Abstract
Background
Distal tip necrosis of random pattern skin flaps is the most occurring complication in skin flap surgery. Delay phenomenon augments flap vascularity and increases survival of skin flaps. In this study, hyaluronic acid dermal filler was used in the rat dorsal skin via subcutaneous injection to reveal its role in the flap viability and the delay phenomenon.
Methods
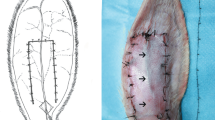
Eighteen rats were randomized in 3 groups. Group 1 rats were the control group. Group 2 rats underwent surgical delay procedure. Group 3 was pretreated with 1 mL of hyaluronic acid dermal filler injection. Seven days after, a caudally based dorsal skin flap was elevated. Flap necrosis area, intensity of the newly formed vessels, subdermal vascular architecture, and inflammation severity in the flaps were evaluated.
Results
Flap necrosis areas were found statistically significant among the groups. The mean number of subdermal capillaries increased significantly in group 3. The mean values of vessel diametres were statistically significant among the groups. Inflammation scores of groups 2 and 3 were low or moderate levels.
Conclusions
HA injection increases the survival of rat dorsal flaps; however, it is not superior or equivalent to surgical delay at least with this volume, concentration, and delay time.
Level of evidence: Not ratable.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lineaweaver WC, Lei MP, Mustain W, Oswald TM, Cui D, Zhang F (2004) Vascular endothelium growth factor, surgical delay, and skin flap survival. Ann Surg 239(6):866–873
Menevşe GT, TeomanTellioglu A, Altuntas N, Cömert A, Tekdemir I (2014) Polidocanol injection for chemical delay and its effect on the survival of rat dorsal skin flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 67(6):851–856
Doğan F, Özyazgan İ (2015) Flap preconditioning by electrical stimulation as an alternative to surgical delay: experimental study. Ann Plast Surg 75(5):560–564
Pang CY, Forrest CR, Morris SF (1989) Pharmacological augmentation of skin flap viability: a hypothesis to mimic the surgical delay phenomenon or a wishful thought. Ann Plast Surg 22:293–306
Hamilton K, Wolfswinkel EM, Weathers WM, Xue AS, Hatef DA, Izaddoost S, Hollier LH Jr (2014) The delay phenomenon: a compilation of knowledge across specialties. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr 7(2):112–118
Ruppert SM, Hawn TR, Arrigoni A, Wight TN, Bollyky PL (2014) Tissue integrity signals communicated by high-molecular weight hyaluronan and the resolution of inflammation. Immunol Res 58(2–3):186–192
Kablik J, Monheit GD, Yu L, Chang G, Gershkovich J (2009) Comparative physical properties of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. Dermatol Surg 35(Suppl 1):302–312
Fallacara A, Baldini E, Manfredini S, Vertuani S (2018) Hyaluronic acid in the third millennium. Polymers (Basel) 10(7):701
Ponomareva T, Sliadovskii D, Timchenko M, Molchanov M, Timchenko A, Sogorin E (2020) The effect of hepatopancreas homogenate of the Red king crab on HA-based filler. PeerJ 8:e8579
Shalom A, Hadad E, Friedman T, Kremer E, Westreich M (2008) Effect of hyaluronic acid on random-pattern flaps in rats. Dermatol Surg 34(9):1212–1215
Inbal A, Lemelman BT, Millet E, Greensmith A (2017) Tissue expansion using hyaluronic acid filler for single-stage ear reconstruction: a novel concept for difficult areas. Aesthet Surg J 37(10):1085–1097
Perng CK, Wang YJ, Tsi CH, Ma H (2011) In vivo angiogenesis effect of porous collagen scaffold with hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides. J Surg Res 168(1):9–15
Khouri RK, Angel MF (1986) Edstrom LE Standardizing the dorsal rat flap. Plast Surg 37:590–591
Funding
This work was supported by Mersin University Scientific Research and Project Unit with project number 2020–1-TP3-4037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Mersin University (date:10/02/2020, no: 01–02). All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. This study was performed in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
Nazım Gümüş, Erkan Pinegöz, and Ferah Tuncel declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gümüş, N., Pinegöz, E. & Tuncel, F. Hyaluronic acid dermal filler injection increases the survival of rat dorsal skin flaps. Eur J Plast Surg 46, 181–188 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-022-02004-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-022-02004-6