Abstract
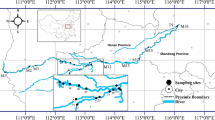
Eleven chlorobenzenes (CBs) in surface water and sediments of Tonghui River, a main urban drainage river of Beijing in China, were determined in October 2003, January 2004, and April 2006. CBs were widely detected and the ∑CB concentrations in water ranged from 89.9 to 6638.0 ng/L, with average values of 1902.8 ng/L in 2003, 2084.0 ng/L in 2004, and 1281.2 ng/L in 2006, respectively. The ∑CB concentrations in surficial sediments varied from 18.2 to 1827.7 ng/g dry weight (dw), with average values of 897.4 ng/g dw in 2003, 653.4 ng/g dw in 2004, and 562.6 ng/g dw in 2006, respectively. Nonparametric statistical analysis (Mann–Whitney U test) showed that there were no statistically significant changes in ∑CB concentrations in either surface water or sediments over the period 2003–2006. The distribution pattern of CBs in the Tonghui River indicates that further effort is warranted in reducing local sources of contaminants. Additionally, the ∑CB levels in sediment samples were found to be dependent on total organic carbon contents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian L, Gorisch H (2002) Microbial transformation of chlorinated benzenes under anaerobic conditions. Res Microbiol 153:131–137. doi:10.1016/S0923-2508(02)01298-6
Aittola JP, Paasivirta J, Vattulainen A, Sinkkonen S, Koistinen J, Tarhanen J (1996) Formation of chloroaromatics at a metal reclamation plant and efficiency of stack filter in their removal from emission. Chemosphere 32:99–108. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(95)00236-7
Barber JL, Sweetman AJ, van Wijk D, Jones KC (2005) Hexachlorobenzene in the global environment: emissions, levels, distribution, trends and processes. Sci Total Environ 349:1–44. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.03.014
BMRIEP (Beijing Municipal Research Institute of Environmental Protection) (1980) Pollution status of the southeastern suburb in Beijing and remediation strategies: 1976–1979. Beijing Municipal Research Institute of Environmental Protection, Beijing, pp 163–227 (in Chinese)
Boutonnet JC, Thompson RS, De Rooij C, Garny V, Lecloux A, Van Wijk D (2004) 1,4-Dichlorobenzene marine risk assessment with special reference to the OSPARCOM region: North Sea. Environ Monit Assess 97:103–117. doi:10.1023/B:EMAS.0000033044.11108.43
Cai Q-Y, Mo C-H, Wu Q-T, Zeng Q-Y, Katsoyiannis A (2007) Occurrence of organic contaminants in sewage sludges from eleven wastewater treatment plants, China. Chemosphere 68:1751–1762. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.041
Chai Y, Qiu X, Davis JW RABJ, Bartels MJ, Saghir SA (2007) Effects of black carbon and montmorillonite clay on multiphasic hexachlorobenzene desorption from sediment. Chemosphere 69:1204–1212. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.010
Chang H, Hu JY, Shao B (2007) Occurrence of natural and synthetic glucocorticoids in sewage treatment plants and receiving river waters. Environ Sci Technol 41:3462–3468. doi:10.1021/es062746o
Chevreuil M, Granier L (1991) Seasonal cycle of polychlorinated biphenyls in the waters of the catchment basin of the river seine (France). Water Air Soil Pollut 59:217–229. doi:10.1007/BF00211831
Ding WH, Aldous KM, Briggs BG (1992) Application of multivariate statistical analysis to evaluate local sources of chlorobenzenes in soil samples. Chemosphere 25:675–690. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(92)90430-Y
Du GS, Wang JT, Zhang WH (2002) Trophic state analysis on urban lakes of Beijing. Beijing Water Resour 6:25–27 (in Chinese)
Du QP, Jia XS, Huang CN (2007) Chlorobenzenes in waterseeds from the Xijiang River (Guangdong section) of the Pearl River. J Environ Sci China 19:1171–1177. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60191-0
Gaudette HE, Flight WR, Toner L, Folger DW (1974) An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments. J Sediment Petrol 44:249–253
Hong SH, Yim UH, Shim WJ, Oh JR, Lee IS (2003) Horizontal and vertical distribution of PCBs and chlorinated pesticides in sediments from Masan Bay, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 46:244–253. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00399-5
Hu JY, Wan Y, Shao B, Jin XH, An W, Jin F, Yang M, Wang XJ, Sugisaki M (2005) Occurrence of trace organic contaminants in Bohai Bay and its adjacent Nanpaiwu River, North China. Mar Chem 95:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2004.06.004
IPCS (2004) Chlorobenzenes other than hexachlorobenzene: environmental aspects. WHO, Geneva
Ju D, Young TM (2005) The influence of the rigidity of geosorbent organic matter on non-ideal sorption behaviors of chlorinated benzenes. Water Res 39:2599–2610. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.058
Karickhoff SW, Brown DS, Scott TA (1979) Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Res 13:241–248. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(79)90201-X
