Abstract
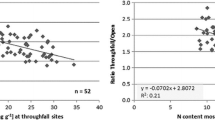
This research used moss biomonitoring to assess the atmospheric deposition of selected trace metals across the whole territory of Albania, a country of diverse lithology, and topography. Here, we assess three elements (Cr, Ni, and Co) that were identified in high concentrations compared to values reported by European moss surveys of 2010 and 2015. The possibility of element uptake by moss from substrate soils was assessed by analyzing moss and topsoil samples from the same areas. For this purpose, moss (Hypnum cupressiforme (Hedw.)) and topsoil samples were collected throughout Albania. Higher concentrations of elements in moss were found in areas of very high element content in soil characterized by no/or thin humus layer and sparse vegetation that stimulates soil dust generation. To compensate for the natural variation of the elements and to show their anthropogenic variation, geochemical normalization was conducted as the ratio of Co, Cr, and Ni concentration data to be concentration. Associations between elements in moss and soil samples, investigated by Spearman-Rho correlation analysis, indicated strong and significant correlations (r > 0.81, p = 0.000) between elements’ data in moss or soil, and weak or no correlations (r < 0.4, p > 0.05) between the same data of moss and soil. Factor analysis revealed two main factors that selectively affect the elements in moss and top soil samples. Findings from this research suggested negligible interactions between moss and substrate soils, with the exception of soils with high concentrations of elements.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aarons SM, Blakowski MA, Aciego SM, Stevenson EI, Sims KWW, Scott SR, Aarons C (2017) Geochemical characterization of critical dust source regions in the American WeSS. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 215:141–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.07.024
Akima H (1978) A method of bivariate interpolation and smooth surface fitting for irregularly distributed data points. ACM Trans Math Softw 2(1):160–164
Allajbeu Sh, Qarri F, Marku E, Bekteshi L, Ibro V, Frontasyeva MV, Stafilov T, Lazo P (2016) Contamination scale of atmospheric deposition for assessing air quality in Albania evaluated from most toxic heavy metal and moss biomonitoring. J Air Qual Atmos Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0453-9
Allajbeu S, Bekteshi L, Lazo P, Qarri F, Stafilov T (2021) Spatial Series and multivariate analysis in assessing the essential (Cu and Zn) and toxic (As, Cd, Cr, Co, Hg, Ni, and Pb) metals linked with health risk and ecological effects of atmospheric deposition by using bryophyte moss as bioindicator. In: Balabanova B, Staflov T (eds) Contaminant levels and ecological effects emerging contaminants and associated treatment technologies. Springer, Cham, pp 33–74
Asami T, Kubota M (1995) Background levels of soil beryllium in several countries. Environ Geochem Health 17:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188630
Astel A, Astel K, Biziuk M (2008) PCA and multidimensional visualization techniques united to aid in the bioindication of elements from transplanted Sphagnum palustre moss exposed in the Gdańsk City area. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 15:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2007.05.422
Bačeva K, Stafilov T, Šajn R, Tănăselia C (2012) Moss biomonitoring of air pollution with heavy metals in the vicinity of a ferronickel smelter plant. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 47(4):645–656. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.650587
Bekteshi L, Lazo P, Qarri F, Stafilov T (2015) Application of normalization process in the survey of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in Albania by using moss biomonitoring. Ecol Indic 56:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.03.001
Boquete MT, Fernández JA, Aboal JR, Carballeira A, Martínez-Abaigar J, Tomás-Las-Heras R, Núñez-Olivera E (2016) Trace element concentrations in the moss Hypnum cupressiforme growing in a presumably unpolluted area. Chemosphere 158:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/jchemosphere201605063
Bussolesi M, Grieco G, Zaccarini F, Cavallo A, Tzamos E, Storni N (2022) Chromite compositional variability and associated PGE enrichments in chromitites from the Gomati and Nea Roda ophiolite, Chalkidiki, Northern Greece. Miner Deposita 57:1323–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-022-01109-z
Capozzi F, Sorrentino MC, Cascone E, Iuliano M, De Tommaso G, Granata A, Giordano S, Spagnuolo V (2023) Biomonitoring of airborne microplastic deposition in semi-natural and rural sites using the moss hypnum cupressiforme. Plants 12:977. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12050977
Cappuyns V, Mallaerts T (2014) Background values of cobalt in Flemish and European soils. Geol Belg 17(2):107–114
