Abstract
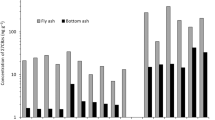
Fly ash and bottom ash samples were collected from a coal-fired power plant located in Anhui province, China. Mineral phases and morphologies of the samples were determined by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. Sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH; 16 compounds specified in United States Environmental Protection Agency Method 610) properties in ash samples were investigated. In fly ashes, ∑16PAH (total amount of 16 PAHs) and ∑CPAH (total amount of 8 carcinogenic PAHs) levels varied from 0.93 to 2.08 μg/g and from 0.26 to 0.87 μg/g, respectively. In bottom ashes, ∑16PAH and ∑CPAH levels varied from 2.83 to 5.32 and 1.76 to 3.76 μg/g, respectively. Fly ashes were dominated by medium molecular-weight PAHs and low molecular-weight PAHs, whereas bottom ashes were abundant in 5- and 6-ring PAH species. The CPAHs levels of some ashes, especially bottom ashes, are greater than the limits regulated by several countries, indicating that this type of coal combustion product requires special treatment before landfill. PAH levels and patterns in fly ash were evidently affected by particle size, and total organic content had a closer correlation with PAH content than particle size in bottom and fly ash, which may be due to unburned carbon existing in bottom ash.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achten C, Hofmann T (2009) Native polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in coals—a hardly recognized source of environmental contamination. Sci Total Environ 407:2461–2473
Ahmaruzzaman M (2010) A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog Energy Combust 36:327–363
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) (1997) Annual book of ASTM standards. ASTM, West Conshohocken, PA; Section 05.05 Gaseous Fuels, Coal and Coke.
Arditsoglou A, Petaloti C, Terzi E, Sofoniou M, Samara C (2004) Size distribution of trace elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fly ashes generated in Greek lignite-fired power plants. Sci Total Environ 323:153–167
Davies IW, Harrison RW, Perry R, Ratnayaka D, Wellings RA (1976) Municipal incinerator as a source of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in environment. Environ Sci Technol 10:451–453
Dugenest S, Casabianca H, Grenier-Loustalot MF (1999) Municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash: physicochemical characterization of organic matter. Analusis 27:75–80
Enell A, Fuhrman F, Lundin L, Warfvinge P, Thelin G (2008) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ash: determination of total and leachable concentrations. Environ Pollut 152:285–292
Ghosh U, Talley JW, Luthy RG (2001) Particle-scale investigation of PAH desorption kinetics and thermodynamics from sediment. Environ Sci Technol 35:3468–3475
Henry J, Towler MR, Stanton KT, Querol X, Moreno N (2004) Characterisation of the glass fraction of a selection of European coal fly ashes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:540–546
Johansson I, Bavel BV (2003a) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in weathered bottom ash from incineration of municipal solid waste. Chemosphere 53:123–128
Johansson I, Bavel BV (2003b) Levels and patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in incineration ashes. Sci Total Environ 311:221–231
Karapanagioti HK, Kleineidam S, Sabatini DA, Grathwohl P, Ligouis B (2000) Impacts of heterogeneous organic matter on phenanthrene sorption: Equilibrium and kinetic studies with aquifer material. Environ Sci Technol 34:406–414
Kong SF, Shi JW, Lu B, Qiu WG, Zhang BS, Peng Y et al (2011) Characterization of PAHs within PM10 fraction for ashes from coke production, iron smelt, heating station and power plant stacks in Liaoning Province, China. Atmos Environ 45:3777–3785
Lee WM, Yen SY, Chen JC (1993) The relation between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organic carbon in fly ash from a municipal incinerator. J Environ Sci Health A 28:1495–1506
Levendis YA, Atal A, Carlson JB (2001) PAH and soot emissions from burning components of medical waste: examination/surgical gloves and cotton pads. Chemosphere 42:775–783
Liu GJ, Wang GL, Zhang W (1999) Study on environmental geochemistry of trace and minor elements in coal—example for Yanzhou mining area [M]. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Liu KL, Xie W, Zhao ZB, Pan WP, Rilley JT (2000) Investigation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fly ash from fluidized bed combustion systems. Environ Sci Technol 34:2273–2279
Liu KL, Heltsley R, Zou DZ, Pan WP, Riley JT (2002) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions in fly ashes from an atmospheric fluidized bed combustor using thermal extraction coupled with GC/TOF-MS. Energy Fuel 16:330–337
Liu GJ, Niu ZY, Daniel VN, Xue J, Zheng LG (2008) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from coal combustion: emissions, analysis and toxicology. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 192:1–28
Liu JJ, Liu GJ, Zhang JM, Yin H, Wang RW (2012) Occurrence and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil from the Tiefa coal mine district, Liaoning, China. J Environ Monit 14:2634–2642
Low GK, Batley GE (1986) Use of liquid chromatography for the measurement of adsorption isotherms for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coal fly ashes. J Chromatogr 355:177–191
Marrero J, Polla G, Rebagliati RJ, Plá R, Gómez D, Smichowski P (2007) Characterization and determination of 28 elements in fly ashes collected in a thermal power plant in Argentina using different instrumental techniques. Spectrochimica Acta B 62:101–108
Masala S, Bergvall C, Westerholm R (2012) Determination of benzo[a]pyrene and dibenzopyrenes in a Chinese coal fly ash certified reference material. Sci Total Environ 432:97–102
