Abstract
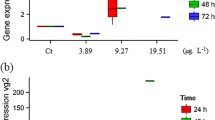
Several endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) have been attributed to the alteration of reproduction in fish through disrupting endogenous sex steroidogenic pathways including aromatisation of androgens to oestrogen by CYP19 aromatase. Here we investigate this hypothesis in adult male and female Melanotaenia fluviatilis by examining the mRNA expression of cyp19a1 isoforms after exposure for ≤96 h to two EDCs with contrasting modes of action: one a weak oestrogen mimic, bisphenol A [BPA (100 or 500 μg/L)], and the other a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor, fadrozole [FAD (10 or 50 µg/L)]. The results suggest that BPA did not affect cyp19a1a expression significantly at both concentrations, whereas 50 µg/L of FAD significantly upregulated its expression in ovary. In contrast, BPA exposures increased expression of cyp19a1b in brain of both males and females, whilst FAD had contrasting effects in brain: It increased in males but decreased in females. Similar contrasting responses of cyp19a1b were induced by BPA in gonads: upregulation in ovary and downregulation in testis. FAD did not have a significant effect on gonadal expression of cyp19a1b. Collectively, the results suggest that BPA and FAD can disrupt cyp19a1b activity more readily than can cyp19a1a, albeit with contrasting effects in either a tissue- or sex-specific context that is conceivably consistent with their (BPA and FAD) opposing modes of action. Enhanced spatial and temporal sensitivity of cyp19a1b compared with cyp19a1a suggests that brain sex of fish is more susceptible to disruption by environmental pollutants such as BPA and FAD. Therefore, we propose that the response of cyp19a1b in brain tissue of M. fluviatilis is a more suitable indicator of oestrogenic pollution in the aquatic environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MA, Bhandari RK, Kobayashi Y, Soyano K, Nakamura M (2006) Induction of sex change within two full moons during breeding season and spawning in grouper. Aquaculture 255:532–535
Ankley GT, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Hornung MW, Korte JJ, Makynen EA et al (2002) Evaluation of the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole in a short-term reproduction assay with the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Toxicol Sci 67:121–130
Balcombe SR, Sheldon F, Capon SJ, Bond NR, Hadwen WL, Marsh N et al (2011) Climate-change threats to native fish in degraded rivers and floodplains of the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Mar Freshw Res 62:1099–1114
Barney ML, Patil JG, Gunasekera RM, Carter CG (2008) Distinct cytochrome P450 aromatase isoforms in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio): sexual dimorphism and onset of ontogenic expression. Gen Comp Endocrinol 156:499–508
Bhandari RK, Higa M, Nakamura S, Nakamura M (2004) Aromatase inhibitor induces complete sex in protogynous honeycomb grouper, Epinephelus merra. Mol Reprod Dev 67:303–307
Bjerselius R, Lundstedt-Enkel K, Olsen H, Mayer I, Dimberg K (2001) Male goldfish reproductive behaviour and physiology are severely affected by exogenous exposure to 17β-estradiol. Aquat Toxicol 53:139–152
Bolognesi C, Perrone E, Roggieri P, Pampanin D, Sciutto A (2006) Assessment of micronuclei induction in peripheral erythrocytes of fish exposed to xenobiotics under controlled conditions. Aquat Toxicol 78:S93–S98
Bonnefoi HR, Smith IE, Dowsett M, Trunet PF, Houston SJ, Da Luz RJ et al (1996) Therapeutic effects of the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole hydrochloride in advanced breast cancer. Br J Can 73:539–542
Cakmak G, Togan I, Severcan F (2006) 17β-Estradiol induced compositional, structural and functional changes in rainbow trout liver, revealed by FT-IR spectroscopy: a comparative study with nonylphenol. Aquat Toxicol 77:53–56
Callard GV, Tchoudakova AV, Kishida M, Wood E (2001) Differential tissue distribution, developmental programming, estrogen regulation and promoter characteristics of cyp19 genes in teleost fish. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 79:305–314
Campbell CG, Sharon E, Borglin SE, Green FB, Grayson A, Wozei E et al (2006) Biologically directed environmental monitoring, fate, and transport of estrogenic endocrine disrupting compounds in water: a review. Chemosphere 65:1265–1280
Carlone DL, Richards JS (1997) Functional interactions, phosphorylation, and levels of 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate regulatory element binding protein and steroidogenic factor-1 mediate hormone-regulated and constitutive expression of aromatase in gonadal cells. Mol Endocrinol 11:292–304
Chang CF, Lin BY (1998) Estradiol-17β stimulates aromatase activity and reversible sex change in protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli. J Exp Zool 280:165–173
