Abstract
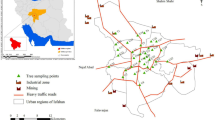
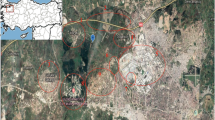
Pine trees are used as biomonitoring agents to evaluate atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Due to industrialization, urban construction, and rapid population growth, the city of Bursa is experiencing air pollution. In this study, PAHs were measured in pine tree branches and needles at a wastewater treatment plant site, an industrial site, and semirural site in Bursa for 12 months. The concentrations fluctuated depending on the characteristics of the areas. The lowest concentration value was measured in the semirural site while the highest value was determined in the wastewater treatment plant site. The PAH concentrations in pine needles ranged from 24 to 2565 ng/g dry weight (DW) and in pine branches from 163 to 2871 ng/g DW for 16 PAHs. Naphthalene, phenanthrene, fluorene, and fluoranthene were determined as dominant species in both tree components. Diagnostic ratios, ring profile, principal component analysis, the coefficient of divergence, and the Pearson correlation coefficient methods were used in the definition of sources of PAHs in the sampling sites, although all source identification methods have advantages and disadvantages. According to the results, the PAHs mainly originated from biomass and coal burning, traffic, and mixed sources. It also was concluded that three sampling sites showed higher PAH concentrations during winter, and the main PAH sources were similar.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal T, Khillare PS, Shridhar V, Ray S (2009) Pattern, sources and toxic potential of PAHs in the agricultural soils of Delhi, India. J Hazard Mater 163:1033–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.058
Agudelo-Castañeda DM, Teixeira EC (2014) Seasonal changes, identification and source apportionment of PAH in PM1.0. Atmos Environ 96:186–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.07.030
Arhami M, Shahne MZ, Hosseini V, Roufigar Haghighat N, Lai AM, Schauer JJ (2018) Seasonal trends in the composition and sources of PM2.5 and carbonaceous aerosol in Tehran, Iran. Environ Pollut 239:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.111
Baniemam M, Moradi AM, Bakhtiari AR, Fatemi MR, Khanghah KE (2017) Seasonal variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface sediments of the southern Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 117:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.027
Bano S, Pervez S, Chow JC, Matawle JL, Watson JG, Sahu RK, Srivastava A, Tiwari S, Pervez YF, Deb MK (2018) Coarse particle (PM10–2.5) source profiles for emissions from domestic cooking and industrial process in Central India. Sci Total Environ 627:1137–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.289
Bedjanian Y, Nguyen ML (2010) Kinetics of the reactions of soot surface-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with O3. Chemosphere 79:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.02.009
Birgul A, Tasdemir Y (2015) Concentrations, gas-particle partitioning, and seasonal variations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at four sites in Turkey. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 68:46–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0105-8
Bu QW, Zhang ZH, Lu S, He FP (2009) Vertical distribution and environmental significance of PAHs in soil profiles in Beijing, China. Environ Geochem Health 31:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9171-z
Cao S, Na G, Li R, Ge L, Gao H, Jin S, Hou C, Gao Y, Zhang Z (2018) Fate and deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Bransfield Strait, Antarctica. Mar Pollut Bull 137:533–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.10.045
Cesari D, De Benedetto GE, Bonasoni P, Busetto M, Dinoi A, Merico E, Chirizzi D, Cristofanelli P, Donateo A, Grasso FM, Marinoni A, Pennetta A, Contini D (2018) Seasonal variability of PM2.5 and PM10 composition and sources in an urban background site in Southern Italy. Sci Total Environ 612:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.230
Cetin B, Yurdakul S, Gungormus E, Ozturk F, Sofuoglu SC (2018) Source apportionment and carcinogenic risk assessment of passive air sampler-derived PAHs and PCBs in a heavily industrialized region. Sci Total Environ 633:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.145
Cheng LH, Yeh CF, Tsai KC, Lee PF, Tseng TP, Huang LJ, Yeh SH, Hsu HT, Lin CH, Lai CH, Brimblecombe P, Chen MJ (2019) Effect of pool fire scale of heavy fuel oil on the characteristics of PAH emissions. Fuel 235:933–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.08.022
Choi SD (2014) Time trends in the levels and patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in pine bark, litter, and soil after a forest fire. Sci Total Environ 470–471:1441–1449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.100
