Abstract
Background
When performing breast augmentation in patients affected by mild-moderate ptosis or pseudoptosis, the plastic surgeon often has to choose whether to perform a glandular mastopexy or not. This decision is controversial not only due to the residual scarring, but also breast reshaping with potential asymmetries, often poorly tolerated or directly rejected by the patient herself.
Methods
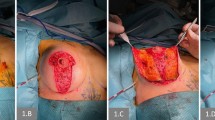
We performed the “slip sliding technique” on nine Caucasian female patients from July 2011 to April 2014. By this technique, a glandular reshaping is performed with a single superior half-moon-shaped periareolar access and an undermining above and underneath the muscle. The breast implant is positioned in the submuscular plane and the breast parenchyma is lifted cranially, resulting in a mastopexy-augmented breast without its traditional scars.
Results
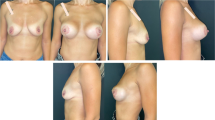
Ptosis and pseudoptosis correction were satisfactory in all cases to both patients and surgeons. No ptosis recurrence or asymmetries were observed.
Conclusions
Despite the recent introduction and a limited number of treated patients, the slip sliding technique has proven to reach good results in patients where breast augmentation alone is doubtful. In our opinion, the slip sliding is a valid technique when mastopexy has to be associated to breast augmentation surgery in selected patients.
Level of Evidence: Level V, therapeutic study.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Regnault P (1966) The hypoplastic and ptotic breast: a combined operation with prosthetic augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 37:31
Davison SP, Spear SL (2004) Simultaneous breast augmentation with periareolar mastopexy. Semin Plast Surg 18(3):189
Medard de Chardon V, Balaguer T, Chignon-Sicard B, Lebreton E (2010) Double breast contour in primary aesthetic breast augmentation: incidence, prevention and treatment. Ann Plast Surg 64(4):390
Maxwell GP, Birchenugh SA, Gabriel A (2009) Efficacy of neopectoral pocket in revisionary breast surgery. Aesthet Surg J 29(5):379
Baran CN, Peker F, Ortak T, Sensöz O, Baran NK (2001) Unsatisfactory results of periareolar mastopexy with or without augmentation and reduction mammoplasty: enlarged areola with flattened nipple. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 25(4):286
Spear SL, Low M, Ducic I (2003) Revision augmentation mastopexy: indications, operation, and outcomes. Ann Plast Surg 51(6):540
Rohrich RJ, Thornton JF, Jakubietz RG, Jakubietz MG, Grünert JG (2004) The limited scar mastopexy: current concepts and approaches to correct breast ptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(6):1622–1630
Persof MM (2003) Mastopexy with expansion augmentation. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 27(2):13
Karnes J, Morrison W, Salisbury M, Schaeferle M, Beckman P, Ersek RA (2000) Simultaneous breast augmentation and lift. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 24(2):148
Tebbets JB (2001) Dual plane breast augmentation: optimizing implant-soft-tissue relationship in a wide range of breast types. Plast Reconstr Surg 107(5):1255
Mahabir RC, Zamboni WA (2008) A new technique of internal suture mastopexy for mild to moderate breast ptosis. Can J Plast Surg 16(1):11–13
Khan UD (2011) Multiplane technique for simultaneous submuscular breast augmentation and internal glandulopexy using inframammary crease incision in selected patients with early ptosis. Eur J Plast Surg 34(5):337–343
Güven E, Sakinsel A, Başaran K, Yazar M, Bozkurt M, Kuvat SV (2012) Combined superior crescentic total glandular augmentation mastopexy: report of 37 cases. Eur J Plast Surg 35(1):43–48
Conflict of interest
None
Ethical standards
For this type of retrospective study formal consent is not required.
Patient consent
Patients provided written consent for the use of their images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruschi, S., Bocchiotti, M.A., Ruka, E. et al. “Slip sliding” technique. A new method to perform mastopexy-augmentation. Eur J Plast Surg 38, 117–122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-014-1027-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-014-1027-4