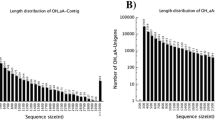
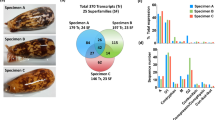
Abstract
The Asian genus Boiga (Colubridae) is among the better studied non-front-fanged snake lineages, because their bites have minor, but noticeable, effects on humans. Furthermore, B. irregularis has gained worldwide notoriety for successfully invading Guam and other nearby islands with drastic impacts on the local bird populations. One of the factors thought to allow B. irregularis to become such a noxious pest is irditoxin, a dimeric neurotoxin composed of two three-finger toxins (3FTx) joined by a covalent bond between two newly evolved cysteines. Irditoxin is highly toxic to diapsid (birds and reptiles) prey, but roughly 1000 × less potent to synapsids (mammals). Venom plays an important role in the ecology of all species of Boiga, but it remains unknown if any species besides B. irregularis produce irditoxin-like dimeric toxins. In this study, we use transcriptomic analyses of venom glands from five species [B. cynodon, B. dendrophila dendrophila, B. d. gemmicincta, B. irregularis (Brisbane population), B. irregularis (Sulawesi population), B. nigriceps, B. trigonata] and proteomic analyses of B. d. dendrophila and a representative of the sister genus Toxicodryas blandingii to investigate the evolutionary history of 3FTx within Boiga and its close relative. We found that 92.5% of Boiga 3FTx belong to a single clade which we refer to as denmotoxin-like because of the close relation between these toxins and the monomeric denmotoxin according to phylogenetic, sequence clustering, and protein similarity network analyses. We show for the first time that species beyond B. irregularis secrete 3FTx with additional cysteines in the same position as both the A and B subunits of irditoxin. Transcripts with the characteristic mutations are found in B. d. dendrophila, B. d. gemmicincta, B. irregularis (Brisbane population), B. irregularis (Sulawesi population), and B. nigriceps. These results are confirmed by proteomic analyses that show direct evidence of dimerization within the venom of B. d. dendrophila, but not T. blandingii. Our results also suggest the possibility of novel dimeric toxins in other genera such as Telescopus and Trimorphodon. All together, this suggests that the origin of these peculiar 3FTx is far earlier than was appreciated and their evolutionary history has been complex.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SA, Yang DC, Jackson TN, Undheim EA, Koludarov I, Wood K, Jones A, Hodgson WC, McCarthy S, Ruder T (2013) Venom proteomic characterization and relative antivenom neutralization of two medically important Pakistani elapid snakes (Bungarus sindanus and Naja naja). J Proteomics 89:15–23
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Baig KJ, Masroor R, Arshad M (2011) Biodiversity and ecology of the herpetofauna of Cholistan Desert, Pakistan. Russ J Herpetol 15:193–205
Benson DA, Cavanaugh M, Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW (2013) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D36–D42
Boquet P (1979) History of snake venom research. Springer, New York, pp. 3–14
Brahma RK, McCleary RJR, Kini RM, Doley R (2015) Venom gland transcriptomics for identifying, cataloging, and characterizing venom proteins in snakes. Toxicon 93:1–10
Broaders M, Ryan MF (1997) Enzymatic properties of the Duvernoy’s secretion of Blanding’s tree snake (Boiga blandingi) and of the mangrove snake (Boiga dendrophila). Toxicon 35:1143–1148
Burbrink FT, Lawson R (2007) How and when did Old World ratsnakes disperse into the New World? Mol Phylogenet Evol 43:173–189
Cascardi J, Young BA, Husic HD, Sherma J (1999) Protein variation in the venom spat by the red spitting cobra, Naja pallida (Reptilia: Serpentes). Toxicon 37:1271–1279
Casewell NR, Wüster W, Vonk FJ, Harrison RA, Fry BG (2013) Complex cocktails: the evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol Evol 28:219–229
Chiszar D, Dunn TM, Smith HM (1993) Response of brown tree snakes (Boiga irregularis) to human blood. J Chem Ecol 19:91–96
Cipriani V, Debono J, Goldenberg J, Jackson TNW, Arbuckle K, Dobson J, Koludarov I, Li B, Hay C, Dunstan N et al (2017) Correlation between ontogenetic dietary shifts and venom variation in Australian brown snakes (Pseudonaja). Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 197:53–60
