Abstract
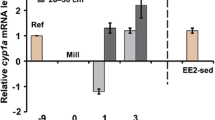
Many types of pulp and paper mill effluents have the ability to induce mixed-function oxygenase (MFO) activity and vitellogenin (VTG) protein in exposed male fish. The search for the compounds responsible for MFO induction has led to several classes of compounds, among them retene and stilbenes. The objective of this study was to investigate the biological activities of candidate stilbene compounds. Three stilbenes, 3,5-dihydroxystilbene (pinosylvin; P1), 3-hydroxy-5-methoxystilbene (P2), and 3,5-dimethoxystilbene (P3), were extracted from Scotch pine (Pinus sylvestris) and purified to evaluate their ability to induce MFO activity in vitro using ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity in a rat hepatoma cell line (H4IIE). As these compounds may be chlorinated during pulp bleaching, chlorination of P2 was undertaken, producing di- and trichlorinated isomers (Cl-P2), which were also tested. Compounds were tested for EROD-inducing ability in vivo by exposing juvenile rainbow tout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to waterborne concentrations (0.010 to 1.0 mg/L) for 4 days. Compounds were also tested for their ability to induce VTG in trout primary liver cells in vitro. The stilbenes were weak inducers of EROD and VTG. H4IIE EROD was induced by all four compounds, with the most potent induction by P3, followed by P1, the Cl-P2 mixture, and then P2. Induction for all four stilbenes was from 3.13 × 10−3 to 3.57 × 10−4 as potent as retene and about 1.11 × 10−5 to 1.20 × 10−6 as potent as TCDD. Juvenile rainbow trout did not show EROD induction after exposures to P1, P2, or the Cl-P2 mixture, whereas P3 caused activity fourfold above that of controls. P1, P3, and Cl-P2 all weakly induced VTG in rainbow trout hepatocytes. The most potent inducer of VTG was Cl-P2, followed by P3 and P1. The results show the ability of wood-derived stilbenes to cause weak MFO induction in fish and in rat liver cells and to weakly induce vitellogenin in fish liver cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachelor FW, Loman AA, Snowdon LR (1970) Synthesis of pinosylvin and related heartwood stilbenes. Can J Chem 48:1554–1557
Belknap AM, Solomon KR, MacLatchy DL, Dube MG, Hewitt LM (2006) Identification of compounds associated with testosterone depressions in fish exposed to bleached kraft pulp and paper mill chemical recovery condensates. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2322–2333
Burnison BK, Hodson PV, Nuttley DJ, Efler S (1996) A bleached-kraft mill effluent fraction causing induction of a fish mixed-function oxygenase enzyme. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1524–1531
Burnison K, Comba M, Carey J, Parrott J, Sherry J (1999) Isolation and tentative identification of compounds in bleached kraft mill effluents capable of causing mixed function oxygenase induction in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2882–2887
Chiron H, Drouet A, Ernst D, Heller W, Sanderman H (1998) cDNA cloning and characterization of two putative pinosylvin O-methyltransferases from Scots pine. Extended abstract. 2nd International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry, 1–3 September, 1998
Fragoso NM, Parrott JL, Hahn ME, Hodson PV (1998) Chronic retene exposure caused sustained induction of CYP1A activity and protein in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 17:2347–2353
Fragoso NM, Hodson PV, Kozin IS, Brown RS, Parrott JL (1999) Kinetics of mixed function oxygenase induction and retene excretion in retene-exposed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2268–2274
Haasch ML, Quardokus EM, Sutherland LA, Goodrich MS, Lech JJ (1993) Hepatic cyp1a1 induction in rainbow trout by continuous flowthrough exposure to beta-naphthoflavone. Fund Appl Toxicol 20:72–82
Hewitt LM, Carey JH, Munkittrick KR, Dixon DG (1996) Examination of bleached kraft mill effluent fractions for potential inducers of mixed function oxygenase activity in rainbow trout. In: Servos MR, Munkittrick KR, Carey JH, Van der Kraak G (eds) Environmental fate and effects of bleached pulp mill effluents. St. Lucie Press, Delray Beach, FL, pp 79–94
Hewitt LM, Parrott JL, McMaster ME (2006) A decade of research on the environmental impacts of pulp and paper mill effluents in Canada: sources and characteristics of bioactive substances. J Toxicol Environ Health B 9:341–356
