Abstract
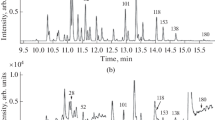
A rapid method has been developed to measure dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congeners as well as other selected PCBs in sediment. The analytes were extracted from sediment by sonication with dichloromethane, and the PCBs were separated from interfering compounds on a gravity-flow cleanup column packed with acidic, basic, and neutral silica gels eluted with 1:1 hexane:pentane (v/v). Subsequently, the dioxin-like PCB congeners were resolved from nonplanar PCBs and other chlorinated compounds by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Two important advantages of PDA over conventional UV detection are the ability to identify individual analytes by comparing their UV spectra with those of reference standards and the ability to establish the spectral homogeneity (purity) of the analytes by comparing spectra within a peak to the apex spectrum. The HPLC-PDA method was tested with reference and marine sediment samples. Concentrations of selected dioxin-like PCBs, selected nonplanar PCBs, and summed PCBs in sediments and National Institute of Standards and Technology standard reference materials determined by our rapid HPLC-PDA method were comparable with the levels in the same samples analyzed by alternative comprehensive methods (i.e., gas chromatography–electron capture detection or high-resolution gas chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (2004) AMAP assessment 2002: Persistent organic pollutants in the Arctic. Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme, Oslo, Norway, p xvi
Aries E, Anderson DR, Ordsmith N, Hall K, Fisher R (2004) Development and validation of a method for analysis of “dioxin-like” PCBs in environmental samples from the steel industry. Chemosphere 54:23–31
Beeton AM, Allen AR, Andren AW, Cristol SJ, Durfee RL, Freeman AM, et al. (1979) Polychlorinated biphenyls. National Research Council, Washington, DC
Besselink HT, Schipper C, Klamer H, Leonards P, Verhaar H, Felzel E, et al. (2004). Intra- and interlaboratory calibration of the DR Calux® bioassay for the analysis of dioxins and dioxin-like chemicals in sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2781–2789
Brinkman UAT, deKok A (1980) Production, properties and usage. In: Kimbrough RD, (ed) Topics in environmental health. Halogenated biphenyls, terphenyls, naphthalenes, dibenzodioxins and related products. Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, p 1
deBoer J, Stronck CJN, Traag WA, Meer JVD (1993). Non-ortho and mono-ortho substituted chlorobiphenyls and chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in marine and freshwater fish and shellfish from The Netherlands. Chemosphere 26:1823–1842
Dobson S, van Esch GJ (1993). Polychlorinated biphenyls and terphenyls, 2nd ed. Environmental Health Criteria 140. Geneva, Switzerland, World Health Organization
Harmon MR, Gottholm BW, Robertson A (1998). A summary of chemical contaminant levels at benthic surveillance project sites (1984-1992). NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS ORCA 124: 2. Silver Spring, MD, United States Department of Commerce
Hartmann PC, Quinn JG, Cairns RW, King JW (2004). Polychlorinated biphenyls in Narragansett Bay surface sediments. Chemosphere 57:9–20
Johnson JC, Van Emon JM, Clarke AN, Wamsley BN (2001). Quantitative ELISA of polychlorinated biphenyls in an oily soil matrix using supercritical fluid extraction. Anal Chim Acta 428:191–199
Koh C-H, Khim JS, Kannan K, Villeneuve DL, Senthilkumar K, Glesy JP (2004). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs), biphenyls (PCBs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and 2,3,7,8-TCDD equivalents (TEQs) in sediment from the Hyeongsan River, Korea. Environ Pollut 132:489–501
Koistinen J (1990). Residues of planar polychloroaromatic compounds in Baltic fish and seal. Chemosphere 20:1043–1048
Krahn MM, Morre LK, Bogar RG, Wigren CA, Chan S-L, Brown DW (1988a). High-performance liquid chromatographic method for isolating organic contaminants from tissue and sediment extracts. J Chromatogr 437:161–175
Krahn MM, Wigren CA, Pearce RW, Morre LK, Bogar RG, MacLeod WDJ, et al. (1988b) Standard analytical procedures of the NOAA National Analytical Facility. New HPLC cleanup and revised extraction procedures for organic contaminants. NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS F/NWC-153. Silver Spring, MD, United States Department of Commerce
Krahn MM, Ylitalo GM, Joss J, Chan S-L (1991). Rapid, semi-quantitative screening of sediments for aromatic compounds using sonic extraction and HPLC/Fluorescence analysis. Mar Environ Res 31:175–196
Krahn MM, Ylitalo GM, Buzitis J, Sloan CA, Boyd DT, Chan S-L, et al. (1994) Screening for planar chlorobiphenyl congeners in tissues of marine biota by high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection. Chemosphere 29:117–139
Lauenstein GG, Cantillo AY, Dolvin SS (1993) NOAA national status and trend program development and methods. Sampling and analytical methods of the National Status and Trends Program, National Benthic Surveillance and Mussel Watch Projects: 1984-1992. Volume I. Overview and summary of methods. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS ORCA 71: 34-38. Silver Spring, MD, United States Department of Commerce
