Abstract
Background
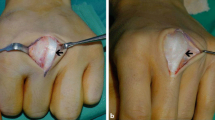
Extensor indicis opponensplasty is the gold standard treatment for the restoration of opposition in individuals with median nerve injuries, and it has excellent outcomes. Most authors have used the Sundraraj and Mani scoring system, which considered a thumb reaching any fingertip as a good or excellent outcome. To refine the technique for extensor indicis opponensplasty, we propose an informative yet simple system to describe outcomes.
Methods
This study included 13 patients who underwent extensor indicis opponensplasty for median nerve injuries, with four isolated and nine combined. Six patients had triple insertions, and seven had single/double insertions. The patients were evaluated using the Sundraraj and Mani system and our proposed system for the primary outcome. Secondary outcomes included return to productivity and complications.
Results
We demonstrated that 92% of the patients achieved excellent results according to the Sundraraj and Mani system. We achieved pulp to little pulp (5A) in seven patients, tip to little pulp (5B) in two patients, pulp to ring pulp (4A) in one patient, tip to ring pulp (4B) in one patient, pulp to middle finger pulp (3A) in one patient, and fair opposition (1) in one patient. A 5A score was achieved in five patients with triple insertion.
Conclusions
The new system proposed in this study better facilitates the comparison of technical variations of opponensplasty.
Level of evidence:Level IV, therapeutic study.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shin EK, Meals RA (2005) The historical importance of the hand in advancing the study of human anatomy. J hand surg 30–2:209–221
Lee CK, Buncke GM (2007) Great toe-to-thumb microvascular transplantation. Clin Plastic Surg 34:223–231
Edmunds JO (2011) Current concepts of the anatomy of the thumb Trapeziometacarpal joint. J Hand Surg 36A:170–182
Jones NF (2013) Tendon transfers in the upper extremity. In: Neligan PC, Chang J (eds) Plastic Surgery, Hand and Upper Extremity, vol 745, 3rd edn. Saunders /Elsevier, Philadelphia, p 776
Burkhalter WE, Christensen RC, Brown P (1973) Extensor indicis proprius opponensplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 55A:725–732
Al-Qattan MH (2012) Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty for isolated traumatic low median nerve palsy: a case series. Can J Plast Surg 20:255–257
Akram M, Farooqi FM, Shahzad ML, Irshad M, Sah RK, Awais SM (2014) Burkhalter opponensplasty; role in isolated median nerve injury. J Pak Med Assoc 64:S172–S174
Guiffre JL, Bishop AT, Spinner RJ, Shin AY (2015) The best of tendon and nerve transfers in the upper extremity. Plast Reconstr Surg 135:617e–630e
Chadderon RC, Gatson RG (2016) Low median nerve transfers (opponensplasty). Hand Clin 32:349–359
Lee DH, Oakes JE, Ferlic RJ (2003) Tendon transfers for thumb opposition: a biomechanical study of pulley location and two insertion sites. J Hand Surg 28:1002–1008
Littler JW (1949) Tendon transfers and arthrodeses in combined median and ulnar nerve paralysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 31A:225–234
Riordan DC (1964) Tendon transfers for nerve paralysis of the hand and wrist. Curr Pract Orthop Surg 2:17–40
Brand PW (1970) Tendon transfers for median and ulnar nerve paralysis. Orthop Clin North Am 1:447–454
Davis TRC (2017) Principles of tendon transfers of median, radial, and ulnar nerves. In: Wolfe SW, Hotchkiss RN, Pederson WC, Kozin SH, Cohen MS (eds) Green's operative hand surgery, 7th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA, pp 19103–2899
Sundararaj GD, Mani K (1984) Surgical reconstruction of the hand with triple nerve palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 66B:260–264
Jacobs B, Thompson TC (1960) Opposition of the thumb and its restoration. J Bone Joint Surg Am 42A:1389–1396
Mehta R, Malaviya GN (1996) Evaluation of the results of opponensplasty. J Hand Surg 21B:622–623
Kapandji A (1986) Clinical test of apposition and counter-apposition of the thumb. Ann Chir Main 5:67–73
Park IJ, Kim HM, Lee SU, Lee JY, Jeong C (2010) Opponensplasty using palmaris longus tendon and flexor retinaculum pulley in patients with severe carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:829–834
Moehrlen U, Mazzone L, Bieli C, Weber DM (2009) Early mobilization after flexor tendon repair in children. Eur J Ped Surg 19:83–86
De Roode CP, James MA, McCarroll HR Jr (2010) Abductor digit minimi opponensplasty: technique, modifications, and measurement of opposition. Tech Hand Surg 14:51–53
Jaquet JB, Luijsterburg JM, Kalmijn S, Kuypers PDL, Hofman A, Hovius SER (2001) Median, ulnar, and combined median-ulnar nerve injuries: functional outcome and return to productivity. J Trauma 51:687–692
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors did not receive any funding for the completion of this work.
Declaration of conflicting interests
Omar Mohamed Nouh, Shaimaa Mostafa Gad, Youssif Ahmed Khashaba, Ashraf Abolfotooh Khalil, Ashraf El-Sebaie Mohamed, and Mostafa Ahmed Abo Elsoud declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical committee approval
Ethical committee approval was obtained.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients who were part of the study. The study included one minor, and informed consent was obtained from his parents. The consent form included details regarding the preoperative measures, the operative procedure, and the postoperative outcomes, including potential complications. Patients or their legal guardian (one patient) also consented to enrolment in the study and the publication of the results.
Patient consent
Patients provided written consent for the use of their images.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Video 2
(MOV 32710 kb)
(MOV 102427 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nouh, O.M., Gad, S.M., Khashaba, Y.A. et al. Extensor indicis opponensplasty: a modified evaluation system. Eur J Plast Surg 42, 473–480 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-019-1505-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-019-1505-9