Chuang H-C, Sun J, Ni H, Tian J, Lui KH, Han Y, Cao J, Huang R-J, Shen Z, Ho K-F (2019) Characterization of the chemical components and bioreactivity of fine particulate matter produced during crop-residue burning in China. Environ Pollut 245:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.119
Cindoruk SS, Esen F, Tasdemir Y (2005) Concentration and gas/particle partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) at an industrial site at Bursa, Turkey. Atmos Res 85:338–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2007.02.004
Dat ND, Chang MB (2017) Review on characteristics of PAHs in atmosphere, anthropogenic sources and control technologies. Sci Total Environ 609:682–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.204
De Nicola F, Concha Graña E, López Mahía P, Muniategui Lorenzo S, Prada Rodríguez D, Retuerto R, Carballeira A, Aboal JR, Fernández JÁ (2017) Evergreen or deciduous trees for capturing PAHs from ambient air? A case study. Environ Pollut 221:276–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.074
Duodu GO, Ogogo KN, Mummullage S, Harden F, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2017) Source apportionment and risk assessment of PAHs in Brisbane River sediment, Australia. Ecol Indic 73:784–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.10.038
Eccleshare L, Selzer S, Woodward S (2017) An efficient synthesis of substituted chrysenes. Tetrahedron Lett 58:393–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.12.004
Esen F, Cindoruk SS, Taşdemir Y (2006) Ambient concentrations and gas/particle partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in an urban site in Turkey. Environ Forensics 7:303–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275920600996099
Esen F, Tasdemir Y, Vardar N (2008) Atmospheric concentrations of PAHs, their possible sources and gas-to-particle partitioning at a residential site of Bursa, Turkey. Atmos Res 88:243–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2007.11.022
Fang GC, Chang KF, Lu C, Bai H (2004) Estimation of PAHs dry deposition and BaP toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) study at Urban, Industry Park and rural sampling sites in central Taiwan, Taichung. Chemosphere 55:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.12.012
Fang M-D, Lee C-L, Jiang J-J, Ko F-C, Baker JE (2012) Diffusive exchange of PAHs across the air-water interface of the Kaohsiung Harbor lagoon, Taiwan. J Environ Manag 110:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.06.001
Gong X, Xiao L, Zhao Z, Li Q, Feng F, Zhang L, Deng Z (2018) Spatial variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from rivers in hilly regions of Southern China in the wet and dry seasons. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 156:322–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.004
Günindi M, Tasdemir Y (2010) Atmospheric polychlorinated biphenyl (pcb) inputs to a coastal city near the marmara sea. Mar Pollut Bull 60:2242–2250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.08.012
Hanedar A, Alp K, Kaynak B, Avşar E (2014) Toxicity evaluation and source apportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) at three stations in Istanbul, Turkey. Sci Total Environ 488–489:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.123
Howsam M, Jones KC, Ineson P (2000) PAH associated with the leaves of three deciduous tree speciesI.pdf. 108
Hwang HM, Wade TL, Sericano JL (2003) Concentrations and source characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in pine needles from Korea, Mexico, and United States. Atmos Environ 37:2259–2267. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00090-6
Keyte IJ, Harrison RM, Lammel G (2013) Chemical reactivity and long-range transport potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons—a review. Chem Soc Rev 42:9333–9391. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60147a
Khuman SN, Chakraborty P, Cincinelli A, Snow D, Kumar B (2018) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface waters and riverine sediments of the Hooghly and Brahmaputra Rivers in the Eastern and Northeastern India. Sci Total Environ 636:751–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.109
Kipopoulou AM, Manoli E, Samara C (1999) Bioconcentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in vegetables grown in an industrial area Bioconcentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in vegetables grown in an industrial area. Environ Pollut 106:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00107-4
Kurre A, Bastiaenen CHG, Van Gool CJAW, Gloor-Juzi T, De Bruin ED, Straumann D (2010) Exploratory factor analysis of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (German version). BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 10:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6815-10-3