Lee CL, Song HJ, Fang MD (2000) Concentrations of chlorobenzenes, hexachlorobutadiene and heavy metals in surficial sediments of Kaohsiung coast, Taiwan. Chemosphere 41:889–899. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00429-4
Lee CL, Song HJ, Fang MD (2005) Pollution topography of chlorobenzenes and hexachlorobutadiene in sediments along the Kaohsiung coast, Taiwan—a comparison of two consecutive years’ survey with statistical interpretation. Chemosphere 58:1503–1516. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.095
Masunaga S, Urushigawa Y, Yonezawa Y (1991a) The distribution of chlorobenzenes in the bottom sediments of Ise Bay. Water Res 25:275–288. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(91)90007-D
Masunaga S, Urushigawa Y, Yonezawa Y (1991b) The distribution of chlorobenzenes in the bottom sediments of Ise Bay. Water Res 25:275–288. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(91)90007-D
Meharg AA, Wright J, Osborn D (1998) The frequency of Environmental Quality Standard (EQS) exceedance for chlorinated organic pollutants in rivers of the Humber catchments. Sci Total Environ 210:219–228. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00014-X
Meharg AA, Wright J, Osborn D (2000) Chlorobenzenes in rivers draining industrial catchments. Sci Total Environ 251:243–253. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00387-9
Oh JE, Gullett B, Ryan S, Touati A (2007) Mechanistic relationships among PCDDs/Fs, PCNs, PAHs, CIPhs, and CIBzs in municipal waste incineration. Environ Sci Technol 41:4705–4710. doi:10.1021/es0629716
Oliver BG, Nicol KD (1982) Chlorobenzenes in sediments, water, and selected fish from Lakes Superior, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. Environ Sci Technol 16:532–536. doi:10.1021/es00102a019
Popp P, Bruggemann L, Keil P, Thuss U, Weiss H (2000) Chlorobenzenes and hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs) in the atmosphere of Bitterfeld and Leipzig (Germany). Chemosphere 41:849–855. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00531-7
Taylor JK (1987) Quality assurance of chemical measurement. Lewis, Chelsea, p 52
USEPA (1994) Locating and estimating air emissions from sources of chlorobenzenes (revised). Report EPA-454/R-93-044. USEPA, Washington, DC
Van Wijk D, Thompson RS, De Rooij C, Garny V, Lecloux A, Kanne R (2004) 1,2-Dichlorobenzene marine risk assessment with special reference to the OSPARCOM region: North Sea. Environ Monit Assess 97:87–102. doi:10.1023/B:EMAS.0000033043.73470.98
Wang Y, Lee HK (1998) Determination of chlorobenzenes in water by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 803:219–225. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(97)01252-1
Wong MH, Leung AOW, Chan JKY, Choi MPK (2005) A review on the usage of POP pesticides in China, with emphasis on DDT loadings in human milk. Chemosphere 60:740–752. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.04.028
Xu ZF, Lei SH, Ke JM, Xu L (1988) A preliminary study on the analysis of organic pollutants in a suburban sewage system of Beijing. Environ Chem 7:69–80. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1988)7[69:EOKBCA]2.0.CO;2 (in Chinese)
Xue ND, Xu XB, Jin ZL (2005) Screening 31 endocrine-disrupting pesticides in water and surface sediment samples from Beijing Guanting reservoir. Chemosphere 61:1594–1606
Yang SR, Xu XP, Li YS (2006) Analysis of river pollution in the near suburban of Beijing. Water Wastewater Eng 32:47–51 (in Chinese)
Zhang JY, Zhao W, Pan J, Qiu LM, Zhu YM (2005) Tissue-dependent distribution and accumulation of chlorobenzenes by vegetables in urban area. Environ Int 31:855–860. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.034
Zhang MY, Lu YM (2005) Market analysis and development trend of chlorobenzenes. Chlor-Alkali Ind 1:26–32 (in Chinese)
Zhang Z, Huang J, Yu G, Hong H (2004) Occurrence of PAHs, PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in the Tonghui River of Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 130:249–261. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2003.12.002
Zheng MH, Bao ZC, Zhang B, Mo HH, Ding ZH, Xu XB (2000) Determination of chlorobeznenes and phenols in surface water and sewage in Datong City. Environ Monit China 16:35–38 (in Chinese)
Zoumis T, Schmidt A, Grigorova L, Calmano W (2001) Contaminants in sediments: remobilisation and demobilisation. Sci Total Environ 266:195–202. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00740-3
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Excellent Young Scientist Fund of China (50625823). The authors thank Tai Wang, Bin Wang, and Yang Lv for help in sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Deng, S., Huang, J. et al. Occurrence and Distribution of Chlorobenzenes in the Tonghui River of Beijing, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57, 32–41 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9233-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9233-3