Abstract
Background
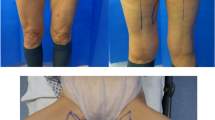
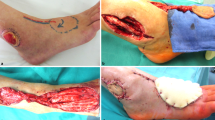
The extensor digitorum brevis muscle (EDB) has been transferred as a pedicled or free flap for various indications, including those requiring functional muscle transfers. It can be used as a muscle flap or as a compound flap (either a composite or a chimeric flap) including skin, fat and/or nerves. This PRISMA-compliant systematic review reports on the use of EDB flaps to provide an evidence-based report of its indications, complications and outcomes and thereby clarify its utility to reconstructive surgeons.
Methods
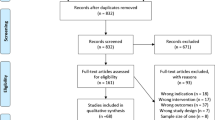
PubMed, Embase, and Medline databases were searched for English-language clinical studies (1990 to 2020) of all evidence levels. Cadaveric and studies relating to orthopaedic foot and ankle procedures were excluded. The main outcomes were flap survival, reoperation, revisions and functional outcomes depending on the aim of the reconstruction.
Results
33 papers were eligible (248 flaps). Procedures were classified according to the recipient site of EDB flaps: face (13%), hand (9%) and lower limb (78%). EDB was used as a free flap in 22.6% of cases. EDB flaps were used as a pure muscle flap, or as a compound flap (composite or chimera). In lower limb reconstruction cases, flap blood flow was either anterograde (n = 150) or retrograde (n = 43). EDB flap dimensions ranged 3–4.5 × 6–6.7 cm. There was a 5.2% total and 4% partial flap failure, all limited to anterograde lower limb pedicled applications. Donor site complications included delayed wound healing (7.3%), wound dehiscence (5.4%), reduced ankle mobility (3.9%), hypertrophic scars (3.4%) and paraesthesia over the dorsum of the foot or first webspace (3.4%), amongst others.
Conclusions
EDB flaps have been successfully used in facial, hand and lower limb reconstruction both as soft tissue cover and as a functional transfer. This versatile flap has reasonable low donor site morbidity, reliable anatomy with options for proximal pedicle lengthening and can be used as a pedicled or a free flap.
Level of Evidence: Not ratable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pai CH, Lin GT, Lin SY, Lin SD, Lai CS (2000) Extensor digitorum brevis rotational muscle flap for lower leg and ankle coverage. J Trauma - Inj Infect Crit Care 49(6):1012–1016. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-200012000-00006
Bakhach J, Demiri E, Chahidi N, Baudet J (1998) Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle Flap: New Refinements. Plast Reconstr Surg 102(1):103–110. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199807000-00016
del Pinal F, Herrero F (2000) Extensor Digitorum Brevis Free Flap: Anatomic Study and Further Clinical Applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 105(4):1347–1356. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200004040-00013
Alagöz MŞ, Alagöz AN, Comert A (2011) Neuroanatomy of extensor digitorum brevis muscle for reanimation of facial paralysis. J Craniofac Surg 22(6):2308–2311. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e318232a806
Sirasanagandla SR, Swamy RS, Nayak SB, Somayaji NS, Rao MKG, Bhat KMR (2013) Analysis of the morphometry and variations in the extensor digitorum brevis muscle: an anatomic guide for muscle flap and tendon transfer surgical dissection. Anat Cell Biol 46(3):198. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2013.46.3.198
Baltensperger MM, Ganzoni N, Jirecek V, Meyer VE (1998) The extensor digitorum brevis island flap: Possible applications based on anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 101(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199801000-00018
Mathes SJ, Nahai F (1981) Classification of the vascular anatomy of muscles: Experimental and clinical correlation. Plast Reconstr Surg 67(2):177–187. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198167020-00007
Giordano PA, Argenson C, Pequignot JP, Giordano PA (1989) Extensor digitorum brevis as an island flap in the reconstruction of soft-tissue defects in the lower limb. Plast Reconstr Surg 83(1):100–109. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198901000-00019
Landi A, Soragni O, Monteleone M (1985) The extensor digitorum brevis muscle Island flap for soft-tissue loss around the ankle. Plast Reconstr Surg 75(6):892–897. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198506000-00024
Gahhos FN, Jaquith M, Hidalgo R (1989) The extended digitorum brevis muscle flap. Ann Plast Surg 23(3):255–262. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-198909000-00011
Man D, Acland R (1980) The Microarterial Anatomy of the Dorsalis Pedis Flap and Its Clinical Applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 65(4):419–423
Kudoh H, Sakai T, Horiguchi M (1999) The consistent presence of the human accessory deep peroneal nerve. J Anat 194(1):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-7580.1999.19410101.x
Van Dijk JG, Van Der Hoeven BJ (1998) Compound muscle action potential cartography of an accessory peroneal nerve. Muscle Nerve 21(10):1331–1333. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199810)21:10%3c1331::AID-MUS15%3e3.0.CO;2-4
Hasegawa O, Wada N (2001) Innervation pattern to the extensor digitorum brevis by deep peroneal nerve and accessory deep peroneal nerve. No To Shinkei 53(5):453–456
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche P C, Ioannidis JPA, et al. (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
National Institute for Health (2014) Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-pro/guidelines/in-develop/cardiovascular-riskreduction/tools/cohort. Accessed on 22 Aug 2022
Terzis JK, Karypidis D (2010) Blink Restoration in Adult Facial Paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 126(1):126–139. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181dbbf34
