Abstract
The rupture of the Fundão dam released about 50 million m3 of mining tailings in the Doce river basin. To assess the potential for environmental contamination and the risks of residual exposure of the human population generated by these tailings, water and fish samples from the Doce river were collected 25 days after the accident and analyzed the physicochemical parameters of the water and levels of metals by ICP-MS, in addition to the temporal variability of the concentration of these elements through other studies. This was the first study to carry out an assessment of the health risk associated with the consumption of fish contaminated by metals from the areas affected by the disaster. The values of turbidity (5460 NTU), electrical conductivity (74.8 μS cm−1), total dissolved solids (892 mg L−1) and total suspended solids (772 mg L−1) were above the maximum limit allowed by Brazilian legislation, due to the presence of large amounts of solid materials released after the dam rupture. The analysis of metals in water samples indicated high concentrations of Al (1,906.71 μg L−1), Mn (370.32 μg L−1), Fe (8,503.50 μg L−1) and Hg (34.25 μg L−1), while for the fish samples, only As (1,033.98 μg kg−1) and Hg (herbivorous: 505.32 μg kg−1; predatory: 1,184.09 μg kg−1) presented levels above those established by Brazilian legislation. The health risk assessment showed that the estimated daily intake for Hg was higher than the reference dose, reinforcing the need for monitoring the area affected by the disaster.

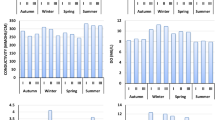
Adapted from IGAM (2010)

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
ANA (2016) Bacia do rio Doce: rompimento da barragem em Mariana/MG. Conjuntura dos recursos hídricos no Brasil, informe 2015. Superintendência de Planejamento de Recursos Hídricos - SPR, Agência Nacional de Águas, Brasília, Brazil, p 50
ANVISA (2013) Resolução - RDC N° 42, de 29 de agosto de 2013. Ministério da Saúde, Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária, Brasília, Brazil, p 11
Arafa A, Ewis A, Eshak E (2022) Chronic exposure to nitrate in drinking water and the risk of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence. Public Health 203:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2021.11.019
ATSDR (2022) Toxicological profile for mercury. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for toxic substances and disease registry, Atlanta, GA, USA, p 847
Baig JA, Chandio IG, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Akhtar K, Junaid M, Naher S, Solangi SA, Malghani NA (2022) Risk assessment of macronutrients and minerals by processed, street, and restaurant traditional Pakistani foods: a case study. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03429-7
Bilal M, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Ali J, Baig JA, Arain MB, Khan M (2017) A new tunable dispersive liquid–liquid micro extraction method developed for the simultaneous preconcentration of lead and cadmium from lakes water: a multivariate study. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 183:417–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.04.037
Biolé FG, Vegh SL, Carvalho BM, Bavio M, Tripodi P, Volpedo AV, Thompson G (2023) Health risk assessment and differential distribution of arsenic and metals in organs of Urophycis brasiliensis a commercial fish from Southwestern Atlantic coast. Mar Pollut Bull 187:114499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114499
Bosch AC, O′Neill B, Sigge GO, Kerwath SE, Hoffman LC (2016) Heavy metal accumulation and toxicity in smoothhound (Mustelus mustelus) shark from Langebaan lagoon, South Africa. Food Chem 190:871–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.034
Burns CJ, LaKind JS, Mattison DR, Alcala CS, Branch F, Castillo J, Clark A, Clougherty JE, Darney SP, Erickson H, Goodman M, Greiner M, Jurek AM, Miller A, Rooney AA, Zidek A (2019) A matrix for bridging the epidemiology and risk assessment gap. Glob Epidemiol 1:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloepi.2019.100005
CETESB (2011) Guia nacional de coleta e preservação de amostras: água, sedimento, comunidades aquáticas e efluentes líquidos, Companhia Ambiental de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, p 327
Chagas SD (2015) Relação entre concentração de sólidos suspensos e turbidez da água medida com sensor de retroespalhamento óptico. Dissertação, Universidade Federal do Recôncavo da Bahia
