Abstract
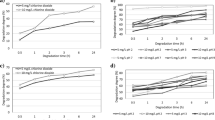
The degradation of selected organophosphorus pesticides (OPs), i.e., malathion and parathion, in river water, has been studied with solar simulator irradiation. The degradation of OPs and formation of degradation products were determined by chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry analysis. The effect of a photosensitizer, i.e., riboflavin, on the photolysis of OPs in a river-water environment was examined. There was no significant increase in the degradation rate in the presence of the photosensitizer. Degradation products of the OPs were identified with gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) after derivatization by pentafluorobenzyl bromide (PFBB) and with high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) with electrospray (ESI) or atomospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI). Malaoxon, paraoxon, 4-nitrophenol, aminoparathion, O,O-dimethylthiophosphoric acid, and O,O-dimethyldithiophosphoric acid, have been separated and identified as the degradation products of malathion and parathion after photolysis in river water. Based on the identified transformation products, a rational degradation pathway in river water for both OPs is proposed. The identities of these products can be used to evaluate the toxic effects of the OPs and their transformation products on natural environments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aires P, Gal E, Chamarro E, Esplugas S (1992) Photochemical degradation of malathion in aqueous solutions. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 68:121–129. doi:10.1016/1010-6030(92)85024-O
Aker WG, Hu X, Wang P, Hwang HM (2008) Comparing the relative toxicity of malathion and malaoxon in blue catfish Ictalurus furcatus. Environ Toxicol 23:548–554
Bavcon M, Trebse P, Zupancic-Kralj L (2003) Investigations of the determination and transformation of diazinon and malathion under environmental conditions using gas chromatography coupled with a flame ionization detector. Chemosphere 50:595–601. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00643-4
Castillo M, Domingues R, Alpendurada MF, Barcelo D (1997) Persistence of selected pesticides and their phenolic transformation products in natural waters using off-line liquid solid extraction followed by liquid chromatographic techniques. Anal Chim Acta 353:133–142. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(97)00353-X
Durand G, Abad JL, Sanchez-Baeza F, Messeguer A, Barcelo D (1994) Unequivocal identification of compounds formed in the photodegradation of fenitrothion in water/methanol and proposal of selected transformation pathways. J Agric Food Chem 42:814–821. doi:10.1021/jf00039a044
Farran A, Pablo J, Barcelo D (1988) Identification of organophosphorus insecticides and their hydrolysis products by liquid chromatography in combination with UV and thermospray-mass spectrometric detection. J Chromatogr 455:163–172. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)82115-4
Ferrer I, Barcelo D (1998) LC-MS methods for trace determination of pesticides in environmental samples. Pestic Anal 26:118–122
Jeannot R, Dagnac T (2006) Organophosphorus compounds in water, soils, water, and air. In: Nollet L (ed) Chromatographic analysis of the environment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Kim TS, Kim JK, Choi K, Stenstrom MK, Zoh KD (2006) Degradation mechanism and the toxicity assessment in TiO2 photocatalysis and photolysis of parathion. Chemosphere 62:926–933. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.038
LaGrega MD, Buckingham PL, Evans JC (2001) Hazardous waste management, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
National Center for Environmental Health (NCEH) (2005) Third national report on human exposure to environmental chemicals. NCEH Publ. No. 05-0570. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA
Pehkonen SO, Zhang Q (2002) The degradation of organophosphorus pesticides in natural waters: a critical review. Crit Rev Env Sci Technol 32:17–72. doi:10.1080/10643380290813444
Stebbins RG, Doane RT (1989) Analysis of malathion and its breakdown products in aquaria containing golden shiners (N. chrysoleucas). Inte J Environ Anal Chem 35:127–137. doi:10.1080/03067318908028387
Walker W, Stojanovic B (1973) Acetylcholinesterase toxicity of malathion and its metabolites. J Environ Qual 2:474–475
Yoshichika H, Hitoshi U, Katsuhiko N (2004) Physiological degradation of organophosphorus insecticides in the environment. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Gakkaishi 11:127–136
Zhao X, Hu X, Hwang HM (2008) Study of toxicity of parathion and its major degradation products to human lymphocytes and epithelial cells. Int J Environ Res Public Health (submitted)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by U.S. Department of the Army Research and Development Grant W912H2-04-2-0002 to Jackson State University. We thank Mr. Winfred G. Aker for proofreading assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Hwang, HM. A Study of the Degradation of Organophosphorus Pesticides in River Waters and the Identification of Their Degradation Products by Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56, 646–653 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9220-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9220-8