Mastral AM, Callén MS (2000) A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) emissions from energy generation. Environ Sci Technol 34:3051–3056
Mastral AM, Garcia T, Callen MS, Lopez JM, Murillo R, Navarro MV (2001) Effects of limestone on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions during coal atmospheric fluidized bed combustion. Energy Fuel 15:1469–1474
Meij R, Henk TW (2007) The emissions of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from modern coal-fired power stations. Atoms Environ 41:9262–9272
Oanh NTK, Albina DO, Ping L, Wang XK (2005) Emission of particulate matter and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from selected cook stove-fuel systems in Asia. Biomass Bioenerg 28:579–590
Pacyna JM, Breivik K, Munch J, Fudala J (2003) European atmospheric emissions of elected persistent organic pollutants 1970–1975. Atmos Environ 37:119–131
Palo CD, Stefanis PD, Massa M, Montani R (1996) Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) from solid waste incinerator equipped with an after-combustion chamber. Polycycl Aromat Compd 9:45–51
Sahu SK, Bhangare RC, Ajmal PY, Sharma S, Pandit GG, Puranik VD (2009) Characterization and quantification of persistent organic pollutants in fly ash from coal fueled thermal power stations in India. Microchem J 92:92–96
Shen CF, Tang XJ, Yao J, Shi DZ, Fang J, Khan MI et al (2010) Levels and patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in municipal waste incinerator bottom ash in Zhejiang province, China. J Hazard Mater 179:197–202
Smith KR (1987) Biofuels, air pollution, and health—a global review. Plenum, New York
Stout SA, Emsbo-Mattingly SD (2008) Concentration and character of PAHs and other hydrocarbons in coals of varying rank—implications for environmental studies of soils and sediments containing particulate coal. Org Geochem 39:801–819
Sun P, Taerakul P, Weavers LK, Walker HW (2005) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in lime spray dryer ash. Energy Fuel 19:1911–1918
Sun P, Weavers LK, Taerakul P, Walker HW (2006) Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) on lime spray dryer (LSD) ash using different extraction methods. Chemosphere 62:265–274
Tsai JH, Lin KH, Chen CY, Ding JY, Choa CG, Chiang HL (2007) Chemical constituents in particulate emissions from an integrated iron and steel facility. J Hazard Mater 147:111–119
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1993) Provisional guidance for quantitative risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. EPA/600/R-93/089. USEPA, Washington, DC
Wang Z, Chen JW, Yang P, Qiao XL, Tian FL (2007) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Dalian soils: distribution and toxicity assessment. J Environ Monit 9:199–204
Wang RW, Liu GJ, Zhang JM, Chou CL, Liu JJ (2010a) The abundances of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in fourteen Chinese and U.S. coals and their relation to coal ranks and weathering. Energy Fuel 24:6061–6066
Wang RW, Liu GJ, Chou CL, Liu JJ, Zhang JM (2010b) Environmental assessment of PAHs in soils around the Anhui Coal district, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59:62–70
Wey MY, Chao CY, Wei MC, Yu LJ (1996) The influence of heavy metals on PAH formation during incineration. Toxicol Environ Chem 56:35–45
Wheatley AD, Sadhra S (2004) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in solid residues from waste incineration. Chemosphere 55:743–749
Wild SR, Mitchell DJ, Yelland CM, Jones KC (1992) Arrested municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash as a source of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to the environment. Waste Manag Res 10:99–111
Xing Y, Lu YL, Dawson RW, Shi YJ, Zhang H, Wang TY et al (2005) A spatial temporal assessment of pollution from PCBs in China. Chemosphere 60:731–739
Xu SS, Liu WX, Tao S (2006) Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China. Environ Sci Technol 40:702–708
Xue J, Liu GJ, Niu ZY, Chou CL, Qi CC, Zheng LG et al (2007) Factors that influence the extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from coal. Energy Fuel 21:881–890
Zhang YX, Tao S, Cao J, Coveney RM (2007) Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China by county. Environ Sci Technol 41:683–687
Zhang Y, Tao S, Shen H, Ma J (2009) Inhalation exposure to ambient polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and lung cancer risk of Chinese population. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21063–21067
Zhao LJ, Zhang FS, Hao ZP, Wang HL (2008) Levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in different types of hospital waste incinerator ashes. Sci Total Environ 397:24–30
Zhao LJ, Zhang FS, Chen MJ, Liu ZG, Bo D, Wu JZ (2010) Typical pollutants in bottom ashes from a typical medical waste incinerator. J Hazard Mater 173:181–185
Zheng HL, Wei JL (2004) Study of mitigation of harmful metal in coal ash with Yard in Huainan Luohe power plant. Min Saf Environ Prot 31:9–12 [in Chinese]
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41173032), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. WK2080000041), and the National Science and Technology Support Program (Grant No. 1012BAC10B02). We thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for giving us many constructive comments, which significantly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruwei, W., Jiamei, Z., Jingjing, L. et al. Levels and Patterns of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Coal-Fired Power Plant Bottom Ash and Fly Ash from Huainan, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65, 193–202 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9902-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9902-8