Channa GM, Baig JA, Solangi IB, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Waris M (2020) Quantitative assessment of some toxic elements and physicochemical parameters in wastewater of dyeing industry: a case study. Pak J Anal Environ Chem 21(1):132–139
CONAMA (2005) Resolução nº 357, de 17 de março de 2005, Dispõe sobre a classificação dos corpos de água e diretrizes ambientais para o seu enquadramento, bem como estabelece as condições e padrões de lançamento de efluentes, e dá outras providências, Diário Oficial da União, Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente, Brasília, Brazil, p 27
Coppo GC, Passos LS, Lopes TOM, Pereira TM, Merçon J, Cabral DS, Barbosa BV, Caetano LS, Kampke EH, Chippari-Gomes AR (2018) Genotoxic, biochemical and bioconcentration effects of manganese on oreochromis niloticus (cichlidae). Ecotoxicology 27(8):1150–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1970-0
Costa PG, Marube LC, Artifon V, Escarrone AL, Hernandes JC, Zebral YD, Bianchini A (2022) Temporal and spatial variations in metals and arsenic contamination in water, sediment and biota of freshwater, marine and coastal environments after the Fundão dam failure. Sci Total Environ 806:151340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151340
CPRM (2015) Monitoramento especial da bacia do rio Doce: relatório I. CPRM, Serviço geológico do Brasil, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, p 33
CPRM (2016) Monitoramento especial da bacia do rio Doce: relatório IV. CPRM, Serviço geológico do Brasil, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, p 61
EMBRAPA (2011) Manual de procedimentos de amostragem e análise físico-química de água, Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária, Embrapa Florestas, Colombo, Paraná, Brazil, p 67
Fuentes-Gandara F, Pinedo-Hernández J, Marrugo-Negrete J, Díez S (2018) Human health impacts of exposure to metals through extreme consumption of fish from the Colombian Caribbean sea. Environ Geochem Health 40:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9896-z
Gabriel FÂ, Hauser-Davis RA, Soares L, Mazzuco ACA, Rocha RCC, Pierre TDS, Saggioro E, Correia FV, Ferreira TO, Bernardino AF (2020) Contamination and oxidative stress biomarkers in estuarine fish following a mine tailing disaster. PeerJ 8:e10266. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10266
Giongo A, Borges LGA, Marconatto L, Palhano PL, Serbent MP, Silva EM, Siqueira TA, Martinho CT, Barili R, Paz LV, Moser LI, Veríssimo CM, Ketzer JMM, Silva RM (2020) Adaption of microbial communities to the hostile environment in the Doce river after the collapse of two iron ore tailing dams. Heliyon 6(8):e04778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04778
Gomes LEO, Correa LB, Sá F, Neto RR, Bernardino AF (2017) The impacts of the samarco mine tailing spill on the rio Doce estuary Eastern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 120(1–2):28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.04.056
Hashempour-baltork F, Jannat B, Tajdar-oranj B, Aminzare M, Sahebi H, Alizadeh AM, Hosseini H (2023) A comprehensive systematic review and health risk assessment of potentially toxic element intakes via fish consumption in Iran. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 249:114349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114349
Kolarova N, Napiórkowski P (2021) Trace elements in aquatic environment. Origin, distribution, assessment and toxicity affect for the aquatic biota. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 1:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03429-7
Man YB, Sun XL, Zhao YG, Lopez BN, Chung SS, Wu SC, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2010) Health risk assessment of abandoned agricultural soils based on heavy metal contents in Hong Kong, the world′s most populated city. Environ Int 36(6):570–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.04.014
Melake BA, Nkuba B, Groffen T, Boeck G, Bervoets L (2022) Distribution of metals in water, sediment and fish tissue. Consequences for human health risks due to fish consumption in lake Hawassa, Ethiopia. Sci Total Environ 843:156968
PIRH (2010) Plano integrado de recursos hídricos da bacia do rio Doce e dos planos de ações de recursos hídricos para as unidades de planejamento e gestão de recursos hídricos no âmbito da bacia do rio Doce. Volume I—relatório final. Consórcio ECOPLAN—LUME, Brazil, p 478