Daltry JC, Wüster W, Thorpe RS (1996) Diet and snake venom evolution. Nature 379:537
Das I (2012) A naturalist’s guide to the snakes of Southeast Asia. John Beaufoy Publishing, Oxford
Dashevsky D, Fry BG (2018) Ancient diversification of three-finger toxins in Micrurus coral snakes. J Mol Evol 86:58–67
Debono J, Cochran C, Kuruppu S, Nouwens A, Rajapakse NW, Kawasaki M, Wood K, Dobson J, Baumann K, Jouiaei M (2016) Canopy venom: proteomic comparison among new world arboreal pit-viper venoms. Toxins 8:210
Debono J, Dobson J, Casewell NR, Romilio A, Li B, Kurniawan N, Mardon K, Weisbecker V, Nouwens A, Kwok HF, Fry BG (2017) Coagulating colubrids: evolutionary, pathophysiological and biodiscovery implications of venom variations between boomslang (Dispholidus typus) and twig snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus). Toxins 9:171
Deufel A, Cundall D (2006) Functional plasticity of the venom delivery system in snakes with a focus on the poststrike prey release behavior. Zool Anzeiger A 245:249–267
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Figueroa A, McKelvy AD, Grismer LL, Bell CD, Lailvaux SP (2016) A species-level phylogeny of extant snakes with description of a new colubrid subfamily and genus. PLoS ONE 11:e0161070
Fritts TH, McCoid MJ, Haddock RL (1994) Symptoms and circumstances associated with bites by the brown tree snake (Colubridae: Boiga irregularis) on Guam. J Herpetol 28:27–33
Fry BG (1999) Structure–function properties of venom components from Australian elapids. Toxicon 37:11–32
Fry BG (2005) From genome to “venome”: molecular origin and evolution of the snake venom proteome inferred from phylogenetic analysis of toxin sequences and related body proteins. Genome Res 15:403–420
Fry BG, Wüster W (2004) Assembling an Arsenal: origin and evolution of the snake venom proteome inferred from phylogenetic analysis of toxin sequences. Mol Biol Evol 21:870–883
Fry BG, Lumsden NG, Wüster W, Wickramaratna JC, Hodgson WC, Kini RM (2003a) Isolation of a Neurotoxin (α-colubritoxin) from a nonvenomous colubrid: evidence for early origin of venom in snakes. J Mol Evol 57:446–452
Fry BG, Wüster W, Ramjan R, Jackson SF, Martelli T, P., and Kini RM (2003b) Analysis of Colubroidea snake venoms by liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry: evolutionary and toxinological implications: LC/MS analysis of Colubroidea snake venoms. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17:2047–2062
Fry BG, Vidal N, Norman JA, Vonk FJ, Scheib H, Ramjan SFR, Kuruppu S, Fung K, Hedges SB, Richardson MK et al (2006) Early evolution of the venom system in lizards and snakes. Nature 439:584–588
Fry BG, Scheib H, Weerd L van der, Young B, McNaughtan J, Ramjan SFR, Vidal N, Poelmann RE, Norman JA (2008) Evolution of an arsenal structural and functional diversification of the venom system in the advanced Snakes (Caenophidia). Mol Cell Proteomics 7:215–246
Fry BG, Roelants K, Champagne DE, Scheib H, Tyndall JDA, King GF, Nevalainen TJ, Norman JA, Lewis RJ, Norton RS et al (2009a) The toxicogenomic multiverse: convergent recruitment of proteins into animal venoms. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 10:483–511
Fry BG, Vidal N, van der Weerd L, Kochva E, Renjifo C (2009b) Evolution and diversification of the Toxicofera reptile venom system. J Proteomics 72:127–136
Fry BG, Undheim EAB, Ali SA, Jackson TNW, Debono J, Scheib H, Ruder T, Morgenstern D, Cadwallader L, Whitehead D et al (2013) Squeezers and leaf-cutters: differential diversification and degeneration of the venom system in toxicoferan reptiles. Mol Cell Proteomics 12:1881–1899
Fry BG, Sunagar K, Casewell NR, Kochva E, Roelants K, Scheib H, Wüster W, Vidal N, Young B, Burbrink F et al (2015a). The origin and evolution of the Toxicofera reptile venom system. In: Fry BG (ed) Venomous reptiles and their toxins: evolution, pathophysiology and biodiscovery. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 1–31