Casalegno C, Schifanella O, Zennaro E, Marroncelli S, Briant R (2015) Collate literature data on toxicity of Chromium (Cr) and Nickel (Ni) in experimental animals and humans. Supporting Publications 2015: EN-478. pp 287. Available online: www.efsa.europa.eu/publications
Corbin JC, Mensah AA, Pieber SM, Orasche J, Michalke B, Zanatta M, Czech H, Massabo D, BuatierMongeot F, Mennucci C, ElHaddad I, Kumar NK, Stengel B, Huang Y, Zimmermann R, Prévôt ASH, Gysel M (2018) Trace metals in soot and PM2. 5 from heavy-fuel-oil combustion in a marine engine. Environ Sci Technol 2018(52):6714–6722. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01764
Ettler V (2016) Soil contamination near non-ferrous metal smelters: a review. Appl Geochem 64:56–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.09.020
Ferronato N, Torretta V (2019) Waste mismanagement in developing countries: a review of global issues. J Environ Res Public Health 16:1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061060
Frontasyeva M, Harmens H, Uzhinskiy A, Chaligava O, participants of the moss survey (2020) Mosses as biomonitors of air pollution: 2015/2016 survey on heavy metals, nitrogen and POPs in Europe and beyond. https://icpvegetation.ceh.ac.uk/mosses-biomonitors-air-pollution-20152016-survey-heavy-metals-nitrogen-and-pops-europe-and-beyond
Harmens H, Norris DA, Koerber GR, Buse A, Steinnes E, Rühling Å (2008) Temporal trends (1990–2000) in the concentration of cadmium, lead and mercury in mosses across Europe. Environ Pollut 151(2):368–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.043
Harmens H, Mills G, Hayes F, Norris D, the participants of the ICP Vegetation moss survey (2011) Air pollution and vegetation: ICP vegetation annual report 2010/2011. https://icpvegetation.ceh.ac.uk/
Harmens H, Norris D, Mills G, the participants of the ICP Vegetation moss survey (2013) Heavy metals and nitrogen in mosses: spatial patterns in 2010/2011 and long-term temporal trends in Europe. ICP Vegetation Programme Coordination Centre, Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Bangor, UK, p 63. https://icpvegetation.ceh.ac.uk/
Harmens H, Norris DA, Sharps K, Mills G, Alber R, Aleksiayenak Y, Blum O, Cucu-Man SM, Dam M, De Temmerman L, Ene A, Fernández JA, Martinez-Abaigar J, Frontasyeva M, Godzik B, Jeran Z, Lazo P, Leblond S, Liiv S, Magnússon SH, Maňkovská B, Pihl Karlsson G, Piispanen J, Poikolainen J, Santamaria JM, Skudnik M, Spiric Z, Stafilov T, Steinnes E, Stihi C, Suchara I, Thöni L, Todoran R, Yurukova L, Zechmeister HG (2015) Heavy metal and nitrogen concentrations in mosses are declining across Europe whilst some “hotspots” remain in 2010. Environ Pollut 200:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/jenvpol201501036
Ho HH, Swennen R, Cappuyns V, Vassilieva E, Tran TV (2012) Necessity of normalization to aluminum to assess the contamination by heavy metals and arsenic in sediments near Haiphong Harbor, Vietnam. J Asian Earth Sci 56:229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.05.015
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kierczak J, Pietranik A, Pędziwiatr A (2021) Ultra-mafic geoecosystems as a natural source of Ni, Cr, and Co to the environment: a review. Sci Total Environ 755:142620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142620
Kika A, Ktona A, Shehu Kane S, Lazo P (2023) Vanadium contamination in soil and atmospheric deposition in Albania. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 110:17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03655-8
Koller F, Hoeck V, Miesel T, Ionescu C, Onuzi K, Ghega D (2006) Cumulates and gabros in southern Albania ophiolites: their bearing on regional tectonic setting, vol 260. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, pp 267–299. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.260.01.12
Lago-Vila M, Arenas-Lago D, Rodríguez-Seijo A, Andrade Couce ML, Vega FA (2015) Cobalt, chromium and nickel concentrations in soils and plants from a serpentinite quarry. Solid Earth 6:323–335. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-6-323-2015
Lazo P, Steinnes E, Qarri F, Allajbeu Sh, Kane S, Stafilov T, Frontasyeva M, Harmens H (2018) Origin and spatial distribution of metals in moss samples in Albania: a hotspot of heavy metal contamination in Europe. Chemosphere 190:337–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.132
Lazo P, Stafilov T, Qarri F, Allajbeu Sh, Bekteshi L, Fronasyeva M, Harmens H (2019) Spatial and temporal trend of airborne metal deposition in Albania studied by moss biomonitoring. Ecol Ind 101:1007–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.11.053
Lazo P, Kika A, Qarri F, Bekteshi L, Allajbeu Sh, Stafilov T (2022) Air quality assessment by moss biomonitoring and trace metals atmospheric deposition. Aerosol Air Qual Res 22:220008. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.220008
Lazo P, Qarri F, Allajbeu S, Kane S, L Bekteshi, Frontasyeva M, Stafilov T (2021) Introduction. In: The Evaluation of Air Quality in Albania by Moss Biomonitoring and Metals Atmospheric Deposition. Springer Briefs in Environmental Science. Springer, Cham. pp. 113 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62355-5
