Abstract.
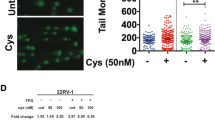
Transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) controls gene expression of a number of genes, including cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), granulocyte-macrophage (GM)-CSF, and interleukin-8 (IL-8). IL-6 is known to play important roles in the growth of prostate cancer cells, activation of androgen receptor, and prostate-specific protein expression. NF-κB is activated by extracellular signals such as proinflammatory cytokines, chemotherapeutic reagents, and radiation. Here we demonstrate that cisplatin (CDDP) and etoposide (VP-16) induce nuclear translocation of NF-κB in prostate cancer cell lines, followed by secretion of IL-6. We also demonstrated that the growth of hormone-independent prostate cancer cell lines can be inhibited by the anti-NF-κB reagent N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). These observations indicate that NF-κB can be a target of new adjuvant therapy against hormone refractory prostate cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tozawa, K., Okamoto, T., Hayashi, Y. et al. N-acetyl-L-cysteine enhances chemotherapeutic effect on prostate cancer cells. Urol Res 30, 53–58 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-001-0226-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-001-0226-1