Kuzu SL (2016) Compositional variation of PCBs, PAHs, and OCPs at gas phase and size segregated particle phase during dust incursion from the saharan desert in the northwestern anatolian peninsula. Adv Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7153286
Lai YC, Tsai CH, Chen YL, Chang-Chien GP (2017) Distribution and sources of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at an industrial region in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual Res 17:776–787. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2016.11.0482
Lehndorff E, Schwark L (2004) Biomonitoring of air quality in the cologne conurbation using pine needles as a passive sampler—Part II: polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH). Atmos Environ 38:3793–3808. https://doi.org/10.1177/1356766705052569
Li L, Lu Y, Shi Y, Wang T, Luo W, Gosens J, Chen P, Li H (2013) Integrated technology selection for energy conservation and PAHs control in iron and steel industry: methodology and case study. Energy Policy 54:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.11.022
Liu JJ, Wang XC, Fan B (2011) Characteristics of PAHs adsorption on inorganic particles and activated sludge in domestic wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 102:5305–5311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.063
Liu Y, Yan C, Ding X, Wang X, Fu Q, Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Duan Y, Qiu X, Zheng M (2017) Sources and spatial distribution of particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 584–585:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.134
Liu Y, Yu Y, Liu M, Lu M, Ge R, Li S, Liu X, Dong W, Qadeer A (2018) Characterization and source identification of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in different seasons from Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 644:725–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.049
Malawska M, Ekonomiuk A, Wilkomirski B (2006) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in peat cores from southern Poland: distribution in stratigraphic profiles as an indicator of PAH sources. Environ Monit Assess 1:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-05722010000400005
Mętrak M, Aneta E, Wiłkomirski B, Staszewski T, Suska-Malawska M (2016) Interspecific differences in foliar 1 PAHs load between Scots pine, birch, and wild rosemary from three polish peat bogs. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5465-2
Nguyen TNT, Jung KS, Son JM, Kwon HO, Choi SD (2018) Seasonal variation, phase distribution, and source identification of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at a semi-rural site in Ulsan, South Korea. Environ Pollut 236:529–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.080
Odabasi M, Ozgunerge Falay E, Tuna G, Altiok H, Kara M, Dumanoglu Y, Bayram A, Tolunay D, Elbir T (2015) Biomonitoring the spatial and historical variations of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in an industrial region. Environ Sci Technol 49:2105–2114. https://doi.org/10.1021/es506316t
Oguntimehin I, Eissa F, Sakugawa H (2010) Negative effects of fluoranthene on the ecophysiology of tomato plants (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill). Fluoranthene mists negatively affected tomato plants. Chemosphere 78:877–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.11.030
Oishi Y (2013) Comparison of pine needles and mosses as bio-indicators for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Environ Prot (Irvine, Calif) 04:106–113. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2013.48A1013
Orecchio S, Gianguzza A, Culotta L (2008) Absorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Pinus bark: analytical method and use for environmental pollution monitoring in the palermo area (Sicily, Italy). Environ Res 107:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2008.02.010
Ozaki N, Takamura Y, Kojima K, Kindaichi T (2015) Loading and removal of PAHs in a wastewater treatment plant in a separated sewer system. Water Res 80:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.002
Ozcan S, Aydin ME (2009) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in urban air of Konya, Turkey. Atmos Res 93:715–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2009.02.012
Ozgunerge Falay E, Tuna G, Altiok H, Kara M, Dumanoglu Y, Bayram A, Tolunay D, Elbir T, Odabasi M (2013) Spatial variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air, soil and tree components in iskenderun industrial region, Turkey. Int J Chem Environ Biol Sci 1:263–267
Piccardo MT, Pala M, Bonaccurso B, Stella A, Redaelli A, Paola G, Valerio F (2005) Pinus nigra and Pinus pinaster needles as passive samplers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Pollut 133:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.034
Ratola N, Lacorte S, Barceló D, Alves A (2009) Microwave-assisted extraction and ultrasonic extraction to determine polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in needles and bark of Pinus pinaster Ait. and Pinus pinea L. by GC-MS. Talanta 77:1120–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.08.010
