Abstract
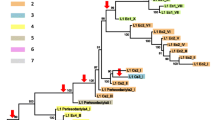
L1P_MA2 is a primate-specific subfamily of L1 retrotransposons. The consensus sequence of this element differs from the canonical L1 consensus by the presence of a 3800-bp region in 5′ (L1M1_5). Part of this region has been proposed to be involved in a dystrophin mutation affecting the correct splicing of the gene and causing an X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. In consideration of the potential involvement in splicing regulation of this element and also because of its atypical structure, we investigated its evolutionary history by analyzing the inter- and intraspecific divergence of L1P_MA2 sequences in various species of primates. The resulting phylogenetic trees show long terminal branches and short basal internodes, as expected for a rapid event of diversification that occurred in the past. The phylogenetic analysis and the intraspecific divergence estimates revealed a pattern of evolution for this element similar in all primates with the exception of lemurs, thus suggesting that the major wave of expansion of L1P_MA2 in primate genomes occurred after the divergence between Prosimiae and Anthropoidea. These results clearly indicate that a phylogenetic approach is more appropriate than methods based on sequence data from a single species, when investigating time and mode of evolution of retro-elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JM Deragon P Capy (2000) ArticleTitleImpact of transposable elements on the human genome. Ann Med 32 264–273 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXms1Ohurg%3D Occurrence Handle10852143
C Esnault J Maestre T Heidmann (2000) ArticleTitleHuman LINE retrotransposons generate processed pseudogenes. Nat Genet 24 363–367 Occurrence Handle10.1038/74184 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXisVCjsbw%3D Occurrence Handle10742098
A Ferlini F Muntoni (1998) ArticleTitleThe 5′ region of intron 11 of the dystrophin gene contains target sequences for mobile elements and three overlapping ORFs. Biochem Biophysical Res Commun 242 401–406 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.1997.7976 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkslGmsg%3D%3D
A Ferlini N Galie L Merlini C Sewry A Branzi F Muntoni (1998) ArticleTitleA novel Alu-like element rearranged in the dystrophin gene causes a splicing mutation in a family with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Hum Genet 63 436–446 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlslWrtbk%3D Occurrence Handle9683584
F Gualandi P Rimessi B Cardazzo L Toffolatti MG Dunckley E Calzolari T Patarnello F Muntoni A Ferlini (2003) ArticleTitleGenomic definition of a pure intronic dystrophin deletion responsible for an XLDC splicing mutation: in vitro mimicking and antisense modulation of the splicing abnormality. Gene 311 23–31 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1119(03)00527-4
H Hamdi H Nishio R Zielinski A Dugaiczyk (1999) ArticleTitleOrigin and phylogenetic distribution of Alu DNA repeats: Irreversible events in the evolution of primates. J Mol Biol 289 861–871 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmbi.1999.2797 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjslKhsbY%3D Occurrence Handle10369767
G Herbert S Easteal (1996) ArticleTitleRelative rates of nuclear DNA evolution in human and old world monkey lineages. Mol Biol Evol 13 1054–1057 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XltlSmsbk%3D Occurrence Handle8752013
InstitutionalAuthorNameInternational Human Genome Sequencing Consortium (2001) ArticleTitleInitial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409 860–921 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhsFCjtLc%3D Occurrence Handle11237011
J Jurka (2000) ArticleTitleRepbase update—A database and an electronic journal of repetitive elements. Trends Genet 16 418–420
S Kumar K Tamura IB Jakobsen M Nei (2001) ArticleTitleMEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17 1244–1245 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmtVCktQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11751241
JV Moran RJ DeBerardinis HH Kazazian (1999) ArticleTitleExon shuffling by L1 retrotransposition. Science 283 1530–1534 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.283.5407.1530 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhs1ymsb4%3D Occurrence Handle10066175
A Nekrutenko WH Li (2001) ArticleTitleTransposable elements are found in a large number of human protein-coding genes. Trends Genet 17 619–621 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-9525(01)02445-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnslemtL8%3D Occurrence Handle11672845
DM Sassaman BA Dombroski JV Moran ML Kimberland TP Naas RJ DeBerardinis et al. (1997) ArticleTitleMany human L1 elements are capable of retrotransposition. Nat Genet 16 37–43 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXivFKhsLY%3D Occurrence Handle9140393
AFA Smit G Toth AD Riggs J Jurka (1995) ArticleTitleAncestral, mammalian-wide subfamilies of LINE-1 repetitive sequences. J Mol Biol 246 401–417
K Tamura M Nei (1993) ArticleTitleEstimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10 512–526 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXks1CksL4%3D Occurrence Handle8336541
JD Thompson TJ Gibson F Plewniak F Jeanmougin DG Higgins (1997) ArticleTitleThe CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25 4876–4882 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntFyntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9396791
NV Tomilin (1999) ArticleTitleControl of genes by mammalian retroposons. Int Rev Cytol 186 1–48 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXps1Sg Occurrence Handle9770296
W Wu M Goodman MI Lomax LI Grossman (1997) ArticleTitleMolecular evolution of cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV: Evidence for positive selection in simian primates. J Mol Evol 44 477–491 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjsVylsbs%3D Occurrence Handle9115172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardazzo, B., Bargelloni, L., Toffolatti, L. et al. Tempo and Mode of Evolution of a Primate-Specific Retrotransposon Belonging to the LINE 1 Family . J Mol Evol 57 (Suppl 1), S268–S276 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-003-0036-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-003-0036-x