Abstract
Background
Since the description of the submental island flap as an alternative flap for reconstructing the lower third of the face, clinical and experimental studies have shown a great versatility in its design. However, just a few advancements in donor site morbidity have been reported if compared to other workhorse flaps. In this presented study, we aimed to analyze what factor influences higher morbidity and poor cosmesis at the donor site.
Methods
A literature search was conducted on EMBASE, Google Scholar, MEDLINE, and Cochrane Library databases. Search terms included submental island flap and submental flap. Identified articles were screened and checked for eligibility by two authors independently.
Results
The average flap size was 11 × 5 cm, and malignancy was the primary etiology. Overall complications were present in 17.5% of patients. However, donor site complication was present in only 3.9% of patients. Temporary paresis of the mandibular branch of the facial nerve was the most common donor site complication (1.7%). Dehiscence and infection were presented in only 1.0% and 0.2%, respectively. From a cosmetic point of view, the most common complication was the presence of dog-ear deformity at the donor site.
Conclusions
This literature review found several limitations being the most important one the lack of comparisons between possible risk factors and donor site complications. Therefore, more clinical studies are needed to find any relationships between them. However, following the different specialties’ recommendations, we should expect more favorable outcomes. Although considered a low morbidity flap, adequate patient selection, planning, and postoperative care can contribute to reduce morbidity even more.
Level of evidence: Not ratable




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin D, Pascal JF, Baudet J et al (1993) The submental island flap: a new donor site anatomy and clinical applications as a free or pedicled flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 92(5):867–873
Shi CL, Wang XC (2012) Reconstruction of lower face defect or deformity with submental artery perforator flaps. Ann Plast Surg 69(1):41–44
Cheng MH, Huang JJ, Nguyen DH et al (2012) A novel approach to the treatment of lower extremity lymphedema by transferring a vascularized submental lymph node flap to the ankle. Gynecol Oncol 126(1):93–98
Schaverien MV, Badash I, Patel KM, Selber JC, Cheng MH (2018) Vascularized Lymph node transfer for lymphedema. Semin Plast Surg 32(1):28–35
Ho OA, Lin CY, Pappalardo M, Cheng MH (2018) Comparisons of submental and groin vascularized lymph node flaps transfer for breast cancer-related lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open 6(12):1–9
Aljaaly HA, Fries CA, Cheng MH (2019) Dorsal wrist placement for vascularized submental lymph node transfer significantly improves breast cancer-related lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open 7(2):10–14
Patel UA (2020) The submental flap for head and neck reconstruction: comparison of outcomes to the radial forearm free flap. Laryngoscope 130(S2):S1–S10
Sittitrai P, Reunmakkaew D, Srivanitchapoom C (2019) Submental island flap versus radial forearm free flap for oral tongue reconstruction: a comparison of complications and functional outcomes. J Laryngol Otol 133(5):413–418
Jørgensen MG, Tabatabaeifar S, Toyserkani NM, Sørensen JA (2019) Submental island flap versus free flap reconstruction for complex head and neck defects. Otolaryngol - Head Neck Surg (United States) 161(6):946–953
Pistre V, Pelissier P, Martin D, Lim A, Baudet J (2001) Ten years of experience with the submental flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 108(6):1576–1581
Sterne GD, Januszkiewicz JS, Hall PN, Bardsley AF (1996) The submental island flap. Br J Plast Surg 49(2):85–89
Vural E, Suen JY (2009) The submental island flap in head and neck reconstruction. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 17(4):263–266
Akan IM, Özdemir R, Uysal AC, Sungur N, Şensöz O (2001) The submental artery flap. Eur J Plast Surg 24(3):134–139
Sioson MS, Martindale R, Abayadeera A et al (2018) Clinical Nutrition ESPEN Nutrition therapy for critically ill patients across the Asia e Paci fi c and Middle East regions : a consensus statement. Clin Nutr ESPEN 24:156–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2017.11.008