Chapin RE, Adams J, Boekelheide K, Gray LE Jr, Hayward SW, Lees PS et al (2008) NTP-CERHR expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of bisphenol A. Birth Defects Res B 83:157–395
Chau YM, Crawford PA, Woodson KG, Polish JA, Olson LM, Sadovsky Y (1997) Role of steroidogenic-factor I in basal and 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated regulation of cytochrome P450 side-chain cleavage enzyme in the mouse. Biol Rep 57:765–771
Cheshenko K, Pakdel F, Segner H, Kah O, Eggen RIL (2008) Interference of endocrine disrupting chemicals with aromatase CYP19 expression or activity, and consequences for reproduction of teleost fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 155:31–62
Devlin RH, Nagahama Y (2002) Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: an overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 208:191–364
Fenske M, Segner H (2004) Aromatase modulation alters gonadal differentiation in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 67:105–126
Flint S, Markle T, Thompson S, Wallace E (2012) Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: a wildlife perspective. J Environ Manag 104:19–34
Guigen Y, Fostier A, Piferrer F, Chang CF (2010) Ovarian aromatase and estrogens: a pivotal role for gonadal sex differentiation and sex change in fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 165:352–366
Hayashi H, Nishimoto A, Oshima N, Iwamuro S (2007) Expression of the estrogen receptor alpha gene in the anal fin of Japanese medaka, Oryzias latipes, by environmental concentrations of bisphenol A. J Toxicol Sci 32:91–96
Hearn MTW, Gomme PT (2000) Molecular architecture and biorecognition processes of the cystine knot protein superfamily: Part I. The glycoprotein hormones. J Mol Recognit 13:223–278
Kang JH, Asai D, Katayama Y (2007) Bisphenol A in the aquatic environment and its endocrine-disruptive effects on aquatic organisms. Crit Rev Toxicol 37:607–625
Kazeto Y, Ijiri S, Place AR, Zohar Y, Trant JM (2001) The 5′-flanking regions of CYP19A1 and CYP19A2 in zebrafish. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 288:503–508
Kibria G, Haroon Y, Nugegoda D, Rose G (2010) Climate change and chemicals: environmental biology aspects. New Delhi Publishing, New Delhi, p 460
Kishida M, Callard GC (2001) Distinct cytochrome P450 aromatase isoforms in zebrafish Danio rerio brain and ovary are differentially programmed and oestrogen regulated during early development. Endocrinology 142:740–750
Komatsu T, Nakamura S, Nakamura M (2006) Masculinization of female golden rabbitfish, Siganus guttatus using an aromatase inhibitor treatment during sex differentiation. Comp Biochem Physiol C 143:402–409
Kroon FJ, Munday PL, Westcott DA, Hobbs JPA, Liley NR (2005) Aromatase pathway mediates sex change in each direction. Proc R Soc B 272:1399–1405
Kwon JY, McAndrew BJ, Penman DJ (2002) Treatment with an aromatase inhibitor suppresses high-temperature feminization of genetic male (YY) Nile tilapia. J Fish Biol 60:625–636
Lee YM, Seo JS, Kim IC, Yoon YD, Lee JS (2006) Endocrine disrupting chemicals (bisphenol A, 4-nonylphenol, 4-tert-octylphenol) modulate expression of two distinct cytochrome P450 aromatase genes differently in gender types of the hermaphroditic fish Rivulus marmoratus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:894–903
Li Y, Luh CJ, Burns KA, Arao Y, Jiang Z, Teng CT et al (2013) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs): in vitro mechanism of estrogenic activation and differential effects on ER target genes. Environ Health Perspect 121:459–466
Liu S, Qin F, Wang H, Wu T, Zhang Y, Zheng Y et al (2012) Effects of 17α-ethinylestradiol and bisphenol A on steroidogenic messenger ribonucleic acid levels in the rare minnow gonads. Aquat Toxicol 122–123:19–27
Markey CM, Rubin BS, Soto AM, Sonnenschein C (2002) Endocrine disruptors: from wingspread to environmental developmental biology. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 83:235–244
Minghong W, Hai X, Ming Y, Gang X (2011) Effects of chronic bisphenol A exposure on hepatic antioxidant parameters in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Toxicol Environ Chem 93:270–278
Muller PY, Janovjak H, Miserez AR, Dobbie Z (2002) Processing of gene expression data generated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Biotechniques 32:1372–1379
Oehlmann J, Oetken M, Schulte-Oehlmann U (2008) A critical evaluation of the environmental risk assessment for plasticizers in freshwater environment in Europe, with special emphasis on bisphenol A and endocrine disruption. Environ Res 108:140–149
Page YL, Vosges M, Servili A, Brion F, Kah O (2011) Neuroendocrine effects of endocrine disruptors in teleost fish. J Toxicol Environ Health B 14:370–386
Paquette M (2008) Effects of the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole on gene expression in the zebrafish brain. Master’s Thesis. University of Ottawa, Ottowa, Canada, p 96
