Abstract
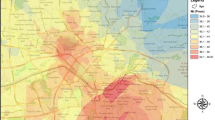
Urban soil pollution is evaluated utilizing an efficient and simple algorithmic model referred to as the entropy method-based Topsis (EMBT) model. The model focuses on pollution source position to enhance the ability to analyze sources of pollution accurately. Initial application of EMBT to urban soil pollution analysis is actually implied. The pollution degree of sampling point can be efficiently calculated by the model with the pollution degree coefficient, which is efficiently attained by first utilizing the Topsis method to determine evaluation value and then by dividing the evaluation value of the sample point by background value. The Kriging interpolation method combines coordinates of sampling points with the corresponding coefficients and facilitates the formation of heavy metal distribution profile. A case study is completed with modeling results in accordance with actual heavy metal pollution, proving accuracy and practicality of the EMBT model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad Q, Mohammad A, Falah BH (2012) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy logic system for heavy metal sorption in aquatic environments. J Water Res Protect 2012.
Amadi Akobundu N (2012) Quality Assessment of Aba River using heavy metal pollution index. Am J Environ Eng 2(1):45–49
Benson VS, VanLeeuwen JA, Sanchez J, Dohoo IR, Somers GH (2006) Spatial analysis of land use impact on ground water nitrate concentrations. J Environ Qual 35(2):421–432
Chung JM, Lee BC, Kim JS, Park CW, Chung MY, Chung MG (2006) Fine-scale genetic structure among genetic individuals of the clone-forming monotypic genus Echinosophora koreensis (Fabaceae). Ann Botany 98(1):165–173
Fang FM, Wang QC (2000) A review on studies on mercury pollution of soil. Soil Environ Sci 9(4)
Gaetke LM, Chow CK (2003) Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 189(1):147–163
Guo G, Wu F, Xie F, Zhang R (2012) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China. J Environ Sci 24(3):410–418
Jovanovic S, Carrot F, Deschamps C, Deschamps N, Vukotic P (1995) A study of the air pollution in the surroundings of an aluminium smelter, using epiphytic and lithophytic lichens. J Trace Microprobe Tech 13(4):463–471
Jung WK, Kitchen NR, Sudduth KA, Anderson SH (2006) Spatial characteristics of claypan soil properties in an agricultural field. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70(4):1387–1397
Lavanpriya C, Manivel M, Lakshmanpriya C (2013) A case study of integrating the Taguchi Loss Function and Topsis Method to select an optimal supplier in a manufacturing industry. SIJ Trans Ind Financ Bus Manag (IFBM), 1(1)
Lee CC, Chiang C, Chen CT (2012) An evaluation model of e-service quality by applying hierarchical fuzzy TOPSIS method. Int J Electron Bus Manag 10(1):38
Marković Z (2013) Modification of TOPSIS method for solving of multicriteria tasks. Yugosl J Oper Res ISSN: 0354-0243 EISSN: 2334–6043, 20(1).
Pen-Mouratov S, Shukurov N, Steinberger Y (2008) Influence of industrial heavy metal pollution on soil free-living nematode population. Environ Pollut 152(1):172–183
Wang YT, Bai XZ, He MY, Huang BX (2009) Enrichment factor appraisal of farming soil heavy metal in Tongzi town land consolidation area of Jiang’an county Yibin City, China. Earth Environ 37(3):258–263
Zhang C (2006) Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ Pollut 142(3):501–511
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Liu, C. & Han, W. Efficiently Evaluating Heavy Metal Urban Soil Pollution Using an Improved Entropy-Method-Based Topsis Model. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 71, 377–382 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0304-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0304-6