Abstract
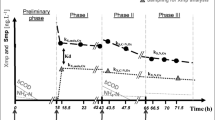
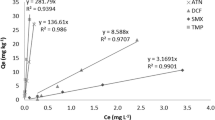
Pharmaceutical substances have been detected in sewage effluents as well as receiving waters in many parts of the world. To assess the fate and removal of these compounds within sewage treatment plants, an understanding of their partitioning behavior between the solid and aqueous phases is critical. Therefore, a preliminary study was conducted to ascertain an understanding of the binding behavior of five drug substances sorbing to the solid phase in a laboratory scale–activated sludge plant (Husmann unit). For comparison, uncontaminated river sediment was also used as a substrate. All of the compounds tested partitioned more readily to the sludge than the sediment, likely because of the former’s higher organic carbon content. Partitioning to the solid phase correlated roughly with predicted log Kow values. A period of initial sorption was followed by a phase of desorption, and net absorption of the selected drugs (with the exception of mefenamic acid) after 5 hours of mixing was minimal.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcock RE, Sweetman A, Jones KC (1999) Assessment of organic contaminant fate in wastewater treatment plants I: Selected compounds and physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 38:2247–2262
Ayscough NJ, Fawell J, Franklin G, Young W (2000) Review of human pharmaceuticals in the environment. Environment Agency of England and Wales, Bristol, UK
Bowman CJ, Kroll KJ, Hemmer MJ, Folmar LC, Denslow ND (2000) Estrogen-induced vitellogenin mRNA and protein in sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 120:300
Boxall ABA, Blackwell P, Cavallo R, Kay P, Tolls J (2002) The sorption and transport of a sulphonamide antibiotic in soil systems. Toxicol Lett 131:19–28
Casey FXM, Larsen GL, Hakk H, Simunek J (2003) Fate and transport of 17 beta-estradiol in soil-water systems. Environ Sci Technol 37:2400–2409
Crane M (2003) Proposed development of sediment quality guidelines under the European water framework directive: A critique. Toxicol Lett 42:195–206
Daughton CG, Ternes TA (1999) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Agents of subtle change? Environ Health Perspect 107:907–942
Diaz-Cruz MS, Lopez de Alda MJ, Barcelo D (2003) Environmental behavior and analysis of veterinary and human drugs in soils, sediments and sludge. Trends Anal Chem 22:340–351
Directive 2000/60/EC (2000) Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framwork for Community action in the field of water policy
Drewes JE, Heberer T, Reddersen K (2002) Fate of pharmaceuticals during indirect potable reuse. Water Sci Technol 46:73–80
Environmental Protection Agency (2001) Estimation program interface (EPI) suite. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics, Washington, DC
Gao JP, Maguhn J, Spitzauer P, Kettrup A (1998a) Sorption of pesticides in the sediment of the Teufelsweiher pond (Southern Germany). I: Equilibrium assessments, effect of organic carbon content and PH. Water Res 32:1662–1672
Gao JP, Maguhn J, Spitzauer P, Kettrup A (1998b) Sorption of pesticides in the sediment of the Teufelsweiher pond (Southern Germany) II: Competitive-adsorption, desorption of aged residues and effect of dissolved organic carbon. Water Res 32:2089–2094
Golet EM, Alder AC, Giger W (2002) Environmental exposure and risk assessment of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents in wastewater and river water of the Glatt Valley Watershed, Switzerland. Environ Sci Technol 36:3645–3651
Golet EM, Xifra I, Siegrist H, Alder AC, Giger W (2003) Environmental exposure assessment of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents from sewage to soil. Environ Sci Technol 37:3243–3249
Hemond HF, Fechner-Levy EJ (2000) Chemical fate and transport in the environment. Academic, Orlando, FL
Hilton MJ, Thomas KV (2003) Determination of selected human pharmaceutical compounds in effluent and surface water samples by high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1015:129–141
Johnson AC, White C, Besien TJ, Jurgens MD (1998) The sorption potential of octylphenol, a xenobiotic oestrogen, to suspended and bed-sediments collected from industrial and rural reaches of three English rivers. Sci Total Environ 210-211:271–282
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2001) Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A review. Environ Technol 22:1383–1394
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester J N (2003) Analytical method development for the simultaneous determination of five human pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater samples by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chromatographia 58:471–477
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2005) The occurrence and removal of selected pharmaceutical compounds in a sewage treatment works utilizing activated sludge treatment. Environ Pollut (in press)
Kallis G, Butler D (2001) The EU water framework directive: Measures and implications. Water Policy 3:125–142
Khan SJ, Ongerth JE (2002) Estimation of pharmaceutical residues in primary and secondary sewage sludge based on quantities of use and fugacity modeling. Water Sci Technol 46:105–113
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer M, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, et al. (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999-2000: A national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211
Krogmann U, Boyles LS, Bamka WJ, Chaiprapat S, Martel CJ (1999) Biosolids and sludge management. Water Environ Res 71:692–695
Lai KM, Johnson KL, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2000) Binding of waterborne steroid estrogens to solid phases in river and estuarine systems. Environ Sci Technol 34:3890–3894
Lester JN, Birkett JW (1999) Microbiology and chemistry for environmental scientists and engineers. E and FN Spon, London, UK
Meakins NC, Bubb JM, Lester JN (1994) The fate and behavior of organic micropollutants during wastewater treatment processes: A review. Int J Environ Pollut 4:27–58
Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (2001) OECD guideline for testing of chemicals. 303: Simulation test—Aerobic sewage treatment. 303A: Activated sludge units. Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development, Paris, France
Shaw LJ, Beaton Y, Glover LA, Killham K, Osborn D, Meharg AA (2000) Bioavailability of 2,4-dichlorophenol associated with soil water-soluble humic material. Environ Sci Technol 34:4721–4726
Soulet B, Tauxe, A, Tarradellas J (2002) Analysis of acidic drugs in Swiss wastewaters. Int J Environ Anal Chem 82:659–667
Stoveland S, Lester JN (1980) A study of the factors which influence metal removal in the activated sludge process. Sci Total Environ 16:37–54
Ternes T, Joss A, Siegrist H (2004) Scrutinizing pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 38:392A-399A
Ternes TA (1998) Occurrence of drugs in German sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Res 32:3245–3257
Tolls J (2000) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: A review. Environ Sci Technol 35:3397–3412
Winkler M, Lawrence JR, Neu TR (2001) Selective degradation of ibuprofen and clofibric acid in two model river biofilm systems. Water Res 35:3197–3205
Yamamoto H, Liljestrand HM, Shimizu Y, Morita M (2003) Effects of physical-chemical characteristics on the sorption of selected endocrine disruptors by dissolved organic matter surrogates. Environ Sci Technol 37:2646–2657
Yu Z, Baohua X, Weilin H, Ping’an P (2004) Sorption of steroid estrogens to soils and sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:531–539
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (O.A.H.J.) is grateful to the United Kingdom Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council for the award of a doctoral scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, O.A.H., Voulvoulis, N. & Lester, J.N. Partitioning Behavior of Five Pharmaceutical Compounds to Activated Sludge and River Sediment. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50, 297–305 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-1095-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-1095-3