Abstract
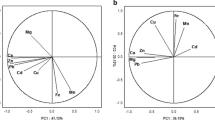
Concentrations of 11 metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, Zn, Na, K, Ca, and Mg) were assayed in the teeth of two populations of the Silesian region. The first group (n = 83) comprised the residents of Katowice–Szopienice, a town located in the center of the Upper Silesian industrial region, in close proximity to a Pb plant, whereas the other was a group of residents of the agricultural community Strumień (n = 44). The concentrations of all the trace metals were found to be higher in the teeth of Katowice–Szopienice residents. The methods of cluster analysis distinguished two clusters of metals in the teeth: essential (Ca, Na, Mg, Zn, and K) and trace (Cd, Mn, Cr, Cu, Fe, and Pb) elements. Euclidean distances reflected the differences in concentrations between the two groups. The results obtained were analyzed using principal component analysis. Four principal factors accounted for 68.1% of the total variance for Katowice–Szopienice residents and for 80.1% for Strumień residents. The first factor showed high contributions of Cu and Cr, elements present in humans as a result of diet, and also Mn for Katowice–Szopienice residents because of environmental contamination. The second factor was characterized by large Zn and Cd fractions and, for Katowice–Szopienice residents, Pb and K as well. The diversified exposure of both populations was reflected by the differences in Euclidean distances and contribution of particular elements with respect of principal components.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfven T, Jarup L, Elinder CG (2002) Cadmium and lead in blood in relation to low bone mineral density and tubular proteinuria. Environ Health Perspect 110:699–702
Appelton J, Lee KM, Sawicka-Kapusta K, Damek M, Cooke M (2000) The heavy metal content of the teeth of the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) as an exposure marker of environmental pollution in Poland. Environ Pollut 110:441–449
Arai N, Mitani Y, Sakamoto W, Yoshida K, Mokuno Y, Baba N (1999) PIXIE analysis of trace elements in northern fur seal teeth. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 150:267–271
Aschner M, Aschner JL (1990) Manganese transport across the blood-brain barrier: Relationship to iron homeostasis. Brain Res Bull 24:857–860
Atmospheric contamination in Silesian Province in 1998-1999 (2000) Ślaska Wojewo´dzka Stacja Sanitarno-Epidemiologiczna (eds.), Katowice (in Polish)
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (1990) Toxicological profile for copper. Syracuse Research Corporation Under Subcontract No. ATSDR-88-0608-02. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, Atlanta, GA
Bercovitz K, Laufer D (1993) Carious teeth as indicators to lead exposure. Environ Contam Toxicol 50:724–729
Bermejo-Barrera P, Moreda-Piñeiro A, Bermejo-Barrera A, Bermejo-Barrera AM (2002) Application of multivariate methods to scalp hair metal data to distinguish between drug-free subjects and drug abusers. Anal Chim Acta 455:253–265
Bhattacharyya MH, Wilson AK, Silbergeld EK, Watson L, Jeffrey E (1995) Metal-induced osteotoxicities. In: Goyer RA, Klaassen CD, Waalkes MP (eds) Metal toxicology. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 465–510
Bremner I, Beattie JH (1990) Metallothionein and the trace minerals. Annu Rev Nutr 10:63–83
Cousins RJ, Leinart AS (1998) Tissue-specific regulation of zinc metabolism and metallothionein genes by interleukin 1. FASEB J 2:2884–2890
Coyle P, Philcox JC, Carey LC, Rofe AM (2002) Metallothionein: the multipurpose protein. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:627–647
De Bartolomeo A, Poletti L, Sanchini G, Sebastiani B, Morozzi G (2004) Relationship among parameters of lake polluted sediments evaluated by multivariate statistical analysis. Chemosphere 55:1323–1329
Eide R, Schionning JD, Ernst E, Wesenberg GBR, Hansen IM (1995) Mercury contents in rat teeth after administration of organic and inorganic mercury—The effect of interrupted exposure and of selenite. Acta Odontol Scand 53:12–16
Ellingsen DG, Haug E, Ulvik RJ, Thomassen Y (2003) Iron status in manganese alloy production workers. J Appl Toxicol 23:239–47
Ericson JE, Rinderknect A, Kleinman MT (2000) Tooth enamel biomarker for heavy metal exposure assessment. International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment, Ann Arbor, MI, August 6–10, 2000
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313-324
Florianczyk B (2003) Zinc and metallothioneins in cancer. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska [Med] 58:102–105
Górny RL, Jçdrzejczak AK (1996) Assessment of lead and cadmium concentrations in deciduous teeth of children additionally exposed to cigarette smoke in flats [in Polish]. Czas Stomatol 49:413–419
Goyer RA (1997) Toxic and essential metal interactions. Annu Rev Nutr 17:37–50
