Abstract
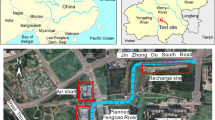
An artificial recharge test was performed in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam to see the geochemical response of a saline coastal plain aquifer to the injected rainwater. The results show that the rainwater injection can cause mobilization of heavy metals due to pyrite oxidation and this phenomenon can persist even after the full recovery of the injected water. In this study, a 30-m-deep well was installed in a confined aquifer. Pyrite framboids were observed in the sediment samples collected during the well drilling. A total of 400 L rainwater was injected into the well for 70 min. After waiting 63 h, the well was extracted at a pump speed of 2.7 L/min and the chemistry of the pumped groundwater was monitored for 10 h. The groundwater showed geochemical features close to rainwater at the early stage of pumping and gradually changed to those of the background waters, especially, in electrical conductivity and Cl− concentration, as the pumping proceeded. However, the groundwater pumped in the later stage showed much increased concentrations in SO42−, total iron (FeT), AsT, Ni, Mn and Zn relative to the calculated mixing concentrations due to pyrite oxidation even though NO3−, the pyrite oxidant, already had disappeared. It was revealed from the geochemical modeling that the persistent pyrite oxidation was the result of the reaction with ferrihydrite, which precipitated in pores of the sediment by the injection of aerated water. We believe our study is a good example showing the importance of careful design of the artificial recharge systems to avoid or minimize the geochemical disturbance of aquifer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniou EA, Hartog N, van Breukelen BM, Stuyfzand PJ (2014) Aquifer pre-oxidation using permanganate to mitigate water quality deterioration during aquifer storage and recovery. Appl Geochem 50:25–36
Antoniou EA, van Breukelen BM, Putters B, Stuyfzand PJ (2012) Hydrogeochemical patterns, processes and mass transfers during aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) in an anoxic sandy aquifer. Appl Geochem 27:2435–2452
Antoniou EA, van Breukelen BM, Stuyfzand PJ (2015) Optimizing aquifer storage and recovery performance through reactive transport modeling. Appl Geochem 61:29–40
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2005) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, 2nd edn. Balkema, Boca Raton, p 683
Bekele E, Toze S, Patterson B, Higginson S (2011) Managed aquifer recharge of treated wastewater: water quality changes resulting from infiltration through the vadose zone. Water Res 45:5764–5772
Berner RA (1984) Sedimentary pyrite formation: an update. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:605–615
Bui TV, Dang TL, Le TM (2015) Groundwater issues and hydrogeological survey of the Mekong River basin in Vietnam. In: Ha K, Nguyen TMN, Lee E, Jayakumar R (eds) Current status and issues of groundwater in the Mekong river basin. KIGAM-CCOP-UNESCO Bangkok Office, Bangkok, pp 93–121
Bui TV, Long PN, Le HN (2016) Groundwater environment in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. In: Shrestha S, Pandey VP, Thatikonda S, and Shivakoti BR (ed) Groundwater environment in Asian cities. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, U.K. p 287–315
Buschmann J, Berg M (2009) Impact of sulfate reduction on the scale of arsenic contamination in groundwater of the Mekong, Bengal and Red River deltas. Appl Geochem 24:1278–1286
Caschetto M, Colombani N, Mastrocicco M, Petitta M, Aravena R (2017) Nitrogen and sulphur cycling in the saline coastal aquifer of Ferrara, Italy. A multi-isotope approach. Appl Geochem 76:88–98
Chandra AP, Gerson AR (2010) The mechanisms of pyrite oxidation and leaching: a fundamental perspective. Surf Sci Rep 65:293–315
Dillon P, Stuyfzand P, Grischek T, Lluria M, Pyne RDG, Jain RC, Bear J, Schwarz J, Wang W, Fernandez E, Stefan C, Pettenati M, van der Gun J, Sprenger C, Massmann G, Scanlon BR, Xanke J, Jokela P, Zheng Y, Rossetto R, Shamrukh M, Pavelic P, Murray E, Ross A, Bonilla Valverde JP, Palma Nava A, Ansems N, Posavec K, Ha K, Martin R, Sapiano M (2018) Sixty years of global progress in managed aquifer recharge. Hydrogeol J 1:30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1841-z