Liu Y, Zhou Q, Wang Y, Cheng S, Hao W (2021) Deriving soil quality criteria of chromium based on species sensitivity distribution methodology. Toxics 9(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9030058
Lodenius M (2013) Use of plants for biomonitoring of airborne mercury in contaminated areas. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2012.10.014i
Loppi S, Bonini I (2000) Lichens and mosses as biomonitors of trace elements in areas with thermal springs and fumarole activity (Mt. Amiata, central Italy). Chemosphere 41(9):1333–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00026-6
Loppi S, Kosonen Z, Meier M (2021) Estimating Background values of potentially toxic elements accumulated in moss: a case study from Switzerland. Atmosphere. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020177
Loring DH, Rantala RTT (1992) Manual for the geochemical analyses of marine sediments and suspended particulate matter. Earth Sci Rev 32:235–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(92)90001-A
Ma Y, Hooda PS (1994) Chromium, nickel and cobalt. In: Hooda PS (ed) Trace elements in soils. Wiley, New York
McGrath SP (1995) Chromium and nickel. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soil, 2nd edn. Blackie Academic & Professional, London, pp 152–178
Mcneill J, Snider G, Weagle CL, Walsh B, Bissonnette P, Stone E, Abboud I, Akoshile C, Anh NX, Balasubramanian R, Brook JR, Coburn C, Cohen A, Dong J, Gagnon G, Garland RM, He K, Holben BN, Kahn R, Kim JS, Lagrosas N, Lestari P, Liu Y, Jeba F, Joy KS, Martins JV, Misra A, Norford LK, Quel EJ, Salam A, Schichtel B, Tripathi SN, Wang C, Zhang Q, Brauer M, Gibson MD, Rudich Y, Martin RV (2020) Large global variations in measured airborne metal concentrationsdriven by anthropogenic sources. Sci Rep 10:21817. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78789-y
Mehri A (2020) Trace elements in human nutrition (II) - an update. Int J Prev Med 3(11):2. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_48_19.PMID:32042399;PMCID:PMC6993532
Meyer M, Diaz-de-Quijano M, Monna F, Franchi M, Toussaint M-L, Gilbert D, Bernard N (2015) Characterisation and distribution of deposited trace elements transported over long and intermediate distances in north-eastern France using Sphagnum peatlands as a sentinel ecosystem. Atmos Environ 101:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.11.041
Motswaiso FS, Nakamura K, Watanabe N, Komai T (2019) Geochemical Investigation of metals and trace elements around the abandoned Cu-Ni mine site in Selibe Phikwe, Botswana. J Geosci Environ Prot 7:275–293. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2019.75020
Qarri F, Lazo P, Bekteshi L, Stafilov T, Frontasyeva M, Harmens H (2015) The effect of sampling scheme in the survey of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in Albania by using moss biomonitoring. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(3):2258–2271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3417-3
Qarri F, Lazo P, Allajbeu Sh, Bekteshi L, Kane S, Stafilov T (2019) The evaluation of air quality in Albania by moss biomonitoring and metals atmospheric deposition. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 76(4):554–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00608-x
Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Garrett RG (2002) Factor analysis applied to regional geochemical data: problems and possibilities. Appl Geochem 17(3):185–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00066-X
Robertson AHF, Ionescu C, Hoeck V, Koller F, Onuzi K, Bucur II, Ghega D (2012) Emplacement of the Jurassic Mirdita ophiolites (southern Albania): evidence from associated clastic and carbonate sediments. J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 101:1535–1558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-010-0603-5
Roblin B, Aherne J (2020) Moss as a biomonitor for the atmospheric deposition of anthropogenic microfibres. Sci Total Environ 1(715):136973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136973
Roblin B, Ryan M, Vreugdenhil A, Aherne J (2020) Ambient atmospheric deposition of anthropogenic microfibers and microplastics on the western periphery of Europe (Ireland). Environ Sci Technol 54(18):11100–11108. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c04000
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2003) The composition of the continental crust. In: Holland HD, Turekian KK (eds) Treatise on geochemistry, vol 3. Elsevier-Pergamon, Oxford, pp 1–64
Šajn R, Ristović I, Čeplak B (2022) Mining and metallurgical waste as potential secondary sources of metals—a case study for the West Balkan Region. Minerals 12(5):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050547
Salminen R, Batista MJ, Bidovec M, Demetriades A, De Vivo B et al. (2005) Geochemical atlas of Europe. Part 1: Background information, methodology and maps. Espoo, Geological Survey of Finland, http:// www.gtk.fi/publ/foregsatlas/
