Abstract
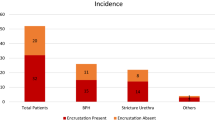
Weekly urinalysis was conducted for 12 weeks on a group of 21 long-term catheter users with confirmed catheter encrustation and urinary tract colonization with urease-positive bacteria, in order to explore the cause of considerable variation in the severity of encrustation between sufferers. The rapidity of catheter blockage correlated significantly with the pH above which crystals precipitated from urine (the nucleation pH) but not the pH of the voided urine itself. Linear regression showed the nucleation pH to be significantly predicted by a combination of urinary calcium and magnesium concentrations, with calcium being the more influential variable. Reducing the rate of catheter encrustation could be achieved by lowering the urinary concentration of calcium and magnesium, which may only require catheter users to increase their fluid intake.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stickler DJ, Zimakoff J (1994) Complications of urinary tract infections associated with devices used for long-term bladder management. J Hosp Infect 28:177–194
Kohler-Ockmore J, Feneley RC (1996) Long-term catheterization of the bladder: prevalence and morbidity. Br J Urol 77:347–351
Cox AJ, Hukins DW (1989) Morphology of mineral deposits on encrusted urinary catheters investigated by scanning electron microscopy. J Urol 142:1347–1350
Mobley HL, Warren JW (1987) Urease-positive bacteriuria and obstruction of long-term urinary catheters. J Clin Microbiol 25:2216–2217
Morris NS, Stickler DJ, McLean RJ (1999) The development of bacterial biofilms on indwelling urethral catheters. World J Urol 17:345–350
Burr RG, Nuseibeh IM (1997) Urinary catheter blockage depends on urine pH, calcium and rate of flow. Spinal Cord 35:521–525
Choong SK, Hallson P, Whitfield HN, Fry CH (1999) The physicochemical basis of urinary catheter encrustation. BJU Int 83:770–775
Getliffe KA (1994) The characteristics and management of patients with recurrent blockage of long-term urinary catheters. J Adv Nurs 20:140–149
Kunin CM, Chin QF, Chambers S (1987) Indwelling urinary catheters in the elderly. Relation of “catheter life” to formation of encrustations in patients with and without blocked catheters. Am J Med 82:405–411
Mathur S, Suller MTE, Stickler DJ, Feneley RCL (2006) A prospective study of individuals with long-term urinary catheters colonized with Proteus species. BJU Int 97:121–128
Jewes LA, Gillespie WA, Leadbetter A, Myers B, Simpson RA, Stower MJ et al (1988) Bacteriuria and bacteraemia in patients with long-term indwelling catheters—a domiciliary study. J Med Microbiol 26:61–65
Ganderton L, Chawla J, Winters C, Wimpenny J, Stickler D (1992) Scanning electron microscopy of bacterial biofilms on indwelling bladder catheters. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 11:789–796
Stickler DJ (2002) Susceptibility of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteria to biocides: a perspective from the study of catheter biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 92(Suppl):163S–170S
McLean RJ, Lawrence JR, Korber DR, Caldwell DE (1991) Proteus mirabilis biofilm protection against struvite crystal dissolution and its implications in struvite urolithiasis. J Urol 146:1138–1142
Bibby JM, Hukins DW (1993) Acidification of urine is not a feasible method for preventing encrustation of indwelling urinary catheters. Scand J Urol Nephrol 27:63–65
Morris NS, Stickler DJ (1998) The effect of urease inhibitors on the encrustation of urethral catheters. Urol Res 26:275–279
Griffith DP, Khonsari F, Skurnick JH, James KE (1988) A randomized trial of acetohydroxamic acid for the treatment and prevention of infection-induced urinary stones in spinal cord injury patients. J Urol 140:318–324
Hugosson J, Grenabo L, Hedelin H, Pettersson S, Tarfusser I (1990) How variations in the composition of urine influence urease-induced crystallization. Urol Res 18:413–417
Suller MT, Anthony VJ, Mathur S, Feneley RC, Greenman J, Stickler DJ (2005) Factors modulating the pH at which calcium and magnesium phosphates precipitate from human urine. Urol Res 33(4):254–260
Morris NS, Stickler DJ (2001) Does drinking cranberry juice produce urine inhibitory to the development of crystalline, catheter-blocking Proteus mirabilis biofilms? BJU Int 88:192–197
Acknowledgement
S.M. was supported by grant GR/R66517/01 from the EPSRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathur, S., Suller, M.T.E., Stickler, D.J. et al. Factors affecting crystal precipitation from urine in individuals with long-term urinary catheters colonized with urease-positive bacterial species. Urol Res 34, 173–177 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-006-0036-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-006-0036-6