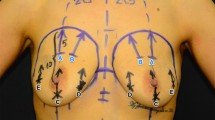
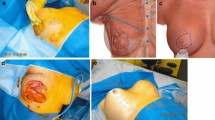
Abstract
Background
Breast augmentation is one of the most highly sought after aesthetic surgeries. For the best outcome, a wide variety of factors such as approach, pocket plane, tissue, and breast characteristics (including asymmetry and ptosis) must be assessed along with the patient’s needs. For patients requiring correction of minor ptosis and breast asymmetry, the current technique involves incisions on the breast, but often the patients are dissatisfied with the visible scars so there is a need for procedures involving less scarring.
Methods
Since 2010, 200 patients with breast hypoplasia have undergone muscle splitting biplane breast augmentation; 32 patients with breast hypoplasia combined either with asymmetry or/and minor ptosis have undergone a technique combining muscle splitting biplane breast augmentation with internal suture mastopexy; 12 patients with dynamic breast following partial submuscular breast augmentation have undergone replacement of the implants using the muscle splitting biplane technique.
Results
Satisfactory long-term outcomes were obtained by using muscle splitting breast augmentation, with or without internal suture mastopexy, with more accurate control of the breast’s natural shape, symmetry, and inframammary fold positions as well as proper cleavage and nipple projection. In this way, a smooth transition between the soft tissue and implant in the breast’s upper pole was possible, and more tissue was available to cover the implant’s upper pole. Nipple sensitivity was preserved with no visible scars on the breast.
Conclusions
The muscle splitting biplane breast augmentation offers improved long-term aesthetic outcomes; is extremely versatile, fast, and easy; and may also be used in patients requiring removal and replacement of breast implants. In combination with the internal mastopexy, this technique is an effective alternative in selected patients requiring correction of breast asymmetry and minor ptosis.
Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cronin TD, Gerow RM (1964) Augmentation mammoplasty: New “natural feel” prosthesis. In the translation of the Third International Congress of the Plastic Surgery. Excerpta Medica International Congress Series, no. 66 Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 41–49
Dempsey WC, Latham WD (1968) Subpectoral implants in augmentation mammoplasty: a preliminary report. Plast Reconstr Surg 42:515
Regnault P (1977) Partially submuscular breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 59:72
Tebbetts JB (2001) Dual-plane breast augmentation: optimizing implant-soft tissue relationship in a wide range of breast types. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:1255
Graf RM, Bernardes A, Rippel R et al (2003) Subfascial breast implant: a new procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:904–908
Sampaio Goes JC, Landecker A (2003) Optimizing outcomes in breast augmentation: seven years experience with the subfascial plane. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27:178–184
Barbato C, Pena M, Triana C et al (2004) Augmentation mammoplasty using the retrofascia approach. Aesthetic Plast Surg 28:148–152
Baxter RA (2005) Subfascial breast augmentation: theme and variations. Aesthet Surg J 25:447–453
Siclovan HR, Jomah JA (2008) Advantages and outcomes in subfascial breast augmentation: a two-year review of experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32:426–431
Tijerina VNE, Saenz RAE, Garcia-Guerrero J (2010) Experience of 1000 cases on subfascial breast augmentation. Aesthet Plast Surg 34:16–22
Khan UD (2007) Muscle-splitting breast augmentation: a new pocket in a different plane. Aesthetic Plast Surg 31:553–558
Khan UD (2009) Dynamic breasts: a common complication following partial submuscular augmentation and its correction using the muscle-splitting biplane technique. Aesthetic Plast Surg 33:353–360
Lang Stümpfle R, Pereira-Lima LF, Alves Valiati A et al (2012) Transaxillary muscle-splitting breast augmentation: experience with 160 cases. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36:343–348
Mahabir RC, Zamboni WA (2008) A new technique of internal suture mastopexy for mild to moderate breast ptosis. Can J Plast Surg 16(1):11–13
Khan UD (2011) Multiplane technique for simultaneous submuscular breast augmentation and internal glandulopexy using inframammary crease incision in selected patients with early ptosis. Eur J Plast Surg 34:337–343
Tebbetts JB, Adams W (2006) Five critical decisions in breast augmentation using five measurements in 5 minutes: the high five decision support process. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(Suppl):35S
Tebbets JB (2002) Breast implants selection based on patient tissue characteristics and dynamics: the TEPID approach. Plast Reconstr Surg 190:1396
Conflict of interest
None
Patient consent
Patients provided written consent for the use of their images.
Ethical Standards
For this type of retrospective study formal consent is not required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siclovan, H.R. Versatility of muscle splitting biplane technique associated with internal mastopexy in breast hypoplasia, ptosis, and asymmetry. Eur J Plast Surg 38, 37–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-014-1029-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-014-1029-2