Drever JI (1997) The geochemistry of natural water: surface and groundwater environments, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Duffy CE, Braun A, Hochschild V (2020) Surface subsidence in urbanized coastal areas: PSI methods based on Sentinel-1 for Ho Chi Minh City. Remote Sens 12:4130
DWRPIS (2015) Annual report on the national groundwater monitoring network for the Southern Vietnam. Division of Water Resources Planning and Investigation for the South of Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh City (in Vietnamese)
Dyrssen D, Sillen LG (1967) Alkalinity and total carbonate in seawater. Tellus 19:110
Edmond JM (1970) High precision determination of titration alkalinity and total carbon dioxide content of sea water by potentiometric titration. Deep Sea Res Oceanogr Abstr 17:737–750
Erban LE, Gorelick SM, Zebker HA (2014) Groundwater extraction, land subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ Res Lett 9:084010
Erban LE, Gorelick SM, Zebker HA, Fendorf S (2013) Release of arsenic to deep groundwater in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam, linked to pumping-induced land subsidence. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:13751–13756
Gröger J, Proske U, Hanebuth TJJ, Hamer K (2011) Cycling of trace metals and rare earth elements (REE) in acid sulfate soils in the Plain of Reeds, Vietnam. Chem Geol 288:162–177
Ha QK, Choi S, Phan NL, Kim K, Phan CN, Nguyen VK (2019a) Occurrence of metal-rich acidic groundwaters in the coastal plain aquifers within and around the Mekong Delta: a phenomenon linked to well installation. Sci Total Environ 654:1100–1109
Ha QK, Kim K, Phan NL, Phung TH, Lee J, Nguyen VK, Phan CN (2019b) A hydrogeological and geochemical review of groundwater issues in southern Vietnam. Geosci J 23:1005–1023
Ha QK, Ngoc TDT, Le Vo P, Nguyen HQ, Dang DH (2022) Groundwater in Southern Vietnam: understanding geochemical processes to better preserve the critical water resource. Sci Total Environ 807:151345
Hartog N, Stuyfzand P (2017) Water quality considerations on the rise as the use of managed aquifer recharge systems widens. Water 9:808
Harvey CF, Swartz CH, Badruzzaman ABM, Keon-Blute N, Yu W, Ali MA, Jay J, Beckie R, Niedan V, Brabander D, Oates PM (2002) Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 298:1602–1606
Ho TMD, Le VT, Le TT (2015) Mapping ground subsidence phenomena in Ho Chi Minh City through the radar interferometry technique using ALOS PALSAR data. Remote Sens 7:8543–8562
Jokela P, Eskola T, Heinonen T, Tanttu U, Tyrväinen J, Artimo A, Jokela P, Eskola T, Heinonen T, Tanttu U, Tyrväinen J, Artimo A (2017) Raw water quality and pretreatment in managed aquifer recharge for drinking water production in Finland. Water 9:138
Kim K (2003) Long‐term disturbance of ground water chemistry following well installation. Groundw 41:780- 789
Kim K, Kim HJ, Choi BY, Kim SH, Park KH, Park E, Koh DC, Yun ST (2008) Fe and Mn levels regulated by agricultural activities in alluvial groundwaters underneath a flooded paddy field. Appl Geochem 23:44–57
Kim K, Kim SH, Park SM, Kim J, Choi M (2010) Processes controlling the variations of pH, alkalinity, and CO2 partial pressure in the porewater of coal ash disposal site. J Hazard Mater 181:74–81
Kim K, Moon JT, Kim SH, Ko KS (2009) Importance of surface geologic condition in regulating As concentration of groundwater in the alluvial plain. Chemosphere 77:478–484
Kim K, Yun ST (2005) Buffering of sodium concentration by cation exchange in the groundwater system of a sandy aquifer. Geochem J 39:273–284
Kim SH, Kim K, Ko KS, Kim Y, Lee KS (2012) Co-contamination of arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of unconsolidated aquifers under reducing environments. Chemosphere 87:851–856
Lasaga AC (1984) Chemical kinetics of water-rock interactions. J Geophys Res 89:4009–4025
Lin CY, Turchyn AV, Steiner Z, Bots P, Lampronti GI, Tosca NJ (2018) The role of microbial sulfate reduction in calcium carbonate polymorph selection. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 237:184–204
