Abstract
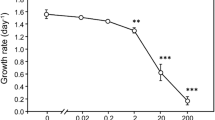
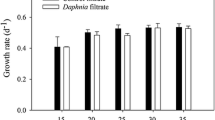
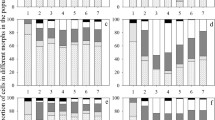
By mimicking the info-chemicals emitted by grazers, the common anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) can induce colony formation in the green algal genus Scenedesmus at environmentally relevant concentrations. The morphometric effects can hinder the feeding efficiency of grazers, reducing energy flow along the pelagic food chain from Scenedesmus to consumers. Despite this potential ecological risk, few studies exist on whether the SDS-triggered induction of colonies is common in other species of the family Scenedesmaceae. Here, we investigated the effects of SDS on the growth and morphology of three species of Scenedesmaceae (Desmodesmus subspicatus, Scenedesmus acutus, and Tetradesmus dimorphus) and on the clearance rates of Daphnia galeata grazing on the SDS-induced colonies. SDS triggered colony formation in all algal species at concentrations nonlethal to them (0.1–10 mg L−1) in 72 h; however, the induction levels of colony formation were generally lower than for those in the Daphnia culture medium. We also found that the SDS-induced colonial algae reduced D. galeata clearance rates. Our results highlight the potential effect of SDS on the Daphnia–Scenedesmaceae system by triggering the morphological response of Scenedesmaceae at concentrations below those that exert toxicity. Such disruptive effects of pollutants on predator–prey interactions should be considered within the framework of ecological risk assessments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aomura K, Ashidate N, Aisawa T, Fujita M, Goto K, Hasebe K, Hikime S, Ikehata A, Kawamura S, Kimura M et al (1981) Mizu no Bunseki. The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry, Hokkaido, Kagaku-Dojin, Kyoto, pp 374–378
Arenzon A, Pinto RF, Colombo P, Raya-Rodriguez MT (2003) Assessment of the freshwater annual fish Cynopoecilus melanotaenia as a toxicity test organism using three reference substances. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(9):2188–2190
Bondi CA, Marks JL, Wroblewski LB, Raatikainen HS, Lenox SR, Gebhardt KE (2015) Human and environmental toxicity of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS): evidence for safe use in household cleaning products. Environ Health Insights 9:EHI-31765
Boyd RS (2010) Heavy metal pollutants and chemical ecology: exploring new frontiers. J Chem Ecol 36(1):46–58
Bulus Rossini GD, Ronco AE (1996) Acute toxicity bioassay using Daphnia obtusa as a test organism. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 11(3):255–258
Chawla G, Viswanathan PN, Devi S (1987) Biochemical studies on the toxicity of linear alkylbenzene sulphonate to Scenedesmus quadricauda in culture. Environ Exp Bot 27(3):311–323
Gerritsen J, Porter KG (1982) The role of surface chemistry in filter feeding by zooplankton. Science 216:1225–1227
Ha K, Jang MH, Takamura N (2004) Colony formation in planktonic algae induced by zooplankton culture media filtrate. J Freshw Ecol 19(1):9–16
Hanazato T (2001) Pesticide effects on freshwater zooplankton: an ecological perspective. Environ Pollut 112:1–10
Hemmer MJ, Barron MG, Greene RM (2010). Comparative toxicity of Louisiana sweet crude oil (LSC) and chemically dispersed LSC to two Gulf of Mexico aquatic test species. USEPA Dispersed Oil Toxicity Testing
Hessen DO, Van Donk E (1993) Morphological changes in Scenedesmus induced by substances released from Daphnia. Arch Hydrobiol 127:129–140
Huang Y, Nan H, Zhu X, Li B, Zhang Z, Yang Z (2016) Waterborne copper impairs grazer-induced colony formation and photosynthetic efficiency in Scenedesmus obliquus. Limnol Oceanogr 61(2):625–634
Jackson M, Eadsforth C, Schowanek D, Delfosse T, Riddle A, Budgen N (2016) Comprehensive review of several surfactants in marine environments: fate and ecotoxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 35(5):1077–1086
Kilham SS, Kreeger DA, Lynn SG, Goulden CE, Herrera L (1998) COMBO: a defined freshwater culture medium for algae and zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 377(1):147–159
Lewis MA (1990) Chronic toxicities of surfactants and detergent builders to algae: a review and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 20(2):123–140
Liwarska-Bizukojc E, Miksch K, Malachowska-Jutsz A, Kalka J (2005) Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of five selected anionic and nonionic surfactants. Chemosphere 58(9):1249–1253
Lürling M (2003) Phenotypic plasticity in the green algae Desmodesmus and Scenedesmus with special reference to the induction of defensive morphology. Annales De Limnologie-Int J Limnol 39:85–101
Lürling M (2006) Effects of a surfactant (FFD-6) on Scenedesmus morphology and growth under different nutrient conditions. Chemosphere 62:1351–1358
Lürling M (2012). Infodisruption: pollutants interfering with the natural chemical information conveyance in aquatic systems. Brönmark C, Hansson LA (Eds.), Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems, Oxford University Press, New York, 250–271.