Sebastian P, Thomas S, Varghese BT, Iype EM, Balagopal PG, Mathew PC (2008) The submental island flap for reconstruction ff intraoral defects in oral cancer patients. Oral Oncol 44(11):1014–1018
Paydarfar JA, Patel UA (2011) Submental island pedicled flap vs radial forearm free flap for oral reconstruction. Arch Otolaryngol - Head Neck Surg 137(1):82–87
Lee JC, Lai W-S, Kao CH, Hsu CH, Chu YH, Lin YS (2013) Multiple-parameter evaluation demonstrates low donor-site morbidity after submental flap harvesting. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 71(10):1800–1808
Lee JC, Chu YH, Lin YS, Kao CH (2013) Reconstruction of hypopharyngeal defects with submental flap after laryngopharyngectomy. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 270(1):319–323
Zhao XP, Zhang H, Yu X, Wang JG, Zhang B, Pan C-B (2013) Reverse facial artery flap to reconstruct the medium-sized defects in the middle facial region following cancer ablation. J Craniofac Surg 24(6):2077–2081
Xuwei D, Jian X, Xueqin L et al (2013) The "Reconstruction of head and neck defects with the submental island flap. Head Neck Oncol 5(2):1–5
Chaudhary B, Gong ZC, Ling B, et al (2014) Application of the submental island flap in the reconstruction of intraoral defects. J Craniofac Surg 25(4). https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000000573
Tsai WC, Yang JM, Liu SC et al (2014) Management of different kinds of head and neck defects with the submental flap for reconstruction. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 272(12):3815–3819
Husso A, Suominen S, Acarturk TO et al (2016) Submental artery flap with sentinel lymph node biopsy in the reconstruction of oral cancer. J Reconstr Microsurg 32(2):153–159
Kramer FJ, Böhrnsen F, Moser N, Schliephake H (2015) The submental island flap for the treatment of intraoral tumor-related defects: no effect on recurrence rates. Oral Oncol 51(7):668–673
Sagüillo K, García-Serrano G, Almeida F, Núñez J, Picón M, Acero J (2015) Submental flap in reconstruction of orofacial defects. Rev Esp Cir Oral y Maxilofac 37(4):196–201
Li P, Fang QG, Luo RH et al (2015) Reconstruction of full-thickness buccal defects with submental island flap. J Craniofac Surg 26(2):e104–e106
Rahpeyma A, Khajehahmadi S (2015) Reconstruction of the maxilla by submental flap. ANZ J Surg 85(11):873–877
Thomas S, Varghese BT, Ganesh SA et al (2016) Oncological safety of submental artery island flap in oral reconstruction - analysis of 229 cases. Indian J Surg Oncol 7(4):420–424
Aslam-Pervez N, Caldroney SJ, Isaiah A, Lubek JE (2018) A retrospective volume matched analysis of the submental artery island pedicled flap as compared to the forearm free flap: is it a good alternative choice for the reconstruction of defects of the oral cavity and oropharynx? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 76(3):656–663
Poccia I, Lin CY, Cheng MH (2017) Platysma-sparing vascularized submental lymph node flap transfer for extremity lymphedema. J Surg Oncol 115(1):48–53
Roshdy S, Elbadrawy M, Khater A et al (2017) Compartmental tongue resection with submental island flap reconstruction for large carcinoma of the oral tongue. Oral Maxillofac Surg 21(3):289–294
Barton BM, Riley CA, Pou JD, Hasney CP, Moore BA (2018) The submental island flap is a viable reconstructive option for a variety of head and neck ablative defects. Ochsner J 18(1):53–58
Karimi E, Badiei R, Aghazadeh K, Sohrabpour S, Yazdani N, Dabiri S (2018) Effect of prior radiotherapy on the outcome of submental island flap in head and neck reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg 29(7):1821–1824
Chen WL, Wang YY, Zhou B, Wen ZZ, Yuan KF, Chen YJ (2020) Survival and functional outcomes of patients who underwent facial-submental artery island flap reconstruction after oral cavity Or HPV-negative oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma ablation. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg 121(4):383–389
Maharaj K, Singh M, Siddiqi J, Ghaly GA (2019) Submental island flap for oropharyngeal reconstruction: UK experience of 25 cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57(10):1102–1106
Ou X-R, Su T, Huang L, et al (2019) A comparative study between submandibular-facial artery island flaps (including perforator flap) and submental artery perforator flap: a novel flap in oral cavity reconstruction. Oral Oncol 99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104446
