Abstract
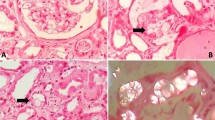
Taraxasterol is one of the important constituents of Taraxacum officinale L. (Compositae) with antioxidant potential. The present study was designed to evaluate and compare the antiurolithiatic effects of taraxasterol and potassium citrate in the ethylene glycol induced urolithiatic rat. Urolithiasis was induced by ammonium chloride and ethylene glycol in adult male rats. Taraxasterol (2, 4 and 8 mg/kg) and potassium citrate (2.5 g/kg) were treated for 33 days by gavage. Then, the animals were anesthetized and weighted and blood, urine, liver and kidney sampling were done. The kidney sections were prepared by hematoxylin & eosin staining. The liver and kidney coefficients, urine pH, calcium, magnesium, oxalate and citrate levels, serum albumin, calcium and magnesium levels, serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and lactate dehydrogenase activities, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities in serum, kidney and liver, number of calcium oxalate crystal deposits, score of crystal deposits, score of histopathological damages and score of inflammation in kidney sections were evaluated. The results showed that taraxasterol decreased liver and kidney coefficients (p < 0.001), serum calcium (p < 0.01) level, serum alanine aminotransferase (p < 0.001), aspartate aminotransferase (p < 0.001), lactate dehydrogenase (p < 0.05) activities, urine magnesium (p < 0.05) and oxalate (p < 0.001) levels, number of crystal deposits (p < 0.001), score of crystal deposits (p < 0.01), score of histopathological damages (p < 0.001) and score of inflammation (p < 0.01) in kidney sections, while increased urine pH (p < 0.01), calcium (p < 0.001) and citrate (p < 0.05), serum magnesium (p < 0.001) and albumin (p < 0.01) levels, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in serum (p < 0.01), kidney (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001, respectively) and liver (p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively) tissue homogenates in treated urolithiatic rats in comparison to the control urolithiatic rats. The effect of potassium citrate is the same as taraxasterol in treated urolithiatic rats. In conclusion, the effect of taraxasterol could be by improving liver function, changing serum and urine parameters, maintaining the antioxidant environment, reducing crystal deposition, excretion of small deposits from kidney and reducing the chance of them being retained in the urinary tract.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AC:
-
Ammonium chloride
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- CaOx:
-
Calcium oxalate
- EG:
-
Ethylene glycol
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- H & E:
-
Hematoxylin-Eosin
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneally
- KIM-1:
-
Kidney injury marker protein
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MCP-1:
-
Monocytes Chemo-attractant Protein-1
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- PCL:
-
Potassium citrate
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Hadjzadeh MA, Khoei A, Hadjzadeh Z, Parizady M (2007) Ethanolic extract of Nigella Sativa L. seeds on ethylene glycol-induced kidney calculi in rats. Urol J 4:86–90
Kambadakone AR, Eisner BH, Catalano OA, Sahani DV (2010) New and evolving concepts in the imaging and management of urolithiasis: urologists’perspective. Radiographics 30:603–623. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.303095146
Jonassen JA, Cao LC, Honeyman T, Scheid CR (2003) Mechanisms mediating oxalate-induced alterations in renal cell functions. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 13:55–72
Khan SR (2014) Reactive oxygen species, inflammation and calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. Transl Androl Urol 3:256–276. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2014.06.04
Zhang XM, Xiong HZ, Li LB (2012) Effects of taraxasterol on inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 14:206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.02.020
Jamshieed S, Das S, Sharma MP, Srivastava PS (2010) Difference in in vitro response and esculin content of Taraxacum officinale Weber. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-010-0038-2
Liu J, Xiong H, Cheng Y, Cui C, Zhang X, Xu L, Zhang X (2013) Effects of taraxasterol on ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 148:787–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.006
Aggarwal D, Gautam D, Sharma M, Singla SK (2016) Bergenin attenuates renal injury by reversing mitochondrial dysfunction in ethylene glycol induced hyperoxaluric rat model. Eur J Pharmacol 791:611–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.10.002
You Y, Yoo S, Yoon HG, Park J, Lee YH, Kim S, Oh KT, Lee J, Cho HY, Jun W (2010) In vitro and in vivo hepatoprotective effects of the aqueous extract from Taraxacum officinale (dandelion) root against alcohol-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1632–1637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.03.037
Krieger NS, Asplin JR, Frick KK, Granja I, Culbertson CD, Ng A, Grynpas MD, Bushinsky DA (2015) Effect of Potassium Citrate on Calcium Phosphate Stones in a Model of Hypercalciuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:3001–3008. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014121223
Divakar K, Pawar AT, Chandrasekhar SB, Dighe SB, Divakar G (2010) Protective effect of the hydro-alcoholic extract of Rubia cordifolia roots against ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1013–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.01.011
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) Simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Vysakh A, Raji NR, Suma D, Jayesh K, Jyothis M, Latha MS (2017) Role of antioxidant defence, renal toxicity markers and inflammatory cascade in disease progression of acute pyelonephritis in experimental rat model Microb Pathog 31: pii: S0882–4010(16)30883-X. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.05.047
Yamaguchi S, Wiessner JH, Hasegawa AT, Hung LY, Mandel GS, Mandel NS (2005) Study of a rat model for calcium oxalate crystal formation without severe renal damage in selected conditions. Int J Urol 12:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2042.2005.01038.x