Lürling M, Beekman W (2002) Extractable substances (anionic surfactants) from membrane filters induce morphological changes in the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus (Chlorophyceae). Environ Toxicol Chem 21(6):1213–1218
Lürling M, Van Donk E (1996) Zooplankton-induced unicell-colony transformation in Scenedesmus acutus and its effect on growth of herbivore Daphnia. Oecologia 108(3):432–437
Lürling M, Van Donk E (2000) Grazer-induced colony formation in Scenedesmus: are there costs to being colonial? Oikos 88(1):111–118
Lürling M, De Lange HJ, Peeters E (2011) Effects of an anionic surfactant (FFD-6) on the energy and information flow between a primary producer (Scenedesmus obliquus) and a consumer (Daphnia magna). Ecotoxicology 20(8):1881–1889
Mariani L, De Pascale D, Faraponova O, Tornambè A, Sarni A, Giuliani S, Ruggiero G, Onorati F, Magaletti E (2006) The use of a test battery in marine ecotoxicology: the acute toxicity of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Environ Toxicol 21(4):373–379
Marker AFH, Nusch EA, Rai H, Riemann B (1980) The measurement of photosynthetic pigments in freshwaters and standardization of methods: conclusions and recommendations. Archiv Für Hydrobiologie Beihefte Ergebnisse Der Limnologie 14:91–106
Martínez-Jerónimo F, García-González R (1994) Effect of food concentration on the chronic toxicity of sodium dodecyl sulphate to Daphnia magna. J Aquat Ecosyst Health 3(4):247–253
Miner BG, Sultan SE, Morgan SG, Padilla DK, Relyea RA (2005) Ecological consequences of phenotypic plasticity. Trends Ecol Evol 20:685–692
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) (2011). OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals, no. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test. OECD, Paris
Reátegui-Zirena EG, Whatley A, Chu-Koo F, Stewart PM (2013) Acute toxicity testing of crude oil using Piaractus brachypomus, and Pimephales promelas. Int J Environ Protection 3(12):1
Rebello S, Asok AK, Mundayoor S, Jisha MS (2014) Surfactants: toxicity, remediation and green surfactants. Environ Chem Lett 12(2):275–287
Ritz C, Cedergreen N, Jensen JE, Streibig JC (2006) Relative potency in nonsimilar dose–response curves. Weed Sci 54:407–412
Ritz C, Strebig JC, Ritz MC (2016) Package ‘drc.’ Mountain View, CA, USA, Creative Commons
Shedd TR, Widder MW, Toussaint MW, Sunkel MC, Hull E (1999) Evaluation of the annual killifish Nothobranchius guentheri as a tool for rapid acute toxicity screening. Environ Toxicol Chem 18(10):2258–2261
Van Donk E (2007) Chemical information transfer in freshwater plankton. Ecol Inform 2(2):112–120
Van Donk E, Peacor S, Grosser K, Domis LNDS, Lürling M (2016). Pharmaceuticals may disrupt natural chemical information flows and species interactions in aquatic systems: ideas and perspectives on a hidden global change. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 91–105
Verschoor AM, Vos M, Van Der Stap I (2004) Inducible defences prevent strong population fluctuations in bi- and tritrophic food chains. Ecol Lett 7(12):1143–1148
Wheeler MW, Park RM, Bailer AJ (2006) Comparing median lethal concentration values using confidence interval overlap or ratio tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1441–1444
Yasumoto K, Nishigami A, Yasumoto M, Kasai F, Okada Y, Kusumi T, Ooi T (2005) Aliphatic sulfates released from Daphnia induce morphological defense of phytoplankton: isolation and synthesis of kairomones. Tetrahedron Lett 46(28):4765–4767
Yasumoto K, Nishigami A, Kasai F, Kusumi T, Ooi T (2006) Isolation and absolute configuration determination of aliphatic sulfates as the Daphnia kairomones inducing morphological defense of a phytoplankton. Chem Pharm Bull 54:271–274
Yasumoto K, Nishigami A, Aoi H, Tsuchihashi C, Kasai F, Kusumi T, Ooi T (2008a) Isolation and absolute configuration determination of aliphatic sulfates as the Daphnia kairomones inducing morphological defense of a phytoplankton—Part 2. Chem Pharm Bull 56:129–132
Yasumoto K, Nishigami A, Aoi H, Tsuchihashi C, Kasai F, Kusumi T, Ooi T (2008b) Isolation of new aliphatic sulfates and sulfamate as the Daphnia kairomones inducing morphological change of a phytoplankton Scenedesmus gutwinskii. Chem Pharm Bull 56:133–136
Yokota K, Sterner RW (2011) Trade-offs limiting the evolution of coloniality: ecological displacement rates used to measure small costs. Proc Roy Soc B Biol Sci 278(1704):458–463
Zhu X, Wang Y, Hou X, Kong Q, Sun Y, Wang J, Huang Y, Yang Z (2019) High temperature promotes the inhibition effect of Zn2+ on inducible defense of Scenedesmus obliquus. Chemosphere 216:203–212
Zhu X, Wang Z, Sun Y, Gu L, Zhang L, Wang J, Huang Y, Yang Z (2020) Surfactants at environmentally relevant concentrations interfere the inducible defense of Scenedesmus obliquus and the implications for ecological risk assessment. Environ Pollut 261:114131
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Japan Society for the Promotion of Sciences (JSPS) fellows (Grant No. JP20J11681). We thank Natalie Kim, PhD, from Edanz Group (https://en-author-services.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interests in relation to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oda, Y., Sakamoto, M. & Miyabara, Y. Colony Formation in Three Species of the Family Scenedesmaceae (Desmodesmus subspicatus, Scenedesmus Acutus, Tetradesmus Dimorphus) Exposed to Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate and its Interference with Grazing of DAPHNIA Galeata. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 82, 37–47 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-021-00890-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-021-00890-8