of Cd, failed to aggregate in response to CaCl2[Philp RB (1999) Comp Biochem Physiol 124C:41–49] and also the frequent die-offs of Microciona that have virtually eliminated this sponge from its local habitat.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 September 2000/Accepted: 4 April 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Philp, R. Effects of Experimental Manipulation of pH and Salinity on Cd2+ Uptake by the Sponge Microciona prolifera and on Sponge Cell Aggregation Induced byCa2+ and Cd2+ . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 41, 282–288 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010250
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010250