Karadi RV, Gadge N, Alagawadi KR, Savadi RV (2006) Effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. root-wood on ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 105:306–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.11.004
Atmani F, Slimani Y, Mimouni M, Hacht B (2003) Prophylaxis of calcium oxalate stones by Herniaria hirsute on experimentally induced nephrolithiasis in rats. BJU Int 92:137–140. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410X.2003.04289.x
Yuruk E, Tuken M, Sahin C, Kaptanagasi AO, Basak K, Aykan S, Muslumanoglu AY, Sarica K (2016) The protective effects of an herbal agent tutukon on ethylene glycol and zinc disk induced urolithiasis model in a rat model. Urolithiasis 44(6):501–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-016-0889-2
Shekha MS, Qadir AB, Ali HH, Selim XE (2014) Effect of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) on ethylene glycol induced kidney stone in rats. Jordan J Biol Sci 7:257–260. https://doi.org/10.12816/0008248
Nnemdi Ashibuogwu M, Isaac Adeosun O, Ojo Akomolafe R, Olaniyi Sanni D, Sesan Olukiran O (2016) Diuretic activity and toxicity study of the aqueous extract of Cola nitida seed on markers of renal function and electrolytes in rats. J Complement Integr Med 13(4):393–404. https://doi.org/10.1515/jcim-2015-0115
Moochhala SH, Sayer JA, Carr G, Simmons NL (2008) Renal calcium stones: insights from the control of bone mineralization. Exp Physiol 93:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2007.040790
Lemann J Jr, Worcester EM, Gray RW (1991) Hypercalciuria and stones. Am J Kidney Dis 17:386–391
Saha S, Verma RJ (2015) Antinephrolithiatic and antioxidative efficacy of Dolichos biflorus seeds in a lithiasic rat model. Pharm Biol 53:16–30. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.909501
Soundararajan P, Mahesh R, Ramesh T, Begum VH (2006) Effect of Aerva lanata on calcium oxalate urolithiasis in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 44:981–986
Ghelani H, Chapala M, Jadav P (2016) Diuretic and antiurolithiatic activities of an ethanolic extract of Acorus calamus L. rhizome in experimental animal models. J Tradit Complement Med 6:431–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2015.12.004
Selvam R, Kalaiselvi P, Govindaraj A, Bala Murugan V, Sathish Kumar AS (2001) Effect of A. lanata leaf extract and Vediuppu chunnam on the urinary risk factors of calcium oxalate urolithiasis during experimental hyperoxaluria. Pharmacol Res 43:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1006/phrs.2000.0745
Menon M, Mahle CJ (1983) Urinary citrate excretion in patients with renal calculi. J Urol 129:1158–1160
Xu H, Zisman AL, Coe FL, Worcester EM (2013) Kidney stones: An update on current pharmacological management and future directions. Expert Opin Pharmacother 14:435–447. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2013.775250
Goldberg H, Grass L, Vogl R, Rapoport A, Oreopoulos DG (1989) Urine citrate and renal stone disease. CMAJ 141:217–221
Cerini C, Geider S, Dussol B, Hennequin C, Daudon M, Veesler S, Nitsche S, Boistelle R, Berthezene P, Dupuy P, Vazi A, Berland Y, Dagorn JC, Verdier JM (1999) Nucleation of calcium oxalate crystals by albumin: Involvement in the prevention of stone formation. Kidney Int 55:1776–1786. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00426.x
Veena CK, Josephine A, Preetha SP, Rajesh NG, Varalakshmi P (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction in an animal model of hyperoxaluria: a prophylactic approach with fucoidan. Eur J Pharmacol 579:330–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.09.044
Verhulst A, Asselman M, Persy VP, Schepers MS, Helbert MF, Verkoelen CF, De Broe ME (2003) Crystal retention capacity of cells in the human nephron: involvement of CD44 and its ligands hyaluronic acid and osteopontin in the transition of a crystal binding- into a non-adherent epithelium. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASN.0000038686.17715.42
Verkoelen CF, Van Der Boom BG, Romijn JC (2000) Identification of hyaluronan as a crystal-binding molecule at the surface of migrating and proliferating MDCK cells. Kidney Int 58:1045–1054. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00262.x
Zuo J, Khan A, Glenton PA, Khan SR (2011) Effect of NADPH oxidase inhibition on the expression of kidney injury molecule and calcium oxalate crystal deposition in hydroxy-L-proline-induced hyperoxaluria in the male Sprague-Dawley rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:1785–1796. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr035
Mulay SR, Kulkarni OP, Rupanagudi KV, Migliorini A, Darisipudi MN, Vilaysane A, Muruve D, Shi Y, Munro F, Liapis H, Anders HJ (2013) Calcium oxalate crystals induce renal inflammation by NLRP3-mediated IL-1beta secretion. J Clin Invest 123:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI63679
Xueshibojie L, Duo Y, Tiejun W (2016) Taraxasterol inhibits cigarette smoke induced lung inflammation by inhibiting reactive oxygen species-induced TLR4 trafficking to lipid rafts. Eur J Pharmacol 789:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.07.047
Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P (2013) Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 13:159–175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3399
Likhitpanichkul M, Torre OM, Gruen J, Walter BA, Hecht AC, Iatridis JC (2016) Do mechanical strain and TNF-α interact to amplify pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human annulus fibrosus cells? J Biomech 49:1214–1220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2016.02.029
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Deputy Research of the Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, for support of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
All Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals observed at the Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University and were in agreement with institutional guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH, publication No. 85-23, revised 2010; European Communities Directive 86/609/EEC).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefi Ghale-Salimi, M., Eidi, M., Ghaemi, N. et al. Antiurolithiatic effect of the taraxasterol on ethylene glycol induced kidney calculi in male rats. Urolithiasis 46, 419–428 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-017-1023-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-017-1023-9