Abstract
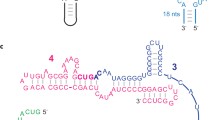
The interstitial liquid phase within frozen aqueous solutions is an environment that minimizes RNA degradation and facilitates reactions that may have relevance to the RNA World hypothesis. Previous work has shown that frozen solutions support condensation of activated nucleotides into RNA oligomers, RNA ligation by the hairpin ribozyme, and RNA synthesis by a RNA polymerase ribozyme. In the current study, we examined the activity of a hammerhead ribozyme (HHR) in frozen solution. The Schistosoma mansoni hammerhead ribozyme, which predominantly cleaves RNA, can ligate its cleaved products (P1 and P2) with yields up to ~23 % in single turnover experiments at 25 °C in the presence of Mg2+. Our studies show that this HHR ligates RNA oligomers in frozen solution in the absence of divalent cations. Citrate and other anions that exhibit strong ion-water affinity enhanced ligation. Yields up to 43 % were observed in one freeze–thaw cycle and a maximum of 60 % was obtained after several freeze–thaw cycles using wild-type P1 and P2. Truncated and mutated P1 substrates were ligated to P2 with yields of 14–24 % in one freeze–thaw cycle. A pool of P2 substrates with mixtures of all four bases at five positions were ligated with P1 in frozen solution. High-throughput sequencing indicated that 70 of the 1024 possible P2 sequences were represented in ligated products at 1000 or more read counts per million reads. The results indicate that the HHR can ligate a range of short RNA oligomers into an ensemble of diverse sequences in ice.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamala K, Szostak JW (2013) Nonenzymatic template-directed RNA synthesis inside model protocells. Science 342:1098
Anderson M, Schultz EP, Martick M, Scott WG (2013) Active-site monovalent cations revealed in a 1.55-angstrom-resolution hammerhead ribozyme structure. J Mol Biol 425:3790
Attwater J, Wochner A, Pinheiro VB, Coulson A, Holliger P (2010) Ice as a protocellular medium for RNA replication. Nat Commun 1:76
Auffinger P, Grover N, Westhof E (2011) Metal ion binding to RNA. Met Ions Life Sci 9:1
Bada JL, Lazcano A (2002) Origin of life. Some like it hot, but not the first biomolecules. Science 296:1982
Biondi E, Maxwell AW, Burke DH (2012) A small ribozyme with dual-site kinase activity. Nucleic Acids Res 40:7528
Birikh KR, Heaton PA, Eckstein F (1997) The structure, function and application of the hammerhead ribozyme. Eur J Biochem 245:1
Canny MD, Jucker FM, Kellogg E, Khvorova A, Jayasena SD, Pardi A (2004) Fast cleavage kinetics of a natural hammerhead ribozyme. J Am Chem Soc 126:10848
Canny MD, Jucker FM, Pardi A (2007) Efficient ligation of the Schistosoma hammerhead ribozyme. Biochemistry 46:3826
Chi YI, Martick M, Lares M, Kim R, Scott WG, Kim SH (2008) Capturing hammerhead ribozyme structures in action by modulating general base catalysis. PLoS Biol 6:2060
Collins KD (2006) Ion hydration: implications for cellular function, polyelectrolytes, and protein crystallization. Biophys Chem 119:271
Darnell J (2011) RNA: life’s indispensable molecule. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
de la Pena M, Garcia-Robles I (2010) Ubiquitous presence of the hammerhead ribozyme motif along the tree of life. RNA 16:1943
De la Pena M, Gago S, Flores R (2003) Peripheral regions of natural hammerhead ribozymes greatly increase their self-cleavage activity. EMBO J 22:5561
Ditzler MA, Lange MJ, Bose D, Bottoms CA, Virkler KF, Sawyer AW, Whatley AS, Spollen W, Givan SA, Burke DH (2013) High-throughput sequence analysis reveals structural diversity and improved potency among RNA inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1873
Fedor MJ (2009) Comparative Enzymology and Structural Biology of RNA Self-Cleavage. Annu Rev Biophys 38:271
Ferris JP, Hill AR Jr, Liu R, Orgel LE (1996) Synthesis of long prebiotic oligomers on mineral surfaces. Nature 381:59
Franks F (2000) Water a matrix of life. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge xii, 225
Gao JY, Xie C, Wang YL, Xu Z, Hao HX (2012) Solubility data of trisodium citrate hydrates in aqueous solution and crystal-solution interfacial energy of the pentahydrate. Cryst Res Technol 47:397
Gilbert W (1986) Origin of Life—the Rna World. Nature 319:618
Hammann C, Luptak A, Perreault J, de la Pena M (2012) The ubiquitous hammerhead ribozyme. RNA 18:871
Han J, Burke JM (2005) Model for general acid-base catalysis by the hammerhead ribozyme: pH-activity relationships of G8 and G12 variants at the putative active site. Biochemistry 44:7864
Haynes CM (2013) The CRC handbook of chemistry and physics. Libr J 94:192
Hertel KJ, Herschlag D, Uhlenbeck OC (1994) A kinetic and thermodynamic framework for the hammerhead ribozyme reaction. Biochemistry 33:3374
Hertel KJ, Herschlag D, Uhlenbeck OC (1996) Specificity of hammerhead ribozyme cleavage. EMBO J 15:3751
Higashi K, Terui Y, Suganami A, Tamura Y, Nishimura K, Kashiwagi K, Igarashi K (2008) Selective structural change by spermidine in the bulged-out region of double-stranded RNA and its effect on RNA function. J Biol Chem 283:32989
Hsiao C, Chou IC, Okafor CD, Bowman JC, O’Neill EB, Athavale SS, Petrov AS, Hud NV, Wartell RM, Harvey SC, Williams LD (2013) RNA with iron(II) as a cofactor catalyses electron transfer. Nat Chem 5:525