Fry BG, Sunagar K, Casewell NR, Kochva E, Roelants K, Scheib H, Wüster W, Vidal N, Young B, Burbrink F, Pyron RA, Vonk FJ, Jackson TNW (2015b) The origin and evolution of the Toxicofera reptile venom system. In: Fry BG (ed) Venomous reptiles and their toxins: evolution, pathophysiology and biodiscovery. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1–31
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W (2012) CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28:3150–3152
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644
Hayes WK, Herbert SS, Harrison JR, Wiley KL (2008) Spitting versus biting: differential venom gland contraction regulates venom expenditure in the black-necked spitting cobra, Naja nigricollis nigricollis. J Herpetol 42:453–460
Heyborne WH, Mackessy SP (2013) Identification and characterization of a taxon-specific three-finger toxin from the venom of the Green Vinesnake (Oxybelis fulgidus; family Colubridae). Biochimie 95:1923–1932
Hill RE, Mackessy SP (1997) Venom yields from several species of colubrid snakes and differential effects of ketamine. Toxicon 35:671–678
Jackson K (2003) The evolution of venom-delivery systems in snakes. Zool J Linn Soc 137:337–354
Jackson TN, Fry BG (2016) A tricky trait: applying the fruits of the “function debate” in the philosophy of biology to the “venom debate” in the science of toxinology. Toxins 8(9):263
Jackson TNW, Sunagar K, Undheim EAB, Koludarov I, Chan AHC, Sanders K, Ali SA, Hendrikx I, Dunstan N, Fry BG (2013) Venom down under: dynamic evolution of australian elapid snake toxins. Toxins 5:2621–2655
Jackson TNW, Young B, Underwood G, McCarthy CJ, Kochva E, Vidal N, van der Weerd L, Nabuurs R, Dobson J, Whitehead D et al (2016) Endless forms most beautiful: the evolution of ophidian oral glands, including the venom system, and the use of appropriate terminology for homologous structures. Zoomorphology 136:107–130
Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJE (2015) The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc 10:845–858
Kessler P, Marchot P, Silva M, Servent D (2017) The three-finger toxin fold: a multifunctional structural scaffold able to modulate cholinergic functions. J Neurochem 142:7–18
Kochva E, Viljoen CC, Botes DP (1982) A new type of toxin in the venom of snakes of the genus Atractaspis (Atractaspidinae). Toxicon 20:581–592
Krueger F (2015) Trim Galore!: a wrapper tool around Cutadapt and FastQC to consistently apply quality and adapter trimming to FastQ files
Larsson A (2014) AliView: a fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. Bioinformatics 30:3276–3278
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
Li W, Godzik A (2006) Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 22:1658–1659
Li M, Fry BG, Kini RM (2005) Eggs-only diet: its implications for the toxin profile changes and ecology of the marbled sea snake (Aipysurus eydouxii). J Mol Evol 60:81–89
Lumsden NG, Fry BG, Kini RM, Hodgson WC (2004) In vitro neuromuscular activity of ‘colubrid’ venoms: clinical and evolutionary implications. Toxicon 43:819–827
Lumsden NG, Fry BG, Ventura S, Kini RM, Hodgson WC (2005) Pharmacological characterisation of a neurotoxin from the venom of Boiga dendrophila (Mangrove catsnake). Toxicon 45:329–334
Mackessy SP (2010) Evolutionary trends in venom composition in the western rattlesnakes (Crotalus viridis sensu lato): toxicity vs. tenderizers. Toxicon 55:1463–1474
Mackessy SP, Sixberry NM, Heyborne WH, Fritts T (2006) Venom of the Brown Treesnake, Boiga irregularis: Ontogenetic shifts and taxa-specific toxicity. Toxicon 47:537–548
Mapleson D, Garcia Accinelli G, Kettleborough G, Wright J, Clavijo BJ (2017) KAT: a K-mer analysis toolkit to quality control NGS datasets and genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 33:574–576
Marçais G, Kingsford C (2011) A fast, lock-free approach for efficient parallel counting of occurrences of k-mers. Bioinformatics 27:764–770
Margres MJ, Aronow K, Loyacano J, Rokyta DR (2013) The venom-gland transcriptome of the eastern coral snake (Micrurus fulvius) reveals high venom complexity in the intragenomic evolution of venoms. BMC Genom 14:1
Margres MJ, Bigelow AT, Lemmon EM, Lemmon AR, Rokyta DR (2017) Selection to increase expression, not sequence diversity, precedes gene family origin and expansion in rattlesnake venom. Genetics 206:1569–1580
