Abstract
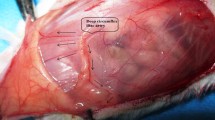
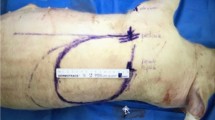
Random-pattern flap transfer is one of the most popular procedures for covering soft tissue defects. Ischemic preconditioning is a protective endogenous mechanism capable of reducing ischemia-reperfusion injury, and it has been shown that preconditioning by proximal pedicle clamping can improve flap survival. However, the method is not suitable for random-pattern flap transfer in the clinical setting. The present study evaluates the effect of ischemic preconditioning of Wistar rat hind limbs upon dorsal random-pattern skin flap survival. Ischemic preconditioning was induced by ischemia of the right hind limb during 10 min, followed by 30 min of reperfusion. Thirty-two animals were divided in two groups. In group 1, a dorsal random-pattern skin flap measuring 2 × 7 cm was raised immediately after the induction of ischemic preconditioning. The animals in group 2 (controls) received the same treatment, but without ischemic preconditioning. The survival area was defined as the surface of the viable tissue (square centimeter) on the fifth postoperative day. The average survival area was 6.57 ± 0.18 cm2 in group 1 and 4.44 ± 0.21 cm2 in group 2. All preconditioned animals presented significantly higher flap survival areas than the controls (p ≤ 0.01, Student’s t test). Our findings show that flap necrosis was reduced by the induction of ischemic preconditioning in a body area distant from the flap harvest site, and that ischemic preconditioning has a systemic protective effect on dorsal random-pattern skin flaps and increase survival. A better understanding of the mechanism involved may improve the clinical condition of patients requiring random-pattern skin flap transfer, especially in high-risk groups.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerrigan CL (1983) Skin flap failure: pathophysiology. Plast Reconstr Surg 72:766–777
Zamierowski DS (2005) Pharmacologic enhancement of rat skin flap survival. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(7):2145
Sarifakioglu N, Gokrem S, Ates L, Akbuga UB, Aslan G (2004) The influence of sildenafil on random skin flap survival in rats: an experimental study. Br J Plast Surg 57(8):769–772
Raposio E, Santi PL (1998) Pharmacological enhancement of cutaneous flap survival with topical dimethyl sulphoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Br J Plast Surg 51(7):551–554
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124–1136
Ghosh S, Galiñanes M (2003) Protection of the human heart with ischemic preconditioning during cardiac surgery: role of cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126(1):133–142
Lloris-Carsi JM, Cejalvo D, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Calvo MA, Suzuki S (1993) Preconditioning: effect upon lesion modulation in warm liver ischemia. Transplant Proc 25(6):3303–3304
Arai M, Tejima K, Ikeda H et al (2007) Ischemic preconditioning in liver pathophysiology. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(Suppl 1):S65–S67
Salehipour M, Khezri A, Monabbati A et al (2007) Ischemic preconditioning protects the dog kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Urol Int 79(4):328–331
Mounsey RA, Pang CY, Forrest C (1992) Preconditioning: a new technique for improved muscle flap survival. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 107(4):549–552
Carroll CM, Carroll SM, Overgoor ML, Tobin G, Barker JH (1997) Acute ischemic preconditioning of skeletal muscle prior to flap elevation augments muscle flap survival. Plast Reconstr Surg 100(1):58–65
Zahir KS, Syed SA, Zink JR, Restifo RJ, Thomson JG (1998) Ischemic preconditioning improves the survival of skin and myocutaneous flaps in a rat model. Plast Reconstr Surg 102(1):140–150, discussion 151-2