Huang W, Fang B, Fang X, Wang C (2009) Extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis transplantation for treatment of long-standing facial paralysis. Chinese J Traumatol English Ed 12:3–9. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-1275.2009.01.001
Tulley PN, Webb A, Chana JS et al (2000) Paralysis of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve: treatment options. Br J Plast Surg 53(5):378–385. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjps.2000.3318
Akdag O, Evin SG, Karamese M, Tosun Z (2017) Simultaneous Reconstruction of Both Facial Paralysis and Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis With a Composite Flap From Dorsum of Foot. J Craniofac Surg 28(7):e694–e697. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000003866
Oh SJ, Chung CH (2011) Upper-lip reconstruction using a free dorsalis pedis flap incorporating the extensor hallucis and digitorum brevis muscles. J Craniofac Surg 22(3):998–999. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3182101524
Tian H, Song D, Jin H et al (2020) Repair of soft tissue and extensor tendon defects on the dorsum of the hand by transfer of dorsal foot flap and extensor digitorum brevis tendon in a 3-year-old child: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 99(34):e21837. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000021837
Wang T, Regmi S, Liu H, Pan J, Hou R (2017) Free lateral tarsal artery perforator flap with functioning extensor digitorum brevis muscle for thenar reconstruction: a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137(2):273–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-016-2615-5
Pappalardo M, Laurence VG, Te LY (2018) Chimeric Free Vascularized Metatarsophalangeal Joint With Toe Fillet Flap: A Technique for Reconstruction of the Posttraumatic Metacarpophalangeal Joint With Concomitant Soft Tissue Defect. J Hand Surg Am 43(2):193.e1-193.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2017.11.011
Cong HB, Chang SM, Qiao YP, Wang CL, Sui HM, Cong L (2007) One-stage reconstruction of complicated thumb injury with combination of microsurgical transplantations. Microsurgery 27(3):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.20328
Lin C-H, Tang P-L, Lin C-H (2009) Second Toe Extensor Digitorum Brevis Provides a Simultaneous Abductorplasty to Free Vascularized Metatarsophalangeal Joint Transfer for Posttraumatic Thumb Composite Metacarpophalangeal Joint Defect. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care 66(5):1374–1378. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31817e5c90
Koul A, Patil R, Philip V (2008) Coverage of defects over toes with distally based local flaps: A report of four cases. Indian J Plast Surg 41(1):62–66. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-0358.41114
Babu V, Chittaranjan S, Abraham G, Korula RJ (1994) Single-stage reconstruction of soft-tissue defects including the Achilles tendon using the dorsalis pedis arterialized flap along with the extensor digitorum brevis as bridge graft. Plast Reconstr Surg 93(5):1090–1094. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199404001-00033
Gibstein LA, Abramson DL, Sampson CE, Pribaz JJ (1996) Musculofascial Flaps Based on the Dorsalis Pedis Vascular Pedicle for Coverage of the Foot and Ankle. Ann Plast Surg 37(2):152–157. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199608000-00006
Touil LL, Lindsay KJ, Anderson K, Bell D (2015) Utilising the MTP plantar fat: A novel approach in Syme’s amputation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 68(1):126–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2014.08.060
Babu NV, Chittaranjan S, Abraham G, Bhattacharjee S, Korula RJ (1994) Vascularized extensor digitorum brevis to reconstruct the achilles tendon: A case report. Acta Orthop 65(1):101–102. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453679408993730
Chattar-Cora D, Pederson WC (2006) Experience with the extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap for foot and ankle reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 57(3):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sap.0000221616.05768.88
Nettelblad H, Lidman D (1997) Clinical experiences of the pedicled extensor digitorum brevis flap. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 31(4):339–343. https://doi.org/10.3109/02844319709008981
Koul AR, Patil RK, Philip V (2009) Extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap: modified approach preserving extensor retinaculum. J Trauma - Inj Infect Crit Care 66(3):835–839. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318165c835
Torres LR, Paganelli PM, Dos Santos RPN, Targa WHDC, Fernandes TD, Mattar JR (2014) Extensor digitorum brevis flap on the treatment of lower limb injuries. Acta Ortop Bras 22(2):86–89. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-78522014220200862
Abdelrahman I, Elmasry M, Steinvall I, Olofsson P, Nettelblad H, Zdolsek J (2018) Versatility of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap in lower limb reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open 6(12):e2071. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002071
Houdek MT, Wagner ER, Pensy RA, Eglseder WA (2016) Extensor Digitorum Brevis Flap for the Coverage of Ankle and Dorsal Foot Wounds. J Orthop Trauma 30(12):e404–e408. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000650
Kodama A, Kurose Y, Mizuseki T, Tanimoto K, Adachi N (2019) Plantar Partial Pressure Analysis in a Patient with Reverse Extensor Digitorum Brevis Flap for the Treatment of Hallux Injury. J Orthop Case Rep 9(3):75–78. https://doi.org/10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.1430
Hirase Y, Kojima T, Fukumoto K, Misu H, Yamaguchi T (2003) Indication and practice of reverse flow extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap transfer. Ann Plast Surg 51(3):273–277. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.SAP.0000068081.06981.F2