Queiroz HM, Nóbrega GN, Ferreira TO, Almeida LS, Romero TB, Santaella ST, Bernardino AF, Otero XL (2018) The Samarco mine tailing disaster: a possible time-bomb for heavy metals contamination? Sci Total Environ 637–638:498–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.370
Queiroz HM, Ying SC, Bernardino AF, Barcellos D, Nóbrega GN, Otero XL, Ferreira TO (2021) Manganese: the overlooked contaminant in the world largest mine tailings dam collapse. Environ Int 146:106284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106284
Richard EC, Duarte AH Jr, Estrada GCD, Bechtold J, Maioli BG, Freitas AHA, Warner KE, Figueiredo LHM (2020) Influence of fundão tailings dam breach on water quality in the Doce river watershed. Integr Environ Assess Manag 16(5):583–595. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.4311
Rudorff N, Rudorff CM, Kampel M, Ortiz G (2018) Remote sensing monitoring of the impact of a major mining wastewater disaster on the turbidity of the Doce river plume off the eastern Brazilian coast. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 145:349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.02.013
Sá F, Longhini CM, Costa ES, Silva CA, Cagnin RC, Gomes LEO, Lima AT, Bernardino AF, Neto RR (2021) Time-sequence development of metal(loid)s following the 2015 dam failure in the Doce river estuary, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 769:144532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144532
Salvador GN, Leal CG, Brejão GL, Pessali TC, Alves CBM, Rosa GR, Ligeiro R, Montag LFA (2020) Mining activity in Brazil and negligence in action. Perspect Ecol Conserv 18(2):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecon.2020.05.003
Santos MS, Metzker MCRM, Rodrigues GL, Corrêa LRS, Silva MLV, Barbosa ALG, Faria MCS, Rodrigues JL (2018) Risk assessment of the drinking water samples in the rural area from MG, Brazil. Int J Environ Res 12(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-018-0136-5
Segura FR, Nunes EA, Paniz FP, Paulelli ACC, Rodrigues GB, Braga GÚL, Filho WRP, Barbosa F Jr, Cerchiaro G, Silva FF, Batista BL (2016) Potential risks of the residue from Samarco′s mine dam burst (Bento Rodrigues, Brazil). Environ Pollut 218:813–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.005
SEMAD-IGAM (2016) Monitoramento da qualidade das águas superficiais do rio Doce no estado de Minas Gerais, relatório técnico de acompanhamento da qualidade das águas do rio Doce após o rompimento da barragem da Samarco no distrito de Bento Rodrigues—Mariana/MG. SEMAD-IGAM, Sistema Estadual de Meio Ambiente—Instituto Mineiro de Gestão das Águas Governo do Estado de Minas Gerais, Minas Gerais, Brazil, p 72
Shah AQ, Kazi TG, Arain MB, Jamali MK, Afridi HI, Jalbani N, Baig JA, Kandhro GA (2009) Accumulation of arsenic in different fresh water fish species—potential contribution to high arsenic intakes. Food Chem 112(2):520–524
USEPA (2019) Guidelines for human exposure assessment. US EPA risk assessment forum, United States environmental protection agency, Washington, DC, USA, p 223
Vieira CED, Marques JA, Silva NG, Bevitório LZ, Zebral YD, Maraschi AC, Costa SR, Costa PG, Damasceno EM, Pirovani JCM, Vale-Oliveira M, Souza MM, Martins CMG, Bianchini A, Sandrini JZ (2022) Ecotoxicological impacts of the fundão dam failure in freshwater fish community: metal bioaccumulation, biochemical, genetic and histopathological effects. Sci Total Environ 832:154878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154878
WHO (2011) Adverse health effects of heavy metals en children. World Health Organization, Children′s Health and the Environment, p 77
Zhu F, Qu L, Fan W, Wang A, Hao H, Li X, Yao S (2015) Study on heavy metal levels and its health risk assessment in some edible fishes from Nansi lake. China Environ Monit Assess 187(4):161
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other supports were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ASVdC, HTdS and LFOM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AOM, MSS and MdVRR, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mourão, A.O., Santos, M.S., da Costa, A.S.V. et al. Assessment of Health Risk and Presence of Metals in Water and Fish Samples from Doce River, Brazil, After Fundão Dam Collapse. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 377–388 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-00991-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-00991-6