Abstract
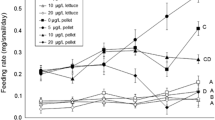
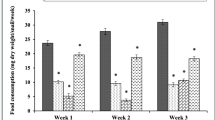
The effects of dietary exposure to copper (Cu), lead (Pb), and zinc (Zn) on feeding activities, growth response, and mortality of Theba pisana snails were studied in 5-week feeding tests. Snails were fed on an artificial diet containing the following Cu, Pb, or Zn concentrations: 0, 50, 100, 500, 1000, 5000, 10,000, and 15,000 μg/g dry food. At the end of 5 weeks, the food consumption rate was decreased with increasinges in both metal concentrations and time of exposure. The estimated concentrations of metals that reduces food consumption to 50% (EC50) after 5 weeks were 56, 118, and 18 μg/g dry food for Cu, Pb, and Zn, respectively. All tested metals in the diet were found to inhibit growth of the snails in a dose-dependent manner. The toxic effect on growth of the tested metals could be arranged in the order Cu > Zn > Pb. The cumulative percentage mortality among snails fed a Cu- or Zn-contaminated diet was 73.3% and the respective value for a Pb-contaminated diet was 13.3%. There was a positive correlation between growth coefficient and food consumption for all tested metals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amusan AAS, Anyaele OO, Lasisi AA (2002) Effect of copper and lead on growth, feeding and mortality of terrestrial gastropod Limicolaria flammea (Muller, 1774). Afr J Biomed Res 5:47–50
Beeby A, Richmond L (2010) Magnesium and the regulation of lead in three populations of the garden snail Cantareus aspersus. Environ Pollut (available online)
Crowe TP, Smith EL, Donkin P, Barnaby DL, Rowland SJ (2004) Measurements of sub lethal effects on individual organisms indicate community-level impacts of pollution. J Appl Ecol 41:114–123
Dallinger R, Berger B, Triebskorn-Kohler R, Kohler H (2001) Soil biology and ecotoxicology. In: Barker GM (ed) The biology of terrestrial molluscs. CABI, Wallingford, pp 489–525
Dallinger R, Chabicovsky M, Berger B (2004) Isoform-specific quantification of metallothionein in the terrestrial gastropod Helix pomatia I. Molecular, biochemical, and methodical background. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:890–901
Dunnett CW (1955) A multiple comparison procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. J Am Stat Assoc 50:1096–1121
El-Gendy KS, Radwan MA, Gad AF (2009) In vivo evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in the land snail, Theba pisana exposed to copper-based pesticides. Chemosphere 77:339–344
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, London, p 318
Godan D (1983) Pest slugs and snails, biology and control. Springer, Berlin, p 443
Gomot A (1997) Effects of heavy metals on snail development. Use of snails as bio-indicators of heavy metal pollution for the preservation of human health. Bull Acad Natl Med 181:59–74
Gomot de Vaufleury A (2000) Standardized growth toxicity testing (Cu, Zn, Pb, and pentachlorophenol) with Helix aspersa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:41–50
Gomot de Vaufleury A, Kerhoas I (2000) Effects of cadmium on the reproductive system of the land snail, Helix aspersa. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64:434–442
Gomot de Vaufleury A, Pihan F (2000) Growing snails used as sentinels to evaluate terrestrial environment contamination by trace elements. Chemosphere 40:275–284
Handy RD, Depledge MH (1999) Physiological responses: their measurement and use as environmental biomarkers in ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicology 8:329–349
Hopkin SP (1993) Ecological implications of “95% protection levels” for metals in soil. Oikos 66:137–141
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:1167–1182
Laskowski R, Hopkin SP (1996) Effect of Zn, Cu, Pb, and Cd on fitness in snails (Helix aspersa). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 34:59–69
Marigomez IA, Angulo E, Saez V (1986) Feeding and growth responses to copper, zinc, mercury and lead in the terrestrial gastropod Arion ater (Linne). J Moll Stud 52:68–78
McLoughlin N, Yin DQ, Maltby L, Wood RM, Yu HX (2000) Evaluation of sensitivity and specificity of two crustacean biochemical biomarkers. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2085–2092
Menon M, Hermle S, Günthardt-Goerg MS, Schulin R (2007) Effect of heavy metal soil pollution and acid rain on growth and water use efficiency of a young model ecosystem. Plant Soil 297:171–183
Notten MJM, Oosthoek AJP, Rozema J, Aerts R (2005) Heavy metal concentrations in a soil–plant–snail food chain along a terrestrial soil pollution gradient. Environ Pollut 135:178–190
Nyholm NEI, Sawicka-Kapusta K, Swiergosz R, Laczewska B (1995) Effects of environmental pollution on breeding populations of birds in southern Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut 85:829–834
Radwan MA, El-Gendy KS, Gad AF (2010) Oxidative stress biomarkers in the digestive gland of Theba pisana exposed to heavy metals. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:828–835
Regoli F, Gorbi S, Fattorini D, Tedesco S, Notti A, Machella N, Bocchetti R, Benedetti M, Piva F (2006) Use of the land snail Helix aspersa as sentinel organism for monitoring ecotoxicologic effects of urban pollution: an integrated approach. Environ Health Perspect 114:63–69
Simkiss K, Watkins B (1990) The influence of gut microorganisms on zinc uptake in Helix aspersa. Environ Pollut 66:263–271
Simkiss K, Taylor M, Mason AZ (1982) Metal detoxification and bioaccumulation in molluscs. Mar Biol Lett 3:187–201
Slijkerman DME, Baird DJ, Conrad A, Jak RG, Van Straalen NM (2004) Assessing structural and functional plankton responses to carbendazim toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:455–462
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1997) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research. W. H. Freeman, New York
Swaileh KM, Ezzughayyar A (2000) Effects of dietary Cd and Cu on feeding and growth rates of the land snail Helix engaddensis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:253–260
Swaileh KM, Ezzughayyar A (2001) Dose-dependent effects of dietary Pb and Zn on feeding and growth rates of the land snail Helix engaddensis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 50:9–14
Triebskorn R, Dittbrenner N, Krais S, Lazzara R, Sawasdee B, Schmidt L, Köhler H-R (2007) Biomarkers as tools to assess the risk of environmental stress for terrestrial and aquatic gastropods. In: World congress of malacology, Antwerp, Belgium, 15–20 July 2007 (abstracts)
Uyar G, Avcil E, Ören M, Karaca F, Öncel MS (2009) Determination of heavy metal pollution in Zonguldak (Turkey) by moss analysis (Hypnum cupressiforme). Environ Eng Sci 26:1–12
Walker EH, Hopkin SP, Sibly RM, Peakall DB (2001) Principles of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis, London
WHO (1965) Molluscicidal screening and evaluation. WHO Bull 38:507–581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Gendy, K.S., Radwan, M.A. & Gad, A.F. Feeding and Growth Responses of the Snail Theba pisana to Dietary Metal Exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60, 272–280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9542-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9542-1