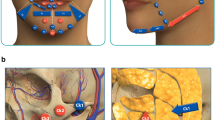
Abstract
Background
Dermal fillers provide an appealing option for facial rejuvenation, but inappropriate filler selection and injection techniques can cause complications requiring surgical correction. This study examined the intraoperative superficial muscular aponeurotic system (SMAS) and tissue abnormalities encountered during facelift after permanent filler removal.
Methods
This preliminary prospective case series describes reconstructive techniques used in 10 women with SMAS defects following facelift with permanent filler extraction. Defects were repaired using temporalis fascia, and mastoid fascia, or combined platysma-SMAS grafts. Pre- and postoperative photographs were evaluated by two independent surgeons for midface volume analysis.
Results
Preoperative complaints included facial contour asymmetry (100%), nodules/irregularities (70%), and disfiguring edema (35%). The mean follow-up was 6 months postoperatively. No lipofilling was required in this period. Patient satisfaction at 6 months was: extremely satisfied (70%), very satisfied (20%), satisfied (10%). Facial symmetry was rated as no asymmetry (80%), moderate asymmetry (10%), and mild asymmetry (10%). Standardized photo review found that 80% of surgeons were satisfied with pre- vs. 6-month postoperative results.
Conclusions
This study shows promising aesthetic outcomes and high patient satisfaction at 6 months after simultaneous facelift and permanent filler removal with volume defect correction using various local tissue grafts. Larger studies with longer follow-ups are warranted to further assess these reconstructive techniques for significant SMAS defects resulting from improper permanent filler placement.
Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen K, Doblhammer G, Rau R, Vaupel JW (2009) Aging populations: the challenges ahead. Lancet 374(9696):1196–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61460-4
Tobin DJ (2017) Introduction to skin aging. J Tissue Viability 26(1):37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtv.2016.03.002
Akinbiyi T, Othman S, Familusi O, Calvert C, Card EB, Percec I (2020) Better Results in facial rejuvenation with Fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 8(10):e2763. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002763
Broder KW, Cohen SR (2006) An overview of permanent and semipermanent fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(3 Suppl):7S–14S. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000234900.26676.0b
Zielke H, Wölber L, Wiest L, Rzany B (2008) Risk profiles of different injectable fillers: results from the Injectable Filler Safety Study (IFS Study). Dermatol Surg 34(3):326–335 discussion 335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2007.34066.x
Smith KC (2008) Reversible vs. nonreversible fillers in facial aesthetics: concerns and considerations. Dermatol Online J 15(8):3
Chacon AH (2015) Fillers in dermatology: from past to present. Cutis 96(5):E17–E19
Ballin AC, Brandt FS, Cazzaniga A (2015) Dermal fillers: an update. Am J Clin Dermatol 16(4):271–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-015-0135-7
Fallacara A, Manfredini S, Durini E, Vertuani S (2017) Hyaluronic Acid Fillers in Soft tissue regeneration. Facial Plast Surg 33(1):87–96. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1597685
Liu MH, Beynet DP, Gharavi NM (2019) Overview of Deep Dermal Fillers. Facial Plast Surg 35(3):224–229. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1688843
Rohrich RJ, Bartlett EL, Dayan E (2019) Practical Approach and Safety of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7(6):e2172. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002172
Dayan SH, Bassichis BA (2008) Facial dermal fillers: selection of appropriate products and techniques. Aesthet Surg J 28(3):335–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2008.03.004
Rossi AM, Wilson B, Hibler BP, Drake LA (2019) Nonphysician practice of Cosmetic Dermatology: a patient and physician perspective of outcomes and adverse events. Dermatol Surg 45(4):588–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/DSS.0000000000001829
Goldberg DJ (2006) Legal ramifications of off-label filler use. Clin Plast Surg 33(4):597–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2006.08.003
Lemperle G, Rullan PP, Gauthier-Hazan N (2006) Avoiding and treating dermal filler complications. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(3 Suppl):92S–107S. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000234672.69287.77
Goldberg RA (2005) The three periorbital hollows: a paradigm for periorbital rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg 116(6):1796–1804. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000185623.36795.38
Rohrich RJ, Sinno S, Vaca EE (2019) Getting better results in Facelifting. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7(6):e2270. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002270
Wolfram D, Tzankov A, Piza-Katzer H (2006) Surgery for foreign body reactions due to injectable fillers. Dermatology 213(4):300–304. https://doi.org/10.1159/000096193
de Melo Carpaneda E, Carpaneda CA (2012) Adverse results with PMMA fillers. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36(4):955–963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9871-8
Limongi RM, Tao J, Borba A et al (2016) Complications and management of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) injections to the Midface. Aesthet Surg J 36(2):132–135. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjv195
Alaslawi AAF, Zeina AM, Zahra T (2022) Facelift Surgery after Permanent Filler: outcomes after removal of Permanent Filler under local anesthesia. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 10(8):e4459. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000004459
Wang W, Xie Y, Huang RL et al (2017) Facial contouring by targeted restoration of facial Fat Compartment volume: the Midface. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(3):563–572. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000003160
Wang X, Chen X, Zhao Q et al (2023) Patient-specific implants for correction of Midfacial Aging. J Craniofac Surg 34(6):1784–1788. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000009269
Zhang JY, Liu K, Liu RX, Xu BH (2023) Safety and Efficacy of Midface Augmentation using Bio-oss Bone Powder and Bio-gide Collagen Membrane in asians. J Clin Med 12(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030959
Aludden HC, Mordenfeld A, Hallman M, Dahlin C, Jensen T (2017) Lateral ridge augmentation with Bio-oss alone or Bio-oss mixed with particulate autogenous bone graft: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46(8):1030–1038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2017.03.008
Xie Y, Huang RL, Wang W, Cheng C, Li Q (2020) Fat Grafting for facial contouring (temporal region and Midface). Clin Plast Surg 47(1):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2019.08.008
Rohrich RJ, Pessa JE (2007) The fat compartments of the face: anatomy and clinical implications for cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(7):2219–2227. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000265403.66886.54
Sezgin B, Tatar S, Boge M, Ozmen S, Yavuzer R (2019) The excision of the Buccal Fat Pad for Cheek refinement: volumetric considerations. Aesthet Surg J 39(6):585–592. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjy188
Delaney S, Kridel RWH (2019) Enhancing Facelift with Simultaneous Submalar Implant Augmentation. Aesthet Surg J 39(4):351–362. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjy135
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The research followed the Helsinki principles, and the study was approved by the Mansoura University Institutional Review Board under NO. R.23.05.2178.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the photos.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zahra, T., Abdelhalim, M., Zayed, A. et al. Restoring facial superfacial muscular aponeurotic system defects after permanent fillers removal using fascial and SMAS grafts: a preliminary study. Eur J Plast Surg 47, 47 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-024-02193-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-024-02193-2