Patel AV, Thuener JE, Clancy K, Ascha M, Manzoor NF, Zender CA (2018) Submental artery island flap versus free flap reconstruction of lateral facial soft tissue and parotidectomy defects: Comparison of outcomes and patient factors. Oral Oncol 78:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.01.027
Mendieta Espinosa M, Palacios Juárez J, Siu Bermúdez A, Fernández RR (2019) Colgajo submentoniano: aplicaciones clínicas y variantes en su diseño. Cirugía Plástica Ibero-Latinoamericana 45(4):395–404
Wang J, Tan Y, Shen Y, Lv M, Li J, Sun J (2020) Oncological safety of submental island flap for reconstruction of pathologically node-negative and node-positive T1–2 oral squamous cell carcinoma-related defects: a retrospective study and comparison of outcomes. Oral Oncol 102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104507
Chang BA, Ryan Hall S, Howard BE et al (2019) Submental flap for reconstruction of anterior skull base, Orbital, And High Facial Defects. Am J Otolaryngol - Head Neck Med Surg 40(2):218–223
Yilmaz M, Menderes A, Barutcu A (1997) Submental artery island flap for reconstruction of the lower and mid face. Ann Plast Surg 39(1):30–35
Abouchadi A, Capon-Degardin N, Patenôtre P, Martinot-Duquennoy V, Pellerin P (2007) The submental flap in facial reconstruction: advantages and limitations. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65(5):863–869
Mashrah MA, Zhou SH, Abdelrehem A et al (2016) Oropharyngeal reconstruction with a pedicled submandibular gland flap. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 54(4):388–393
Demir Z, Kurtay A, Sahin U, Velidedeoğlu H, Celebioğlu S (2003) Hair-bearing submental artery island flap for reconstruction of mustache and beard. Plast Reconstr Surg 2:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000070520.96829.85
Howard BE, Nagel TH, Donald CB, Hinni ML, Hayden RE (2014) Oncologic safety of the submental flap for reconstruction in oral cavity malignancies. In: Otolaryngology - head and neck surgery (United States). Vol 150. Mosby Inc. 558–562. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599814520687
Sittitrai P, Srivanitchapoom C, Reunmakkaew D, Yata K (2017) Submental island flap reconstruction in oral cavity cancer patients with level I lymph node metastasis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55(3):251–255
Yamauchi M, Yotsuyanagi T, Ezoe K, Saito T, Ikeda K, Arai K (2010) Reverse facial artery flap from the submental region. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 63(4):583–588
Strantzias P, Botou A, Manoli A, Skandalakis PN, Filippou D (2019) Variation of marginal mandibular nerve in a Caucasian male cadaver: a study using the anatomage table. Cureus 11(11). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.6168
Marcuzzo AV, Šuran-Brunelli AN, Dal Cin E et al (2020) Surgical anatomy of the marginal mandibular nerve: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Anat 33(5):739–750
Bennett MH, Feldmeier J, Hampson NB, Smee R, Milross C (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for late radiation tissue injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016(4):1–60
Jagetia GC, Rajanikant GK, Mallikarjun Rao KVN (2003) Modulation of radiation-induced delay in the wound healing by ascorbic acid in mice exposed to different doses of hemi-body gamma radiation. Wounds 15(10):324–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
For this type of review study, formal consent from a local ethics committee is not required.
Informed consent
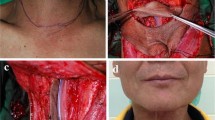
The only patient shown in the study provided verbal and written consent before their inclusion in this study. Additional consent was obtained for the use of his images.
Conflict of interest
Erik Hanson-Viana, Marco Aurelio Rendón-Medina, María de los Ángeles Mendoza-Vélez, Ricardo C. Pacheco-López, and Julio Palacios-Juárez declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanson-Viana, E., Rendón-Medina, M.A., Mendoza-Vélez, M. et al. Refinements of the submental island flap donor site: a literature review and comparison among surgical specialties. Eur J Plast Surg 45, 215–222 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-021-01813-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-021-01813-5