Schraufnagel DE, Balmes JR, Cowl CT, De Matteis S et al (2019) Air pollution and noncommunicable diseases: a review by the Forum of International Respiratory Societies’ Environmental Committee, part 2: air pollution and organ systems. Chest 155(2):417–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cheSS.2018.10.041
Schröder W, Nickel S (2019) Spatial structures of heavy metals and nitrogen accumulation in moss specimens sampled between 1990 and 2015 throughout Germany. Environ Sci Eur 31:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-019-0216-y
Schröder W, Nickel S, Schönrock S, Meyer M, Wosniok W, Harmens H, Frontasyeva MV, Alber R, Aleksiayenak J, Barandovski L, Carballeira A, Danielsson H, de Temmermann L, Godzik B, Jeran Z, Karlsson GP, Lazo P, Leblond S, Lindroos AJ, Liiv S, Magnússon SH, Mankovska B, Martínez-Abaigar J, Piispanen J, Poikolainen J, Popescu IV, Qarri F, Santamaria JM, Skudnik M, Špirić Z, Stafilov T, Steinnes E, Stihi C, Thöni L, Uggerud HT, Zechmeister HG (2016) Spatially valid data of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and nitrogen derived by moss surveys for pollution risk assessments of ecosystems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:10457–10476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6577-5
Shallari S, Schwartz C, Hasko A, Morel JL (1998) Heavy metals in soils and plants of serpentine and industrial sites of Albania. Sci Total Environ 209(2–3):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(98)80104-6
Shrestha N (2021) Factor analysis as a tool for survey analysis. Am J Appl Math Stat 9(1):4–11. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajams-9-1-2
SRC (2013) Dutch—Soil Remediation Circular 2013, version of 1 July 2013. http://enviroeng.eu/wp-concentration/uploads/2022/01/LISTA-HOLANDESA-2013.pdf
Sule K, Umbsaar J (1862) Prenner EJ (2020) Mechanisms of Co, Ni, and Mn toxicity: from exposure and homeostasis to their interactions with and impact on lipids and biomembranes. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 8:183250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183250
Viana M, Amato F, Alastuey A, Querol X, Moreno T, García Dos Santos S, Herce MD, Fernandez-Patier R (2009) Chemical ́ tracers of particulate emissions from commercial shipping. Environ Sci Technol 43(19):7472–7477. https://doi.org/10.1021/es901558t
Wada O (2004) What are Trace Elements?—Their deficiency and excess states. JMAJ 47(8):351–358, Available online at: https://www.med.or.jp/english/pdf/2004_08/351_358.pdf
Wägele IJW, Bodesheim P, Bourlat SJ, Denzler J, Diepenbroek M, Fonseca V, Frommolt KH, Geiger MF, Gemeinholzer B, Glöckner FO, Haucke T, Kirse A, Kölpin A, Kostadinov I, Kühl HS, Kurth F, Lasseck M, Liedke S, Losch F, Müller S, Petrovskaya N, Piotrowski K, Radig B, Scherber C, Schoppmann L, Schulz J, Steinhage V, Tschan GF, Vautz W, Velotto D, Weigend M, Wildermann S (2022) Towards a multisensor station for automated biodiversity monitoring. Basic Appl Ecol 59:105–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2022.01.003
Wang Z, Darilek JL, Zhao Y, Huang B, Sun W (2010) Defining soil geochemical baselines at small scales using geochemical common factors and soil organic matter as normalizers. J Soils Sedim 11(13):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0269-4
Wiemker R (1996) Registration of airborne scanner imagery using Akima local quantic polynomial interpolation. In: Presented at the Second International Airborne Remote Sensing Conference and Exhibition, San Francisco, California, 24–27 June 1996
Funding
This work was supported by the University of Tirana, Faculty of Natural Sciences through the grants for 2-year projects for science that cover the expenses for sampling, chemical analysis, and the publication of research papers. The authors declare that no other funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’ conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by PL and AK. LB was responsible for sampling of all moss and soil samples. The first draft of the manuscript was written by PL, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. FQ actively participated in manuscript revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
We declare that the work described here has not been previously published or submitted to a preprint server prior to submission on Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, and is not under consideration for publication anywhere else. All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee. All authors agree to participate in this research. They have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qarri, F., Kika, A., Bekteshi, L. et al. Are Mosses Used in Atmospheric Trace Metal Deposition Surveys Impacted by Their Substrate Soils? A National Study in Albania. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 400–412 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-00988-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-023-00988-1