Abstract
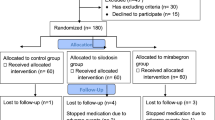
We evaluated the clinical results of tolterodine in treating impacted stones in the intramural ureter with symptoms of vesical irritability. A total of 80 patients with intramural ureter stones were included in the study from December 2007 to November 2009. Patients were randomly divided into two groups. The 41 patients in group A were given a watchful waiting and served as control group. Group B received 2 mg tolterodine (twice a day). Both groups were followed up for 2 weeks. The stone expulsion rate and time and the number of pain episodes were obtained. Subjects rated the urgency associated with each micturition using the Urinary Sensation Scale (USS). Pain descriptions were recorded by the patients using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS). The stone expulsion rate in groups A and B was 56.1 and 56.4%, respectively (P = 0.98). The mean numbers of renal colic episodes of patients in groups A and B had experienced 4.5 and 1.7, respectively. The USS for groups A and B in 3 and 7 days were 2.89 ± 0.56, 1.29 ± 0.60; 1.98 ± 0.79, 1.09 ± 0.3, respectively (P < 0.001). Statistically significant difference was found between groups A and B in relation to the VAS score on days 3 and 7, respectively (P < 0.001). While our study demonstrated no improvement in expulsion rate, Tolterodine reduced the common symptoms of frequency, urgency, intensity of the pain episodes and discomfort often associated with intramural ureter stone.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SWL:
-
Shock wave lithotripsy
- URS:
-
Ureteroscopy
- MET:
-
Medical expulsive therapy
- KUB:
-
X-rays of the kidneys, ureters and bladder
- IVU:
-
Intravenous urogram
- CT:
-
Computer tomography
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- USS:
-
Urinary Sensation Scale
- VAS:
-
Visual Analog Scale
- HRQL:
-
Health-related quality of life
- OAB:
-
Overactive bladder
References
Wolf JS Jr (2007) Treatment selection and outcomes: ureteral calculi. Urol Clin N Am 34:409–410
Wang CJ, Huang SW, Chang CH (2008) Efficacy of an α1 blocker in expulsive therapy of lower ureteral stones. J Endourol 22:41–42
Sigala S, Dellabella M, Milanese S, Fornari S, Faccoli S, Palazzolo F (2005) Evidence for the presence of α1 adrenoceptor subtypes in the human ureter. Neurourol Urodynam 24:142–144
Brewster-Jordan JL, Guan Z, Green HL et al (2005) Establishing the content validity of the Urinary Sensation Scale (USS). Presented at a meeting of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research, Washington, DC, 15–18 May 2005
Shokeir AA (2001) Renal colic: pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Eur Urol 39:241–249
De Sio M, Autorino R, Di Lorenzo G, Damiano R, Giordano D, Cosentino L (2006) Medical expulsive treatment of distal-ureteral stones using tamsulosin: a single-center experience. J Endourol 20:12–15
Cervenàkov I, Fillo J, Mardiak J, Kopecný M, Smirala J, Lepies P (2002) Speedy elimination of ureterolithiasis in lower part of ureters with the alpha 1-blocker—Tamsulosin. Int Urol Nephrol 34:25–27
Porpiglia F, Ghignone G, Fiori C, Fontana D, Scarpa RM (2004) Nifedipine versus tamsulosin for the management of lower ureteral stones. J Urol 172:568–570
Dellabella M, Milanese G, Muzzonigro G (2005) Randomized trial of the efficacy of tamsulosin, nifedipine and phloroglucinol in medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteral calculi. J Urol 174:167–171
Elinoff V, Bavendam T, Glasser DB et al (2006) Symptom-specific efficacy of tolterodine extended release in patients with overactivebladder: the IMPACT trial. Int J Clin Pract 60:745–751
Roberts R, Bavendam T, Glasser DB et al (2006) Tolterodine extended release improves patient-reported outcomes in overactive bladder: results from the IMPACT trial. Int J Clin Pract 60:752–758
Erturhan S, Erbagci A, Yagci F, Celik M, Solakhan M, Sarica K (2007) Comparative evaluation of efficacy of use of tamsulosin and/or tolterodine for medical treatment of distal ureteral stones. Urology 69(4):633–636
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, J.L., Tang, Q.N., Hui, J.H. et al. Efficacy of tolterodine for medical treatment of intramural ureteral stone with vesical irritability. Urol Res 39, 213–216 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-010-0337-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-010-0337-7