Abstract
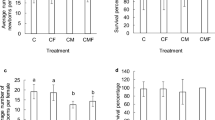
Two forms of ammonium exist in water: un-ionized ammonia NH3 and ionized ammonium NH +4 . The toxicity to many aquatic organisms is primarily attributed to the NH3 (un-ionized) species, with the NH +4 ion (ionized) species being relatively less toxic. The pH level influences the degree of ionization. It is therefore very important that quality criteria be derived for total ammonium levels at several pH values in order to allow correct interpretation of the sediment bioassay with Corophium volutator. The responses of Corophium to total ammonium were studied in a series of pH-controlled experiments. The LC50 of total ammonium showed a significant decrease with increasing pH, in both water-only and sediment experiments. The results indicated a combined NH +4 and NH3 toxicity at pH levels less than 8.3. The results can be used to set pH-dependent water quality criteria for total ammonium in overlying water in a 10-day sediment bioassay with Corophium volutator.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong DA, Chippendale D, Knight AW, Colt JE (1978) Interaction of ionized and un-ionized ammonia on short-term survival and growth of prawn larvae, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Biol Bull 154:15–31
Arthur JW, West CW, Allen KN, Hedtke S (1987) Seasonal toxicity of ammonia to five fish and nine invertebrate species. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 38:324–331
Bat L, Raffaelli D (1998) Sediment toxicity testing: a bioassay approach using the amphipod Corophium volutator and the polychaete Arenicola marina. J Exp Mar Ecol: 217–239
Borgmann U (1994) Chronic toxicity of ammonia to the amphipod Hyalella azteca, importance of ammonium ion and water hardness. Envir Poll 86:329–335
Borgmann U, Borgmann AI (1997) Control of ammonia toxicity to Hyalella azteca by sodium, potassium and pH. Env Poll 95:325–331
Erickson RJ (1985) An evaluation of mathematical models for the effects of pH and temperature on ammonia toxicity to aquatic organisms. Water Res 19:1047–1058
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719; correction 12:417 (1987)
Kater BJ, Hannewijk A, Postma JF, Dubbeldam M (2000) Seasonal changes in acute toxicity of cadmium to amphipod Corophium volutator. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:3032–3035
Kohn NP, Word JQ, Niyogi DK, Ross LT, Dillon T, Moore DW (1994) Acute toxicity of ammonia to four species of marine amphipod. Mar Envir Res 38:1–15
Landau M, Sanchez V (1991) Effect of pH and decapsulation on the toxicity of ammonia to the brine shrimp Artemia franciscana. J World Aquacult Soc 22:178–182
Lin HP, Thuet P, Thrilles JP, Mounet-Guillaume, Charmantier G (1993) Effects of ammonia on survival and osmoregulation of various development stages of the shrimp Penaeus japonicus. Mar Biol 117:591–598
Moore DW, Bridges TS, Gray BR, Duke BM (1997) Risk of ammonia toxicity during sediment bioassays with the estuarine amphipod Leptocheirus plumulosus. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:1020–1027
Mount DR, Mount DI (1992) A simple method of pH control for static and static renewal aquatic toxicity tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:609–614
Noack U, Becker S, Kraetzig G (2003) Marine biotest: Comparative investigations on acute toxicity of ammonium chloride to Corophium volutator. Fresenius Environ Bull 12:608–612
Pedersen F, Bjørnestad E, Andersen HV, Kjølholt J, Poll C (1998) Characterization of sediments from Copenhagen harbour by use of biotests. Wat Sci Tech 37:233–240
Peters C, Becker S, Noack U, Pfitzner S, Bülow W, Barz K, Ahlf W, Berghahn R (2002) A marine test set to assess marine water and sediment quality—its need, the approach and first results. Ecotoxicology 11:379–383
Richardson J, (1997) Acute ammonium toxicity for eight New Zealand indigenous freshwater species. New Zealand J Marine Freshwater Res 31:185–190
Schubauer-Berigan MK, Monson PD, West CW, Ankley GT (1995) Influence of pH on the toxicity of ammonia to Chironomus tentans and Lumbriculus variegatus. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:713–717
Stronkhorst J, Schot ME, Dubbeldam MC, Ho KT (2003) A toxicity identification evaluation of silty marine harbour sediment to characterize persistent and non-persistent constituents. Mar Pol Bull 46:56–64
Tidepool (1995) Toxcalc program version 5.0.12N. Tidepool Scientific Software
Wajsbrot N, Gasith A, Krom MD, Samocha TM (1990) Effect of dissolved oxygen and the molt stage on the acute toxicity of ammonia to juvenile green tiger prawn Penaeus semisulcatus. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:497–504
Whiteman FW, Ankley GT, Kahl MD, Rau DM, Balcer MD (1996) Evaluation of interstitial water as a route of exposure for ammonia in sediment tests with benthic macroinvertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:794–801
Whitfield A (1974) The hydrolysis of ammonium ions in seawater—a theoretical study. J Mar Biol Ass 54:565–580
Williams KA, Green DWJ, Pascoe D (1986) Studies on the acute toxicity of pollutants to freshwater macroinvertebrates. Arch Hydrobiol 106:61–70
Young-Lai WW, Charmantier-Daures M, Charmantier G (1991) Effect of ammonia on survival and osmoregulation in different life stages of the lobster Homarus americanus. Mar Biol 110:293–300
Acknowledgments
Esther Peene and Elfriede Bruger are acknowledged for their assistance during the experiments. Sue McDonnell is acknowledged for improving the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kater, B.J., Dubbeldam, M. & Postma, J.F. Ammonium Toxicity at High pH in a Marine Bioassay Using Corophium volutator . Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51, 347–351 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0163-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0163-z