Hodson PV, Efler S, Wilson JY, El-Shaarawi A, Maj M, Williams TG (1996) Measuring the potency of pulp mill effluents for induction of hepatic mixed function oxygenase activity in fish. J Toxicol Environ Health 49:101–128
Hudlicky M (1980) An improved apparatus for the laboratory preparation of diazomethane. J Org Chem 45:5377–5378
Kohli J, Comba M, Carey J (2003) Isolation and identification of stilbenes compounds in several pulp wood species. Poster presentation at Seventh International Water Association Symposium on Forest Industry Wastewater, Seattle, WA, 1–4 June, 2003
Kovacs T, Martel P, Ricci M, Michaud J, Voss R (2005) Further insights into the potential of pulp and paper mill effluents to affect fish reproduction. J Toxicol Environ Health A 68:1621–1641
Lowell RB, Ribey SC, Ellis IK, Porter EL, Culp JM, Grapentine LC, McMaster ME, Munkittrick KR, Scroggins RP (2003) National assessment of the pulp and paper environmental effects monitoring data. Report No. 03-521. National Water Research Institute, Burlington, ON, Canada
Marlatt VL, Hewitt LM, Van Der Kraak G (2006) Utility of in vitro test methods to assess the activity of xenoestrogens. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:3204–3212
Martel PH, Kovacs TG, O’Connor BI, Voss RH (1997) Source and identity of compounds in a thermomechanical pulp mill effluent inducing hepatic mixed-function oxygenase activity in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:2375–2383
Martel P, Kovacs T, Voss R (2004) Survey of pulp and paper mill effluents for their potential to affect fish reproduction. In: Borton DL, Hall TJ, Fisher RP, Thomas JF (eds) Pulp and paper mill effluent environmental fate and effects. DEStech, Lancaster, PA, pp 78–91
Osborne N, Sherry JP, Currie S (2007) The role of hsp90 in 17α-ethynylestradiol-induced endocrine disruption in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Ecotox Environ Safety 68:13–19
Parrott JL, Burnison BK, Hodson PV, Comba ME, Fox ME (1994) Retene-type compounds – inducers of hepatic mixed function oxygenase (MFO) in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)? Poster presented at 2nd international conference on environmental fate and effects of bleached pulp mill effluents, Vancouver, BC, 6–9 November 1994
Parrott JL, McMaster ME, Hewitt LM (2006) A decade of research on the environmental impacts of pulp and paper mill effluents in Canada: development and application of bioassays. J Toxicol Environ Health B 9:297–317
Schreer A, Tinson C, Sherry JP, Schirmer K (2005) Application of Alamar blue/5-carboxyfluorescein diacetate acetoxymethyl ester as a noninvasive cell viability assay in primary hepatocytes from rainbow trout. Anal Biochem 344:76–85
Simmons DB, Trudeau VL, Marlatt VL, Moon TW, Sherry JP, Metcalfe CD (2008) Interaction of stilbene compounds with human and rainbow trout estrogen receptors. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:442–451
Tillitt DE, Giesy JP, Ankley GT (1991) Characterization of the H4IIE rat hepatoma cell bioassay as a tool for assessing toxic potency of planar halogenated hydrocarbons (PHHs) in environmental samples. Environ Sci Technol 25:87–92
Tysklind M, Tillitt D, Eriksson L, Lundgren K, Rappe C (1994) A toxic equivalency factor scale for polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Fund Appl Toxicol 22:277–285
Van der Kraak G, Munkittrick K, McMaster ME, MacLatchy DL (1998) A comparison of bleached kraft mill effluent, 17-estradiol and B-sitosterol effects on reproductive function in fish. In: Kendall RJ, Dickerson RL, Suk WA, Giesy JP (eds) Principles and processes for evaluating endocrine disruption in wildlife. SETAC Press, Pensacola, FL, pp 249–265
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Tina Hooey, Beverley Blunt, and Mark Baker for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parrott, J.L., Kohli, J., Sherry, J.P. et al. In Vivo and In Vitro Mixed-Function Oxygenase Activity and Vitellogenin Induction in Fish and in Fish and Rat Liver Cells by Stilbenes Isolated from Scotch Pine (Pinus sylvestris). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60, 116–123 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9539-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9539-9