Abstract
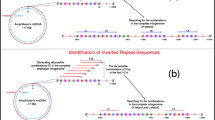
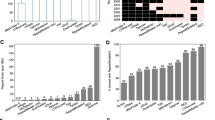
The evolution of a multigene family (MGF) is affected by the structure and function of its regulatory elements, specifically by the link between recombination and DNA transcription and/or replication. The ribosomal DNA (rDNA) MGF is often hierarchically repetitive, combining function with repetition in a single genic system. Its tandemly repeated operons contain the transcription unit of the 45S ribosomal RNA precursor alternating with an intergenic spacer (IGS) that commonly includes repeated transcription regulatory elements. To study the evolution of repeated sequences and the influence of repeat characteristics on their sequence divergence, we sequenced and characterized a single complete IGS from 11 daphniid species and analyzed their repeat arrays along with those from an additional 21 species of arthropods. We tested the hypotheses that sequence similarity is higher among tandemly arrayed repeats than among interleaved or dispersed repeats, and that the homogeneity of repeat arrays is affected by the number and the length of repeats, as well as by the presence of putative regulatory elements. We found that both tandem repeat organization and the presence of a TATA motif are significantly correlated with increased sequence similarity among homologous IGS repeats. We also observed that some repeat types are only found in a single species, while others appear to have persisted for >100 MY, with evidence for homologous repeat types in sister species. Taken together, these data suggest that both drift and natural selection influence repeat evolution within the IGS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnheim N (1983) Concerted evolution of multigene families. In: Nei M, Koehn RK (eds) Evolution of genes and proteins. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, pp 38–61
Baldridge GD, Fallon AM (1992) Primary structure of the ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer from the Mosquito, Aedes albopictus. DNA Cell Biol 11:51–59
Baldwin BG, Markos S (1998) Phylogenetic utility of the external transcribed spacer (ETS) of 18S–26S rDNA: congruence of ETS and ITS trees of Calycadenia (Compositae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 10:449–463
Burton RS, Metz EC, Flowers JM, Willett CS (2005) Unusual structure of ribosomal DNA in the copepod Tigriopus californicus: intergenic spacer sequences lack internal subrepeats. Gene 344:105–113
Caudy AA, Pikaard CS (2002) Xenopus ribosomal RNA gene intergenic spacer elements conferring transcriptional enhancement and nucleolar dominance-like competition in oocytes. J Biol Chem 277:31577–31584
Coen ES, Dover GA (1982) Multiple Pol I initiation sequences in rDNA spacers of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 10:7017–7026
Colbourne JK, Hebert PDN (1996) The systematics of North American Daphnia (Crustacea: Anomopoda): a molecular phylogenetic approach. Philos Trans R Soc B 351:349–360
Colbourne JK, Crease TJ, Weider LJ, Hebert PDN, Dufresne F, Hobaek A (1998) Phylogenetics and evolution of a circumarctic species complex (Clardocera: Daphnia pulex). Biol J Linn Soc 65:347–365
Crease TJ (1993) Sequence of the intergenic spacer between the 28S and 18S rRNA encoding genes of the crustacean, Daphnia pulex. Gene 134:245–249
Crease TJ (1995) Ribosomal DNA evolution at the population level: nucleotide variation in intergenic spacer arrays of Daphnia pulex. Genetics 141:1327–1337
Da Rocha PS, Bertrand H (1995) Structure and comparative analysis of the rDNA intergenic spacer of Brassica rapa. Implications for the function and evolution of the Cruciferae spacer. Eur J Biochem 229:550–557
Dermitzakis ET, Clark AG (2002) Evolution of transcription factor binding sites in Mammalian gene regulatory regions: conservation and turnover. Mol Biol Evol 19:1114–1121
Dover GA, Tautz D (1986) Conservation and divergence in multigene families: alternatives to selection and drift. Philos Trans Roy Soc B 312:275–289
Dvorak J, Jue D, Lassner M (1987) Homogenization of tandemly repeated nucleotide sequences by distance-dependent nucleotide sequence conversion. Genetics 116:487–498
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinformatics 1:47–50
Glass SK, Moszczynska A, Crease TJ (2008) The effect of transposon Pokey insertions on sequence variation in the 28S rRNA gene of Daphnia pulex. Genome 51:988–1000
Gonzales IL, Sylvester JE (2001) Human rDNA: evolutionary patterns within the genes and tandem arrays derived from multiple chromosomes. Genomics 73:255–263
González-Barrera S, Garcia-Rubio M, Aguilera A (2002) Transcription and double-strand breaks induce similar mitotic recombination events in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 162:603–614
Grummt I (1999) Regulation of mammalian ribosomal gene transcription by RNA polymerase I. Prog Nucl Acid Res Mol Biol 62:109–154
Guryev V, Makarevitch I, Blinov A, Martin J (2001) Phylogeny of the genus Chironomus (Diptera) inferred from DNA sequences of mitochondrial cytochrome b and cytochrome oxidase I. Mol Phylogenet Evol 19:9–21
Haubold B, Wiehe T (2001) Statistics of divergence times. Mol Biol Evol 18:1157–1160
Hayworth DA (2000) Hierarchical domains in concerted evolution of ribosomal DNA intergenic spacers in Arabidopsis (Brassicaceae). PhD Thesis, Washington University
Hibner BL, Burke WD, Eickbush TH (1991) Sequence identity in an early chorion multigene family is the result of localized gene conversion. Genetics 128:595–606