Parker KL, Schimmer BP (1995) Transcriptional regulation of the genes encoding the cytochrome P-450 steroid hydroxylases. Vitam Horm 51:339–369
Patil JG, Gunasekera RM (2008) Tissue and sexually dimorphic expression of ovarian and brain aromatase mRNA in the Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes): implications for their preferential roles in ovarian and neural differentiation and development. Gen Comp Endocrinol 158:131–137
Piferrer F, Zanuy S, Carrillo M, Solar II, Devlin RH, Donaldson EM (1994) Brief treatment with an aromatase inhibitor during sex differentiation causes chromosomally female salmon to develop as normal, functional males. J Exp Zool 270:255–262
Pollino CA, Georgiades E, Holdway DA (2007) Use of the Australian crimson-spotted rainbowfish (Melanotaenia fluviatilis) as a model test species for investigating the effects of endocrine disruptors. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:2171–2178
Ponza P (2006) Molecular markers of ecotoxicological interest in the rainbowfish Melanotaenia fluviatilis. Doctoral Thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Ruksana S, Pandit NP, Nakamura M (2010) Efficacy of exemestane, a new generation of aromatase inhibitor, on sex differentiation in a gonochoristic fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C 152:69–74
Shanthanagouda AH, Patil JG, Nugegoda D (2012) Ontogenic and sexually dimorphic expression of cyp19 isoforms in the rainbowfish, Melanotaenia fluviatilis (Castelnau 1878). Comp Biochem Physiol A 161:250–258
Shanthanagouda AH, Patil JG, Nugegoda (2013a) Effects of exposure to oestrogenic compounds on aromatase gene expression are gender dependent in the rainbowfish, Melanotaenia fluviatilis. Comp Biochem Physiol C 57:162–171
Shanthanagouda AH, Nugegoda D, Hassell KL, Patil JG (2013b) Exposure to estrogenic chemicals induces ectopic expression of vtg in the testis of Rainbowfish, Melanotaenia fluviatilis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:438–443
Staples CA, Dome BP, Klecka GM, Oblock ST, Harris LR (1998) A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 36:1249–2179
Steele R, Mellor L, Sawyer W, Wasvary J, Browne L (1987) In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrating potent and selective inhibition with the non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor. Steroids 50:147–161
Tompsett AR, Park JW, Zhang X, Jones PD, Newsted JL, Au DWT et al (2009) In situ hybridization to detect spatial gene expression in medaka. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1257–1264
Uchida D, Yamashita M, Kitano T, Iguchi T (2004) An aromatase inhibitor or high water temperature induce oocyte apoptosis and depletion of P450 aromatase activity in the gonads of genetic female zebrafish during sex-reversal. Comp Biochem Physiol A 137:11–20
Villeneuve DL, Knoebl I, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Hammermeister DE, Greene KJ et al (2006) Relationship between brain and ovary aromatase activity and isoform-specific aromatase mRNA expression in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Aquat Toxicol 76:353–368
Villeneuve DL, Wang RL, Bencic DC, Biales AD, Martinović D, Lazorchak JM et al (2009) Altered gene expression in the brain and ovaries of zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole: microarray analysis and hypothesis generation. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1767–1782
Wang J, Liu X, Wang H, Wu T, Hu X, Qin F, Wang Z (2010) Expression of two cytochrome P450 aromatase genes is regulated by endocrine disrupting chemicals in rare minnow, Gobiocypris rarus juveniles. Comp Biochem Physiol C 152:313–320
Wibbels T, Cowan J, LeBoeuf R (1998) Temperature-dependent sex determination in the red-eared slider turtle, Trachemys scripta. J Exp Zool 281:409–416
Yue W, Brodie A (1997) Mechanisms of the actions of aromatase inhibitors 4-hydroxyandrostenedione, fadrozole, and aminoglutethimide on aromatase in cell culture. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 63:317–328
Zhang P, Mellon SH (1997) Multiple orphan nuclear receptors converge to regulate rat P450c17 gene transcription: novel mechanisms for orphan nuclear receptor action. Mol Endocrinol 11:891–904
Acknowledgments
A. H. Shanthanagouda was awarded an RMIT University Scholarship (RUIS). The authors thank anonymous reviewers’ suggestions on the manuscript, which helped to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shanthanagouda, A.H., Nugegoda, D. & Patil, J.G. Effects of Bisphenol A and Fadrozole Exposures on cyp19a1 Expression in the Murray Rainbowfish, Melanotaenia fluviatilis . Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67, 270–280 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0047-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0047-1