Minderhoud PSJ, Erkens G, Pham VH, Bui VT, Erban L, Kooi H, Stouthamer E (2017) Impacts of 25 years of groundwater extraction on subsidence in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Environ Res Lett 12:064006
Moses CO, Nordstrom DK, Herman JS, Mills AL (1987) Aqueous pyrite oxidation by dissolved oxygen and by ferric iron. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 51:1561–1571
Neil CW, Jun YS (2015) Fe3+ addition promotes arsenopyrite dissolution and iron (III)(Hydr)oxide formation and phase transformation. Environ Sci Technol Lett 3:30–35
Ngo MT, Lee JM, Lee HA, Woo NC (2015) The sustainability risk of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, due to saltwater intrusion. Geosci J 19:547–560
Nguyen VK, Nguyen DT (2011) The pilot model of capacity of supplement for groundwater by rainfall resource in dormitory area of Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM). Sci Technol Dev 14:16–24 (in Vietnamsese)
Page DW, Peeters L, Vanderzalm J, Barry K, Gonzalez D (2017) Effect of aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) on recovered stormwater quality variability. Water Res 117:1–8
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (2013) Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3—A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods, book 6, chap. A43, 497. https://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a43/
Pavelic P, Dillon PJ, Barry KE, Vanderzalm JL, Correll RL, Rinck-Pfeiffer SM (2007) Water quality effects on clogging rates during reclaimed water ASR in a carbonate aquifer. J Hydrol 334:1–16
Phan NL (2019) A Geochemical Study and Mass Balance Analysis on Groundwater in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Dissertation, Kunsan National University
Phien-wej N, Giao PH, Nutalaya P (1998) Field experiment of artificial recharge through a well with reference to land subsidence control. Eng Geol 50:187–201
Pye K, Dickson JAD, Schiavon N, Coleman ML, Cox M (1990) Formation of siderite-Mg-calcite-iron sulphide concretions in intertidal marsh and sandflat sediments, north Norfolk, England. Sedimentology 37:325–343
Scanlon BR, Reedy RC, Faunt CC, Pool D, Uhlman K (2016) Enhancing drought resilience with conjunctive use and managed aquifer recharge in California and Arizona. Environ Res Lett 11:035013
Schafer D, Donn M, Atteia O, Sun J, MacRae C, Raven M, Pejcic B, Prommer H (2018) Fluoride and phosphate release from carbonate-rich fluorapatite during managed aquifer recharge. J Hydrol 562:809–820
Schoonen MAA (2004) Mechanisms of sedimentary pyrite formation. In: Amend JP, Edwards KJ, Lyons TW (eds) Sulfur biogeochemistry—past and present. Geological Society of America, Boulder, pp 117–134
Seibert S, Atteia O, Ursula Salmon S, Siade A, Douglas G, Prommer H (2016) Identification and quantification of redox and pH buffering processes in a heterogeneous, low carbonate aquifer during managed aquifer recharge. Water Resour Res 52:4003–4025
SGMD (2004) Classification and characteristics of Neogene and Quaternary sediments in the southern Vietnam. In: Nguyen HD (ed) Research of geological structure and classification of neogene and quaternary sediments in the Southern Vietnam. Southern Geological Mapping Division (SGMD), Ho Chi Minh City (in Vietnamese)
Shammas MI (2008) The effectiveness of artificial recharge in combating seawater intrusion in Salalah coastal aquifer. Oman Environ Geol 55:191–204
Sprenger C, Hartog N, Hernández M, Vilanova E, Grützmacher G, Scheibler F, Hannappel S (2017) Inventory of managed aquifer recharge sites in Europe: historical development, current situation and perspectives. Hydrogeol J 25:1909–1922
Stefan C (2014) Groundwater vulnerability in Vietnam and innovative solutions for sustainable exploitation. J Viet Environ 6:13–21
Stefan C, Ansems N (2018) Web-based global inventory of managed aquifer recharge applications. Sustain Water Resour Manag 4:153–162
Stuyfzand PJ, Smidt E, Zuurbier KG, Hartog N, Dawoud MA (2017) Observations and prediction of recovered quality of desalinated seawater in the strategic ASR project in Liwa. Abu Dhabi Water 9:177
Thoang TT, Giao PH (2015) Subsurface characterization and prediction of land subsidence for HCM City. Eng Geol 199:107-124.