Goyer RA, Liu J, Waalkes MP (2004) Cadmium and cancer of prostate and testis. Bio Metals 17:555–558
Grobler SR, Theunissen FS, Kotze TJV (2000) The relation between lead concentrations in human dental tissues and in blood. Arch Oral Biol 45:607–609
Gulson B, Wilson D (1994) History of lead exposure in children revealed from isotopic analyses of teeth. Arch Environ Health 49:279–283
Indulski JA, Jakubowski M (1991) Biological monitoring in the epidemiology of chronic effects of cadmium in workers. In: Tardiff RG, Goldstein BD (eds) Methods for assessing exposure of human and non-human biota. SCOPE 46. Wiley, Chiches, OK, pp 287–295
Jarup L, Berglund M, Elinder CG, Nordberg G, Vahter M (1998) Health effects of cadmium exposure—A review of the literature and a risk estimate. Scand J Work Environ Health 24:1–51
Jennrich RI, Sampson PF (1968) Application of stepwise regression to nonlinear estimation. Technometrics 10:63–72
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1999) Biochemics of trace elements [in Polish]. PWN, Warsaw, Poland
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20:141–151
Karakaya A, Ilko M, Ulusu T, Akal N, Isimer A, Karakaya E (1996) Lead levels in deciduous teeth of children from urban and suburban regions in Ankara (Turkey). Environ Contam Toxicol 56:16–20
Klaassen CD, Liu J, Choudhuri S (1999) Metallothionein: An intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:267–294
Kwapuliński J, Fischer A, Wiechuła D (2001) Changes in metal concentrations in teeth of smoking and non-smoking women living in close proximity to HMN “Szopienice” smelter in Katowice. In: Florek E, Piekoszewski W, Wrzosek J (eds) Woman and tobacco—Present opinions [in Polish]. Akademia Medyczna, Poznan, Poland, pp 127–137
Liu J, Liu Y, Michalska AE, Choo KH, Klaassen CD (1996a) Metallothionein plays less of a protective role in cadmium-metallothionein–induced nephrotoxicity than in cadmium chloride-induced hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:1216–1223
Liu YP, Liu J, Palmiter RD, Klaassen CD (1996b) Metallothionein-I-transgenic mice are not protected from acute cadmium-metallothionein–induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 137:307–315
Loska K, Wiechuła D (2003) Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere 51:723–733
Morrison D (1967) Multivariate statistical methods. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill
Nowak B (1995) Occurrence of heavy metals and sodium, potassium and calcium in human teeth. Analyst 120:747–750
Odland JO, Nieboer E., Romanova N, Thomassen Y (2004) Elements in placenta and pregnancy outcome in arctic and subartic areas. Int J Circ Health 63:169–187
Odland JO, Nieboer E, Romanova N, Thomassen Y, Hofoss D, Lund E (2001) Factor analysis of essential and toxic elements in human placentas from deliveries in artic and subartic areas of Russia and Norway. J Environ Monit 3:177–184
Onosaka S, Tetsuchikawahara N, Min KS (2002) Paradigm shift in zinc: Metal pathology. Tohoku J Exp Med 196:1–7
Patrick L (2003) Toxic metals and antioxidants: Part II. The role of antioxidants in arsenic and cadmium toxicity. Altern Med Rev 8:106–128
Paustenbach DJ, Hays SM, Brien BA (1996) Observation of steady state in blood and urine following human ingestion of hexavalent chromium in drinking water. J Toxicol Environ Health 49:453–461
Pearson K (1901) On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Phil Mag 6:559–572
Rossander-Hulten L, Brune M, Sandstrom B, Lonnerdal B, Hallberg L (1991) Competitive inhibition of iron absorption by manganese and zinc in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 54:152–156
Szymański A (1991) Biomineralization and biominerals [in Polish]. PWN, Warsaw, Poland
Waalkes MP, Kovatch R, Rehm S (1991) Effect of chronic dietary zinc-deficiency on cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis in the male Wistar [Hsd(WI)BR] rat. Toxicol Appl Phamacol 108:448–456
Wakamura M, Kandori K, Ishikawa T (1998) Surface composition of calcium hydroxyapatite modified with metal ions. Colloids Surf, A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 142:107–116
Ward JH (1963) Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc 58:236–244
Wiechuła D, Kwapuliński J, Manderla J (2001) Application of the principal component analysis and cluster analysis to the estimation of environmental impact on a population of women in the perinatal period [in Polish]. Bromat Chem Toksykol 34:249–257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiechuła, D., Fischer, A., Kwapuliński, J. et al. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Metal Concentrations in Teeth of Residents of Silesian Region, Southern Poland. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51, 314–320 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0202-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0202-1