Abstract
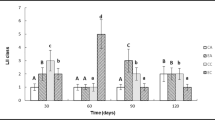
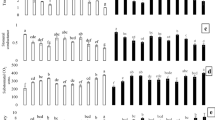
Plants of Ricinus communis L. in the city of Porto Alegre, in southern Brazil, were exposed to urban traffic exhaust emissions for 5 months and compared with controls kept at a site essentially free of direct motor vehicle emissions. No symptomatic visible injuries were observed, but significant differences could be measured in growth, enzymatic activities of total peroxidase and nitrate reductase, chlorophyll content, leaf buffering capacity, and N contents in leaves. Additionally, these data were compared with results from fumigation experiments under controlled conditions. The study showed that some physiological parameters in R. communis L. plants could be used as an appropriate bioindicator system for urban traffic contamination, and therefore it is recommended that dose-response relationships should be developed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 August 1999/Accepted: 20 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kammerbauer, J., Dick, T. Monitoring of Urban Traffic Emissions Using Some Physiological Indicators in Ricinus communis L. Plants. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 39, 161–166 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010092
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010092