Hutchins CJ, Rathjen PD, Forster AC, Symons RH (1986) Self-cleavage of plus and minus Rna transcripts of avocado sunblotch viroid. Nucleic Acids Res 14:3627
Johnston WK, Unrau PJ, Lawrence MS, Glasner ME, Bartel DP (2001) RNA-catalyzed RNA polymerization: accurate and general RNA-templated primer extension. Science 292:1319
Joyce GF (1989) RNA evolution and the origins of life. Nature 338:217
Kanavarioti A, Monnard PA, Deamer DW (2001) Eutectic phases in ice facilitate nonenzymatic nucleic acid synthesis. Astrobiology 1:271
Kazakov SA, Balatskaya SV, Johnston BH (1998) Freezing-induced self-ligation of the hairpin ribozyme: cationic effects. Struct Motion Interact Expr Biol Macromol 2:155
Kazakov SA, Balatskaya SV, Johnston BH (2006) Ligation of the hairpin ribozyme in cis induced by freezing and dehydration. Rna 12:446
Khvorova A, Lescoute A, Westhof E, Jayasena SD (2003) Sequence elements outside the hammerhead ribozyme catalytic core enable intracellular activity. Nat Struct Biol 10:708
Kupakuwana GV, Crill JE 2nd, McPike MP, Borer PN (2011) Acyclic identification of aptamers for human alpha-thrombin using over-represented libraries and deep sequencing. PLoS One 6:e19395
Lambert D, Draper DE (2007) Effects of osmolytes on RNA secondary and tertiary structure stabilities and RNA-Mg2+ interactions. J Mol Biol 370:993
Levy M, Miller SL (1998) The stability of the RNA bases: implications for the origin of life. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7933
Li YF, Breaker RR (1999) Kinetics of RNA degradation by specific base catalysis of transesterification involving the 2 ‘-hydroxyl group. J Am Chem Soc 121:5364
Murray JB, Seyhan AA, Walter NG, Burke JM, Scott WG (1998) The hammerhead, hairpin and VS ribozymes are catalytically proficient in monovalent cations alone. Chem Biol 5:587
Mutschler H, Holliger P (2014) Non-canonical 3′-5′ extension of RNA with prebiotically plausible ribonucleoside 2′,3′-cyclic phosphates. J Am Chem Soc 136:5193
Mutschler H, Wochner A, Holliger P (2015) Freeze-thaw cycles as drivers of complex ribozyme assembly. Nat Chem 7:502
O’Rear JL, Wang SL, Feig AL, Beigelman L, Uhlenbeck OC, Herschlag D (2001) Comparison of the hammerhead cleavage reactions stimulated by monovalent and divalent cations. Rna 7:537
Pace NR (1991) Origin of life–facing up to the physical setting. Cell 65:531
Perreault J, Weinberg Z, Roth A, Popescu O, Chartrand P, Ferbeyre G, Breaker RR (2011) Identification of hammerhead ribozymes in all domains of life reveals novel structural variations. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002031
Prody GA, Bakos JT, Buzayan JM, Schneider IR, Bruening G (1986) Autolytic processing of dimeric plant-virus satellite Rna. Science 231:1577
Renz M, Lohrmann R, Orgel LE (1971) Catalysts for polymerization of adenosine cyclic 2′,3′-phosphate on a poly (U) template. Biochim Biophys Acta 240:463
Roy S (2008) Cleavage and ligation studies in hairpin and hammerhead ribozymes using site specific nucleotide modifications. University of Vermont, Burlington, p 176
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Serganov A, Patel DJ (2009) Amino acid recognition and gene regulation by riboswitches. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1789:592
Shepotinovskaya IV, Uhlenbeck OC (2008) Catalytic diversity of extended hammerhead ribozymes. Biochemistry 47:7034
Stage-Zimmermann TK, Uhlenbeck OC (1998) Hammerhead ribozyme kinetics. RNA 4:875
Stage-Zimmermann TK, Uhlenbeck OC (2001) A covalent crosslink converts the hammerhead ribozyme from a ribonuclease to an RNA ligase. Nat Struct Biol 8:863
Sun X, Li JM, Wartell RM (2007) Conversion of stable RNA hairpin to a metastable dimer in frozen solution. RNA 13:2277
Tokumoto Y, Saigo K (1992) RNA-RNA and RNA-DNA ligation with the sTobRV(+) hammerhead ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 27:21
Trinks H, Schroder W, Biebricher CK (2005) Ice and the origin of life. Orig Life Evol Biosph 35:429
Turk RM, Chumachenko NV, Yarus M (2010) Multiple translational products from a five-nucleotide ribozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:4585
Uhlenbeck OC (1987) A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature 328:596
Vlassov AV, Johnston BH, Landweber LF, Kazakov SA (2004) Ligation activity of fragmented ribozymes in frozen solution: implications for the RNA world. Nucleic Acids Res 32:2966
Vlassov AV, Kazakov SA, Johnston BH, Landweber LF (2005) The RNA world on Ice: a new scenario for the emergence of RNA information. J Mol Evol 61:264
Acknowledgments
We thank Rachel Hutto for assistance with ligation experiments and Prof. Klemens Hertel for advice on the carbodiimide reaction. We gratefully acknowledge support during the course of this study from the NASA Astrobiology Institute, and a Dept. of Education GAANN Fellowship awarded to L. Lie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lie, L., Biliya, S., Vannberg, F. et al. Ligation of RNA Oligomers by the Schistosoma mansoni Hammerhead Ribozyme in Frozen Solution. J Mol Evol 82, 81–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-016-9729-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-016-9729-9