Thompson N (1971) Autogenous free grafts of skeletal muscle: A preliminary experimental and clinical study. Plast Reconstr Surg 48(1):11–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197107000-00004
Thompson N, Gustavson EH (1976) The use of neuromuscular free autografts with microneural anastomosis to restore elevation to the paralysed angle of the mouth in cases of unilateral facial paralysis - With an analysis of late results of muscle grafts in the treatment of 103 cases of facial hemiparesis. Chir Plast 3(3):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00274290
Ghali S, MacQuillan A, Grobbelaar AO (2011) Reanimation of the middle and lower face in facial paralysis: Review of the literature and personal approach. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 64(4):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BJPS.2010.04.008
Buncke HJ (1976) Toe Digital Transfer. Clin Plast Surg 3(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0094-1298(20)30246-7
Vela-Romera A, Carriel V, Martín-Piedra MA et al (2019) Characterization of the human ridged and non-ridged skin: a comprehensive histological, histochemical and immunohistochemical analysis. Histochem Cell Biol 151(1):57–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-018-1701-x
Abdelrahman I, Moghazy A, Abbas A, Elmasry M, Adly O, Elbadawy M, Steinvall I, Sjoberg F (2016) A prospective randomized cost billing comparison of local fasciocutaneous perforator versus free Gracilis flap reconstruction for lower limb in a developing economy. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 69(8):1121–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2016.04.013
Reddy V, Stevenson TR (2008) MOC-PS(SM) CME article: lower extremity reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(4 Suppl):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000305928.98611.87
Rajacic N, Darweesh M, Jayakrishnan K, Gang RK, Jojic S (1996) The distally based superficial sural flap for reconstruction of the lower leg and foot. Br J Plast Surg 49(6):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-1226(96)90007-7
Hasegawa M, Torii S, Katoh H, Esaki S (1994) The distally based superficial sural artery flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 93(5):1012–1020. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199404001-00016
Jeng SF, Wei FC (1997) Distally based sural island flap for foot and ankle reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 99(3):744–750. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199703000-00022
Mandrekas AD, Zambacos GJ, Grivas TM (1995) The extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap for the reconstruction of soft tissue defects in the lower limb. Eur J Plast Surg 18(2–3):82–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168890
Noblet TM, Jackson PC, Foster P, Taylor DM, Harwood PJ, Wiper JD (2018) Managing soft tissues in severe lower limb trauma in an ageing population. Injury 49(6):1197–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2018.03.010
De Silva D, Hsieh F, Gillies R (2016) Unusual Vascular Supply to Extensor Digitorum Brevis. Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open 4(4):e673. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000000608
Kurata S, Hashimoto H, Terashi H, Honda T, Takayasu S (1992) Reconstruction of the distal foot dorsum with a distally based extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap. Ann Plast Surg 29(1):76–79. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199207000-00015
Bekara F, Herlin C, Mojallal A, Sinna R, Ayestaray B, Letois F, Pierre Chavoin J, Garrido I, Grolleau JL, Chaput B (2016) A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Perforator-Pedicled Propeller Flaps in Lower Extremity Defects: Identification of Risk Factors for Complications. Plast Reconstr Surg 137(1):314–331. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001891
Liu L, Zou L, Li Z, Zhang Q, Cao X, Cai J (2014) The extended distally based sural neurocutaneous flap for foot and ankle reconstruction: a retrospective review of 10 years of experience. Ann Plast Surg 72(6):689–694. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31826c4284
Ebrahiem AA, Manas RK, Vinagre G (2017) Distally Based Sural Artery Peroneus Flap (DBSPF) for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 5(4):1276-e1276
Ghareeb FM (2002) Using the Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle to Improve Donor-Site Morbidity of the Dorsalis Pedis Flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 109(6):2031–2036. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200205000-00038
Kim JK, Choi SJ, Chung MS, Baek GH (2009) Extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap using parallel incision. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 62(10):1317–1320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2008.03.054
Kiehn MW, Gutowski KA (2004) A recurrent foot ganglion managed with extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap coverage. J Foot Ankle Surg 43(6):423–425. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2004.09.009
Acknowledgements
Mr John Lossaso, deputy librarian, for assistance in locating full texts of potentially eligible studies.
Funding
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organisation or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Francisco Serra E. Moura, Christopher Lalemi and Nigel Tapia Mabvuure declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
As a non-interventional study, ethical approval was not required.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Serra E Moura, F., Lalemi, C. & Mabvuure, N.T. Systematic review of the reconstructive uses of the extensor digitorum brevis flap. Eur J Plast Surg 46, 163–180 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-022-01993-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-022-01993-8