McGivern JJ, Wray KP, Margres MJ, Couch ME, Mackessy SP, Rokyta DR (2014) RNA-seq and high-definition mass spectrometry reveal the complex and divergent venoms of two rear-fanged colubrid snakes. BMC Genomics 15:1061
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M et al (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Minton SA (1990) Venomous bites by nonvenomous snakes: an annotated bibliography of colubrid envenomation. J Wilderness Med 1:119–127
Mitchell SW (1861) Researches upon the venom of the rattlesnake: with an investigation of the anatomy and physiology of the organs concerned. Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC
Modahl CM, Mackessy SP (2016) Full-length venom protein cDNA sequences from venom-derived mRNA: exploring compositional variation and adaptive multigene evolution. PLOS Negl Trop Dis 10:e0004587
Murrell B, Wertheim JO, Moola S, Weighill T, Scheffler K, Pond SLK (2012) Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLOS Genet 8:e1002764
Murrell B, Moola S, Mabona A, Weighill T, Sheward D, Pond K, L, S., and Scheffler K (2013) FUBAR: a fast, unconstrained Bayesian AppRoximation for inferring selection. Mol Biol Evol 30:1196–1205
Nelsen DR, Nisani Z, Cooper AM, Fox GA, Gren ECK, Corbit AG, Hayes WK (2014) Poisons, toxungens, and venoms: redefining and classifying toxic biological secretions and the organisms that employ them. Biol Rev 89:450–465
Oulion B, Dobson JS, Zdenek CN, Arbuckle K, Lister C, Coimbra FCP, op den Brouw B, Debono J, Rogalski A, Violette A et al (2018) Factor X activating Atractaspis snake venoms and the relative coagulotoxicity neutralising efficacy of African antivenoms. Toxicol Lett 288:119–128
Panagides N, Jackson TNW, Ikonomopoulou MP, Arbuckle K, Pretzler R, Yang DC, Ali SA, Koludarov I, Dobson J, Sanker B et al (2017) How the cobra got its flesh-eating venom: cytotoxicity as a defensive innovation and its co-evolution with hooding, aposematic marking, and spitting. Toxins 9:103
Pawlak J, Mackessy SP, Fry BG, Bhatia M, Mourier G, Fruchart-Gaillard C, Servent D, Ménez R, Stura E, Ménez A et al (2006) Denmotoxin, a three-finger toxin from the colubrid snake Boiga dendrophila (Mangrove Catsnake) with bird-specific activity. J Biol Chem 281:29030–29041
Pawlak J, Mackessy SP, Sixberry NM, Stura EA, Le Du MH, Ménez R, Foo CS, Ménez A, Nirthanan S, Kini RM (2008) Irditoxin, a novel covalently linked heterodimeric three-finger toxin with high taxon-specific neurotoxicity. FASEB J 23:534–545
Pei J, Grishin NV (2001) AL2CO: calculation of positional conservation in a protein sequence alignment. Bioinformatics 17:700–712
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Pla D, Sanz L, Whiteley G, Wagstaff SC, Harrison RA, Casewell NR, Calvete JJ (2017) What killed Karl Patterson Schmidt? Combined venom gland transcriptomic, venomic and antivenomic analysis of the South African green tree snake (the boomslang), Dispholidus typus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1861:814–823
Pla D, Petras D, Saviola AJ, Modahl CM, Sanz L, Pérez A, Juárez E, Frietze S, Dorrestein PC, Mackessy SP et al (2018a) Transcriptomics-guided bottom-up and top-down venomics of neonate and adult specimens of the arboreal rear-fanged Brown Treesnake, Boiga irregularis, from Guam. J Proteomics 174:71–84
Pla D, Petras D, Saviola AJ, Modahl CM, Sanz L, Pérez A, Juárez E, Frietze S, Dorrestein PC, Mackessy SP, Calvete (2018b) Transcriptomics-guided bottom-up and top-down venomics of neonate and adult specimens of the arboreal rear-fanged Brown Treesnake, Boiga irregularis, from Guam. J. Proteomics 174:71–84
Pond SLK, Frost SDW, Muse SV (2005) HyPhy: hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 21:676–679
Pyron RA, Burbrink FT, Wiens JJ (2013a) A phylogeny and revised classification of Squamata, including 4161 species of lizards and snakes. BMC Evol Biol 13:93
Pyron RA, Kandambi HKD, Hendry CR, Pushpamal V, Burbrink FT, Somaweera R (2013b) Genus-level phylogeny of snakes reveals the origins of species richness in Sri Lanka. Mol Phylogenet Evol 66:969–978
Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26:841–842