Lebo JA, Zajicek JL, May TW (1989) Large-scale preparation of potassium hydroxide-modified silica gel adsorbent. J Assoc of Anal Chem 72:371–373
Loganathan B, Kannan K, Watanabe I, Kawano M, Irvine K, Kumar S, et al. (1995) Isomer-specific determination and toxic evaluation of polychlorinated biphenyls, polychlorinated/brominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, polybrominated biphenyl ethers, and extractable organic halogen in carp from the Buffalo River, New York. Environ Sci Technol 29:1832–1838
MacDonald DD, Ikonomou MG, Rantalaine A-L, Rogers IH, Sutherland D, Van Oostdam J (1997) Contaminants in white sturgeon (Acipenser Transmontanus) from the upper Fraser River, British Columbia, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:479–490
Nakata H, Hirakawa Y, Kawazoe M, Nakabo T, Arizono K, Abe S-I, et al. (2005) Concentrations and compositions of organochlorine contaminants in sediments, soils, crustaceans, fishes and birds collected from Lake Tai, Hangzhou Bay and Shanghai city region, China. Environ Pollut 133:415–429
Nilsson T, Bøwadt S, Björklund E (2002). Development of a simple selective SFE method for the determination of desorption behavior of PCBs in two Swedish sediments. Chemosphere 46:469–476
Nilsson T, Sporring S, Björklund E (2003) Selective supercritical fluid extraction to estimate the fraction of PCB that is bioavailable to a benthic organism in a naturally contaminated sediment. Chemosphere 53:1049–1052
Numata M, Yarita T, Aoyagi Y, Takatsu A (2003) Microwave-assisted steam distillation for simple determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in sediments. Anal Chem 75:1450–1457
Petreas MX, Wiesmuller T, Palmer FH, Winkler JJ, Stephens RD (1992) Aquatic life as biomonitors of dioxin/furan and coplanar polychlorinated biphenyl contamination in the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta. Chemosphere 25:621–631
Sloan CA, Adams NG, Pearce RW, Brown DW, Chan S-L (1993) Northwest Fisheries Science Center organic analytical procedures. In: Lauenstein GG, Cantillo AY (eds) Sampling and analytical methods of the National Status and Trends Program, National Benthic Surveillance and Mussel Watch Projects: 1984-1992. Volume IV. Comprehensive descriptions of trace organic analytical methods. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS ORCA 71:53–97. Silver Spring, MD, United States Department of Commerce
Smith LM, Stalling DL, Johnson JL (1984) Determination of part-per-trillion levels of polychlorinated dibenzofurans and dioxins in environmental samples. Anal Chem 56:1830–1842
Smith LM, Schwartz TR, Feltz K, Kubiak TJ (1990). Determination and occurrence of AHH-active polychlorinated biphenyls, 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro-p-dioxin and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in Lake Michigan sediment and biota. The question of their relative toxicological significance. Chemosphere 21:1063–1085
Szostek B, Tinklenberg JA, Aldstadt JH (1999). A simple method for the quantitative microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from soils and sediments. Chemosphere 38:3131–3139
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld ATC, Brunstrom B, Cook P, Feeley M, et al. (1998) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 106:775–792
Ylitalo GM, Buzitis J, Krahn MM (1999). Analyses of tissues of eight marine species from Atlantic and Pacific coasts for dioxin-like chlorobiphenyls (CBs) and total CBs. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:205–219
Ylitalo GM, Buzitis J, Boyd DT, Herman DP, Tilbury KL, Krahn MM (2005). Improvements to high-performance liquid chromatography/photodiode array detection (HPLC/PDA) method that measures dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls and other selected organochlorines in marine biota. In: Ostrander GK (ed) Techniques in aquatic toxicology. Volume 2. Boca Raton, FL, Taylor and Francis, pp 449–464
Zar JH (1984). Biostatistical analysis, 2nd ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Prentice Hall
Zhang Z, Huang J, Yu G, Hong H (2004). Occurrence of PAHs, PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in the Tonghui River of Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 130:249–261
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the technical assistance or advice of Donald Brown, Jennie Bolton, Daryle Boyd, Richard Boyer, Catherine Sloan, Larry Hufnagle, Sena Camarata, and Carol Pitzel. We thank Erika Hoffman from the United States EPA for providing data from HRGC-HRMS analyses, Catherine Sloan and Jennie Bolton for providing GC-ECD data, and Jim Meador for assistance with the statistical analysis and interpretation. We appreciate the helpful suggestions and manuscript review by Doug Burrows and Dave Herman.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buzitis, J., Ylitalo, G.M. & Krahn, M.M. Rapid Method for Determination of Dioxin-Like Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Other Congeners in Marine Sediments Using Sonic Extraction and Photodiode Array Detection. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51, 337–346 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0162-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0162-0