Huang X, Miller W (1991) A time-efficient, linear-space local similarity algorithm. Adv Appl Math 12:337–357
Huang X, Hardison RC, Miller W (1990) A space-efficient algorithm for local similarities. Comput Appl Biosci 6:373–381
Jiang C, Liao D (1999) Striking bimodal methylation of the repeat unit of the tandem array encoding human U2 snRNA (the RNU2 locus). Genomics 62:508–518
Kao WY, Trewitt PM, Bergtrom G (1994) Intron-containing globin genes in the insect Chironomus thummi. J Mol Evol 38:241–249
Kobayashi T, Nomura M, Horiuchi T (2001) Identification of DNA cis elements essential for expansion of ribosomal DNA repeats in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 21:136–147
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinformatics 5:150–163
Kwon OY, Ishikawa H (1992) Unique structure in the intergenic and 5′ external transcribed spacer of the ribosomal RNA gene from the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Eur J Biochem 206:935–940
Lassner M, Dvorak J (1986) Preferential homogenization between adjacent and alternate subrepeats in wheat rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res 14:5499–5512
Liao D (1999) Concerted evolution: molecular mechanism and biological implications. Am J Hum Genet 64:24–30
Liao D, Weiner AM (1995) Concerted evolution of the tandemly repeated genes encoding primate U2 small nuclear RNA (the RNU2 locus) does not prevent rapid diversification of the (CT)n. (GA)n microsatellite embedded within the U2 repeat unit. Genomics 30:583–593
Lin YH, Keil RL (1991) Mutations affecting RNA polymerase I-stimulated exchange and rDNA recombination in yeast. Genetics 127:31–38
Luchetti A, Scanabissi F, Mantovani B (2006) Molecular characterization of ribosomal intergenic spacer in the tadpole shrimp Triops cancriformis (Crustacea, Branchipoda, Notostraca). Genome 49:888–893
Mancera E, Bourgon R, Brozzi A, Huber W, Steinmetz LM (2008) High-resolution mapping of meiotic crossovers and non-crossovers in yeast. Nature 454:479–485
Markos S, Baldwin BG (2002) Structure, molecular evolution, and phylogenetic utility of the 5(‘) region of the external transcribed spacer of 18S–26S rDNA in Lessingia (Compositae, Astereae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 23:214–228
Nei M, Rooney AP (2005) Concerted and birth-and-death evolution of multigene families. Ann Rev Genet 39:121–152
Omilian AR, Taylor DJ (2001) Rate acceleration and long-branch attraction in a conserved gene of cryptic daphniid (Crustacea) species. Mol Biol Evol 18:2201–2212
Ota T, Nei M (1994) Divergent evolution and evolution by the birth-and-death process in the immunoglobulin VH gene family. Mol Biol Evol 11:469–482
Polanco C, Gonzalez AI, de la Fuente A, Dover GA (1998) Multigene family of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster reveals contrasting patterns of homogenization for IGS and ITS spacer regions. A possible mechanism to resolve this paradox. Genetics 149:243–256
Reeder RH (1999) Regulation of RNA polymerase I transcription in yeast and vertebrates. Prog Nucl Acid Res Mol Biol 62:293–327
Reese MG (2001) Application of a time-delay neural network to promoter annotation in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Comput Chem 26:51–56
Ren X-J, Eisenhour L, Hong C-S, Lee Y, McKee BD (1997) Roles of rDNA spacer and transcription unit-sequences in X-Y meiotic chromosome pairing in Drosophila melanogaster males. Chromosoma 106:29–36
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet 16:276–277
Rose KM, Szopa J, Han FS, Cheng YC, Richter A, Scheer U (1988) Association of DNA topoisomerase I and RNA polymerase I: a possible role for topoisomerase I in ribosomal gene transcription. Chromosoma 96:411–416
Russo CA, Takezaki N, Nei M (1995) Molecular phylogeny and divergence times of drosophilid species. Mol Biol Evol 12:391–404
Takeuchi Y, Horiuchi T, Kobayashi T (2003) Transcription-dependent recombination and the role of fork collision in yeast rDNA. Genes Dev 17:1497–1506
Tautz D, Tautz C, Webb D, Dover GA (1987) Evolutionary divergence of promoters and spacers in the rDNA family of four drosophila species. J Mol Biol 195:525–542
Wang S, Zhao M, Li T (2003) Complete sequence of the 10.3 kb silkworm Attacus ricini rDNA repeat, determination of the transcriptional initiation site and functional analysis of the intergenic spacer. DNA Seq 14:95–101
Weider LJ, Elser J, Crease T, Mateos M, Cotner J, Markow T (2005) The functional significance of ribosomal(r)DNA variation: impacts on the evolutionary ecology of organisms. Ann Rev Eco Evol Syst 36:219–242
Wu CCN, Fallon AM (1998) Analysis of ribosomal DNA Intergenic spacer region from the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol Biol 7:19–29
Zhang H, Wang JC, Liu LF (1988) Involvement of DNA topoisomerase I in transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1060–1064
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada to TJC. CDA was supported by Ontario Graduate Scholarships. We thank A. Holliss for assistance with the DNA sequencing. D. Irwin, R. Danzmann, L. Weider, S. McTaggart, and two anonymous reviewers provided helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ambrose, C.D., Crease, T.J. Evolution of Repeated Sequences in the Ribosomal DNA Intergenic Spacer of 32 Arthropod Species. J Mol Evol 70, 247–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9324-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9324-4