Salihoglu NK, Karaca G, Salihoglu G, Tasdemir Y (2012) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from municipal sludge using UV light. Desalin Water Treat 44:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.691689
Shen R, Liu Z, Chen X, Wang Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Li X (2019) Atmospheric levels, variations, sources and health risk of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during winter over the North China Plain. Sci Total Environ 655:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.220
Sun F, Wen D, Kuang Y, Li J, Li J, Zuo W (2010) Concentrations of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in needles of Masson pine (Pinus massoniana L.) growing nearby different industrial sources. J Environ Sci 22:1006–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60211-4
Taghvaee S, Sowlat MH, Hassanvand MS, Yunesian M, Naddafi K, Sioutas C (2018) Source-specific lung cancer risk assessment of ambient PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in central Tehran. Environ Int 120:321–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.08.003
Tasdemir Y, Esen F (2007) Urban air PAHs: Concentrations, temporal changes and gas/particle partitioning at a traffic site in Turkey. Atmos Res 84:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2006.04.003
Tipmanee D, Deelaman W, Pongpiachan S, Schwarzer K, Sompongchaiyakul P (2012) Using Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) as a chemical proxy to indicate Tsunami 2004 backwash in Khao Lak coastal area, Thailand. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12:1441–1451. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-12-1441-2012
Tobiszewski M, Namieśnik J (2012) PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environ Pollut 162:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.10.025
Tomashuk TA, Truong TM, Mantha M, McGowin AE (2012) Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon profiles and sources in pine needles and particulate matter in Dayton, Ohio, USA. Atmos Environ 51:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.01.028
Torretta V (2012) PAHs in wastewater: Removal efficiency in a conventional wastewater treatment plant and comparison with model predictions. Environ Technol 33:851–855. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2011.599430
Tripathi BD, Chaturvedi SS, Tripathi RD (1996) Seasonal variation in ambient air concentration of nitrate and sulfate aerosols in a tropical city, Varanasi. Atmos Environ 30:2773–2778. https://doi.org/10.1016/1352-2310(95)00435-1
Vardar N, Tasdemir Y, Odabasi M, Noll KE (2004) Characterization of atmospheric concentrations and partitioning of PAHs in the Chicago atmosphere. Sci Total Environ 327:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.05.002
Wołejko E, Wydro U, Jabłońska-Trypuć A, Butarewicz A, Łoboda T (2018) The effect of sewage sludge fertilization on the concentration of PAHs in urban soils. Environ Pollut 232:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.120
Yadav V, Turner J (2014) Gauging intraurban variability of ambient particulate matter arsenic and other air toxic metals from a network of monitoring sites. Atmos Environ 89:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.02.030
Yunker MB, Macdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Mitchell RH, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser river basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org Geochem 33:489–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00002-5
Zhang P, Wang Y, Yang B, Liu C, Shu J (2014) Heterogeneous reactions of particulate benzo[b]fluoranthene and benzo[k]fluoranthene with NO3radicals. Chemosphere 99:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.093
Zhang J, Li R, Zhang X, Bai Y, Cao P, Hua P (2019) Vehicular contribution of PAHs in size dependent road dust: a source apportionment by PCA-MLR, PMF, and Unmix receptor models. Sci Total Environ 649:1314–1322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.410
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) (Project Number 114Y577) and The Commission of Scientific Research Projects of the Bursa Uludag University (Project Number: OUAP (MH) 2014/22). The authors thank Nihan DURAK and Berfu BUKLER for their worthy help during the tiresome laboratory studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sari, M.F., Esen, F. & Tasdemir, Y. Biomonitoring and Source Identification of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Using Pine Tree Components from Three Different Sites in Bursa, Turkey. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 78, 646–657 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00722-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00722-1