van Beek CGEM (2010) Cause and prevention of clogging of wells abstracting groundwater from unconsolidated aquifers. PhD Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam
van Beek CGEM, Hubeek AA, de la Loma GB, Stuyfzand PJ (2017) Chemical and mechanical clogging of groundwater abstraction wells at well field Heel, the Netherlands. Hydrogeol J 25:67–78
Vanderzalm JL, Dillon PJ, Barry KE, Miotlinski K, Kirby JK, Le Gal La Salle C (2011) Arsenic mobility and impact on recovered water quality during aquifer storage and recovery using reclaimed water in a carbonate aquifer. Appl Geochem 26:1946–1955
Vanderzalm JL, Page DW, Barry KE, Dillon PJ (2010) A comparison of the geochemical response to different managed aquifer recharge operations for injection of urban stormwater in a carbonate aquifer. Appl Geochem 25:1350–1360
Wang Y, Le Pape P, Morin G, Asta MP, King G, Bártová B, Suvorova E, Frutschi M, Ikogou M, Pham VHC, Le VP, Herman F, Charlet L, Bernier-Latmani R (2018) Arsenic speciation in Mekong Delta sediments depends on their depositional environment. Environ Sci Technol 52:3431–3439
WHO (2022) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: Fourth edition incorporating the first and second addenda. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045064.
Wiese B, Massmann G, Jekel M, Heberer T, Dünnbier U, Orlikowski D, Grützmacher G (2011) Removal kinetics of organic compounds and sum parameters under field conditions for managed aquifer recharge. Water Res 45:4939–4950
Wikipedia (2018) Goldschmidt classification. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Goldschmidt_classification&oldid=849983348.
Zhang YC, Slomp CP, Broers HP, Passier HF, Van CP (2009) Denitrification coupled to pyrite oxidation and changes in groundwater quality in a shallow sandy aquifer. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:6716–6726
Zhou J, Zheng X, Flury M, Lin G (2009) Permeability changes during remediation of an aquifer affected by sea-water intrusion: a laboratory column study. J Hydrol 376:557–566
Zuurbier KG, Hartog N, Stuyfzand PJ (2016) Reactive transport impacts on recovered freshwater quality during multiple partially penetrating wells (MPPW-)ASR in a brackish heterogeneous aquifer. Appl Geochem 71:35–47
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the supports of Division of Water Resources Planning and Investigation of the South of Vietnam while performing our field works.
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant #2016r1d1a1b03931992). This research is also funded by Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) under Grant Number C2023-02-06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, QK., Kim, K., Ko, K. et al. Mobilization of Heavy Metals in a Saline Confined Aquifer as a Consequence of Rainwater Injection: A Case Study in Southern Vietnam. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 85, 277–289 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-01016-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-01016-y