Ramadhan G, Iskandar DT, Subasri DR (2010) A new species of Cat Snake (Serpentes: Colubridae) morphologically similar to Boiga cynodon from the Nusa Tenggara Islands, Indonesia. Asian Herpetol Res 1:22–30
Rochelle MJ, Kardong KV (1993) Constriction versus envenomation in prey capture by the brown tree snake, Boiga irregularis (Squamata: Colubridae). Herpetologica 1993:301–304
Rodda GH, Fritts TH (1992) The impact of the introduction of the colubrid snake Boiga irregularis on Guam’s lizards. J Herpetol 26:166–174
Rodda GH, Savidge JA (2007) Biology and impacts of Pacific island invasive species. 2. Boiga irregularis, the brown tree snake (Reptilia: Colubridae). Pac Sci 61:307–324
Rokyta DR, Lemmon AR, Margres MJ, Aronow K (2012) The venom-gland transcriptome of the eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus). BMC Genomics 13:312
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542
Savidge JA (1986) The Role of Disease and Predation in The Decline of Guam’s Avifauna (Extinction, Boiga irregularis). PhD Thesis. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign
Savidge JA (1988) Food habits of Boiga irregularis, an introduced predator on Guam. J Herpetol 22:275–282
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Shivik JA (2006) Are vultures birds, and do snakes have venom, because of macro- and microscavenger conflict? BioScience 56:819–823
Stuebing RB, Inger RF, Tan FL (1999) Field guide to the snakes of Borneo. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu
Sunagar K, Jackson T, Undheim E, Ali S, Antunes A, Fry B (2013) Three-fingered RAVERs: rapid accumulation of variations in exposed residues of snake venom toxins. Toxins 5:2172–2208
Sunagar K, Undheim EAB, Scheib H, Gren ECK, Cochran C, Person CE, Koludarov I, Kelln W, Hayes WK, King GF et al (2014) Intraspecific venom variation in the medically significant Southern Pacific Rattlesnake (Crotalus oreganus helleri): Biodiscovery, clinical and evolutionary implications. J Proteomics 99:68–83
Terrat Y, Sunagar K, Fry BG, Jackson TNW, Scheib H, Fourmy R, Verdenaud M, Blanchet G, Antunes A, Ducancel F (2013) Atractaspis aterrima toxins: the first insight into the molecular evolution of venom in side-stabbers. Toxins 5:1948–1964
The Uniprot Consortium (2017) UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D158–D169
Utkin YN, Kukhtina VV, Kryukova EV, Chiodini F, Bertrand D, Methfessel C, Tsetlin VI (2001) “Weak toxin” from Naja kaouthia is a nontoxic antagonist of α7 and muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem 276:15810–15815
Utkin Y, Sunagar K, Jackson T, Reeks T, Fry B (2015). Three-finger toxins (3FTxs). In: Fry BG (ed) Venomous reptiles and their toxins: evolution, pathophysiology and biodiscovery. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 215–227
Vonk FJ, Casewell NR, Henkel CV, Heimberg AM, Jansen HJ, McCleary RJ, Kerkkamp HM, Vos RA, Guerreiro I, Calvete JJ (2013) The king cobra genome reveals dynamic gene evolution and adaptation in the snake venom system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:20651–20656
Whittington AC, Mason AJ, Rokyta DR (2018) A single mutation unlocks cascading exaptations in the origin of a potent pitviper neurotoxin. Mol Biol Evol 35(4):887–898
Xie Y, Wu G, Tang J, Luo R, Patterson J, Liu S, Huang W, He G, Gu S, Li S (2014) SOAPdenovo-Trans: de novo transcriptome assembly with short RNA-Seq reads. Bioinformatics 30:1660–1666
Zhang J, Kobert K, Flouri T, Stamatakis A (2013) PEAR: a fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 30:614–620
Acknowledgements
DD was funded by a UQ Centennial Scholarship from The University of Queensland DD and JD were funded by Research Training Program scholarships from the Australian Government Department of Education and Training. DRR was funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF DEB 1638902). BGF was funded by an Australian Research Council Future Fellowship and by the University of Queensland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dashevsky, D., Debono, J., Rokyta, D. et al. Three-Finger Toxin Diversification in the Venoms of Cat-Eye Snakes (Colubridae: Boiga). J Mol Evol 86, 531–545 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-018-9864-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-018-9864-6