Abstract
Background
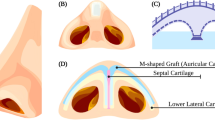
Secondary rhinoplasty is a much more complex operation than primary rhinoplasty, because previously operated and fibrotic tissue is involved. The predictability of results, both aesthetic and functional, is thus inherently lower, demanding greater attention and safety. Even more intricate are those instances in which cartilaginous septum is absent, either in part or almost entirely. This comparative analysis targeted long-term outcomes of secondary rhinoseptoplasties using either auricular or rib cartilage as grafts.
Methods
All patients selected for study met the following criteria: (a) required secondary rhinoplasty for functional and/or cosmetic problems, (b) voids of septal cartilage, (c) follow-up of ~ 2 years, (d) availability of standard pre- and postoperative photos, (e) fair command of the Italian language, and (f) signed participatory consent. Each subject was randomly assigned to group 1 (costal cartilage graft for secondary rhinoplasty) or group 2 (auricular cartilage graft for secondary rhinoplasty). In follow-up, patients completed the Italian version of the FACE-Q rhinoplasty module. Anthropometric measurements were also acquired in AutoCAD for MAC. We determined angles of deviation pre- and postoperatively for comparison and analysed patient satisfaction levels by group using the chi-squared test for unpaired data. Two plastic surgeons reviewed all postoperative photographs of study subjects, rating them on a scale of 1–5.
Results
A total of 135 patients undergoing primary rhinoplasties between January 2008 and September 2019 in our Department of Plastic Surgery and meeting all inclusion criteria qualified for study. Mean patient age was 48.5 years, and mean follow-up time was 3 years. Pre- and postoperative FACE-Q values in group 1 differed significantly (p < 0.05). Anthropometric measurements revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) in pre- and postoperative angles of septal deviation determined for group 1 vs group 2. In long-term follow-up, group 1 maintained an angle close to 180° (p < 0.015), and results in group 1 (vs group 2) remained stable (p < 0.05). Members of group 2 underwent more secondary procedures by comparison (p < 0.05). Ultimately, the two reviewers determined that outcomes in group 1 (vs group 2) proved more satisfactory (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
This effort is the first to compare grafting of auricular and costal cartilage in secondary rhinoplasty procedures. Implants from the 5th rib are preferential to ensure satisfactory long-term outcomes and durable, natural aesthetics in patients lacking septal cartilage.
Level of evidence: Level V, Therapeutic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Persichetti P, Cogliandro A, Barone M (2013) Nasal aesthetics: a cross-cultural analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(4):664e–665e
Broer PN, Buonocore S, Morillas A, Liu J, Tanna N, Walker M, Ng R, Persing JA (2012) Nasal aesthetics: a cross-cultural analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 130(6):843e–850e
Barone M, Cogliandro A, Salzillo R, Colapietra A, Alessandri Bonetti M, Morelli Coppola M, List E, Ciarrocchi S, Tenna S, Persichetti P (2019) Role of spreader flaps in rhinoplasty: analysis of patients undergoing correction for severe septal deviation with long-term follow-up. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43(4):1006–1013
Gode S, Benzer M, Uslu M, Kaya I, Midilli R, Karci B (2018) Outcome of in situ septoplasty and extracorporeal subtotal septal reconstruction in crooked noses: a randomized self-controlled study. Aesthetic Plast Surg 42(1):234–243
Barone M, Cogliandro A, Salzillo R, List E, Panasiti V, Tenna S, Persichetti P (2019) Definition of “Gender Angle” in Caucasian population. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43(4):1014–1020
Fedok FG (2016) Costal cartilage grafts in rhinoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 43(1):201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2015.08.002
Cottle MH, Loring RM, Fischer GG, Gaynon IE (1958) The maxilla-premaxilla approach to extensive nasal septum surgery. AMA Arch Otolaryngol 68:301–313
Barone M, Cogliandro A, Di Stefano N, Aronica R, Tambone V, Persichetti P (2017) Linguistic validation of the “FACE-Q Rhinoplasty Module” in Italian. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(3):1771–1772
Çakır B, Öreroğlu AR, Daniel RK (2016) Surface aesthetics and analysis. Clin Plast Surg 43(1):1–15
Klassen AF, Cano SJ, East CA, Baker SB, Badia L, Schwitzer JA, Pusic AL (2016) Development and psychometric evaluation of the FACE-Q scales for patients undergoing rhinoplasty. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 18(1):27–35
Buckwalter JA, Mankin HJ (1998) Articular cartilage: tissue design and chondrocyte-matrix interactions. Instr Course Lect 47:477–486 (PMID: 9571449)
Buyuklu F, Hizal E, Yilmaz Z, Sahin FI, Cakmak O (2011) Viability of crushed human auricular and costal cartilage chondrocytes in cell culture. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 39(3):221–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2010.03.013
Pascali M, Gentile P, Di Pasquali C, Bocchini I, Cervelli V (2016) The auricular cartilage in 197 secondary and tertiary rhinoplasties. J Craniofac Surg 27(2):339–344. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000002380
Gentile P, Cervelli V (2009) Nasal dorsum reconstruction with 11th rib cartilage and auricular cartilage grafts. Ann Plast Surg 62(1):63–66. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31817433dc
Lee M, Callahan S, Cochran CS (2011) Auricular cartilage: harvest technique and versatility in rhinoplasty. Am J Otolaryngol. 32(6):547–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2010.11.008
Cochran CS, Gunter JP (2010) Secondary rhinoplasty and the use of autogenous rib cartilage grafts. Clin Plast Surg 37(2):371–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2009.11.001
Marin VP, Landecker A, Gunter JP (2008) Harvesting rib cartilage grafts for secondary rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(4):1442–1448. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000302467.24489.42
Jang YJ, Kim DY (2016) Treatment strategy for revision rhinoplasty in Asians. Facial Plast Surg 32(6):615–619. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1594254
Calvert JW, Patel AC, Daniel RK (2014) Reconstructive rhinoplasty: operative revision of patients with previous autologous costal cartilage grafts. Plast Reconstr Surg 133(5):1087–1096. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000000119
Miranda N, Larocca CG, Aponte C (2013) Rhinoplasty using autologous costal cartilage. Facial Plast Surg 29(3):184–192. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1346999
Gunter JP, Cochran CS, Marin VP (2008) Dorsal augmentation with autogenous rib cartilage. Semin Plast Surg 22(2):74–89. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1063567
Liang X, Wang K, Malay S, Chung KC, Ma J (2018) A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparison between autologous costal cartilage and alloplastic materials in rhinoplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 71(8):1164–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2018.03.017
Mohan R, Shanmuga Krishnan RR, Rohrich RJ (2019) Role of fresh frozen cartilage in revision rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 144(3):614–622. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005996
Rohrich RJ, Abraham J, Alleyne B, Bellamy J, Mohan R (2022) Fresh frozen rib cartilage grafts in revision rhinoplasty: a 9-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000009203
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Due to the retrospective nature of this study, approval from the ethics committee was not required.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for sharing their data and publication of their images.
Competing interests
Mauro Barone, Annalisa Cogliandro, and Paolo Persichetti declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barone, M., Cogliandro, A. & Persichetti, P. Use of auricular versus costal cartilaginous grafts for secondary rhinoplasty procedures: comparison of long-term outcomes. Eur J Plast Surg 46, 343–350 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-022-02028-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-022-02028-y