Abstract
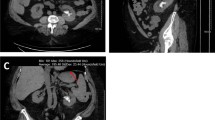
We describe the first case of efavirenz-induced urolithiasis in a 47-year-old HIV-positive patient. Urinary obstruction led to pyelonephritis and septic shock, requiring emergency ureteral catheterisation. The subsequent clinical course was favourable, allowing the patient’s discharge on day 5. A 7 mm, radio-translucent, non-crystalline, beige stone was extracted during catheterisation. Stone analysis by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry revealed a stone composed of efavirenz (EFV) metabolites M4, M5, M8 (as described by Mutlib et al. in 1999) and approximately 50% of unspecified proteins. EFV is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor introduced to European markets in 1999. It is principally metabolised by cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2B6. Of the dose, 14–34% is excreted in the urine, 1% as unchanged drug. The patient had been taking 600 mg EFV per day for 3 years. As EFV-induced urolithiasis has not been reported so far, we would like to draw the attention of the medical community to this potentially severe complication.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products of the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products: European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) on Stocrin/Efavirenz. http://www.emea.eu.int/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/Stocrin/StocrinM.htm
Staszewski S, Morales-Ramirez J, Tashima KT, Rachlis A, Skiest D, Stanford J, et al (1999) Efavirenz plus zidovudine and lamivudine, efavirenz plus indinavir, and indinavir plus zidovudine and lamivudine in the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults. Study 006 Team. N Engl J Med 341:1865
Daudon M, Jungers P (2004) Drug-induced renal calculi: epidemiology, prevention and management. Drugs 64:245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wirth, G.J., Teuscher, J., Graf, J.D. et al. Efavirenz-induced urolithiasis. Urol Res 34, 288–289 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-006-0052-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-006-0052-6