Wang WZ, Anderson G, Firrell JC, Tsai TM (1998) Ischemic preconditioning versus intermittent reperfusion to improve blood flow to a vascular isolated skeletal muscle flap of rats. J Trauma 45(5):953–959
Wang WZ, Anderson G, Maldonado C, Barker J (1996) Attenuation of vasospasm and capillary no-reflow by ischemic preconditioning in skeletal muscle. Microsurgery 17(6):324–329
Pang CY, Neligan P, Xu H et al (1997) Role of ATP-sensitive K + channels in ischemic preconditioning of skeletal muscle against infarction. Am J Physiol 273(1 Pt 2):H44–H51
Restifo RJ, Thomson JG (1998) The preconditioned TRAM flap: preliminary clinical experience. Ann Plast Surg 41(4):343–347
Küntscher MV, Schirmbeck EU, Menke H, Klar E, Gebhard MM, Germann G (2002) Ischemic preconditioning by brief extremity ischemia before flap ischemia in a rat model. Plast Reconstr Surg 109(7):2398–2404
McFarlane RM, De Young G, Henry R (1965) The design of a pedicle flap in the rat to study necrosis and its prevention. Plast Reconstr Surg 35:177–182
Hammond DC, Brooksher RD, Mann RJ, Beernink JH (1993) The dorsal skin-flap model in the rat: factors influencing survival. Plast Reconstr Surg 91(2):316–321
Pal S, Khazanchi RK, Moudgil K (1991) An experimental study on the effect of nifedipine on ischaemic skin flap survival in rats. Br J Plast Surg 44(4):299–301
Israeli D, Zhang WX, Senderoff DM, Urken ML, Weinberg H (1994) Use of urokinase during secondary ischemia in experimental skin flaps. Ann Plast Surg 32(3):305–309
Forrest CR, Pang CY, Zhong AG, Kreidstein ML (1991) Efficacy of intravenous infusion of prostacyclin (PGI2) or prostaglandin El (PGE1) in augmentation of skin flap blood flow and viability in the pig. Prostaglandins 41(6):537–558
Zamboni WA, Roth AC, Russell RC, Smoot EC (1992) The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on reperfusion of ischemic axial skin flaps: a laser Doppler analysis. Ann Plast Surg 28(4):339–341
Odland RM, Poole DV, Rice RD Jr, Koobs DH (1995) Use of the tunable dye laser to delay McFarlane skin flaps. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121(10):1158–1161
Addison P, Neligan P, Forrest C, Zhong A, Perri L, Pang CY (2003) Acute adenosine treatment is effective in augmentation of ischemic tolerance in muscle flaps in the pig: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg 111(2):842–845
Küntscher MV, Kastell T, Altmann J, Menke H, Gebhard MM, Germann G (2002) Acute remote ischemic preconditioning II: the role of nitric oxide. Microsurgery 22(6):227–231
Küntscher MV, Kastell T, Sauerbier M, Nobiling R, Gebhard MM, Germann G (2002) Acute remote ischemic preconditioning on rat cremasteric muscle flap model. Microsurgery 22(6):221–226
Gürke L, Marx A, Sutter PM, Frentzel A, Salm T, Harder F, Seelig J, Heberer M (1996) Ischemic preconditioning improves post-ischemic skeletal muscle function. Am Surg 62(5):391–394
Saito T, Komiyama T, Aramoto H, Miyata T, Shigematsu H (2004) Ischemic preconditioning improves oxygenation of exercising muscle in vivo. J Surg Res 120(1):111–118
Peralta C, Closa D, Hotter G, Gelpí E, Prats N, Roselló-Catafau J (1996) Liver ischemic preconditioning is mediated by the inhibitory action of nitric oxide on endothelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 229(1):264–270
Yin DP, Sankary HN, Chong AS, Ma LL, Shen J, Foster P, Williams JW (1998) Protective effect of ischemic preconditioning on liver preservation-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation 66(2):152–157
Arai M, Peng XX, Currin RT, Thurman RG, Lemasters JJ (1999) Protection of sinusoidal endothelial cells against storage/reperfusion injury by prostaglandin E2 derived from Kupffer cells. Transplantation 68(3):440–445
Peralta C, Fernández L, Panés J, Prats N, Sans M, Piqué JM, Gelpí E, Roselló-Catafau J (2001) Preconditioning protects against systemic disorders associated with hepatic ischemia-reperfusion through blockade of tumor necrosis factor-induced P-selectin up-regulation in the rat. Hepatology 33(1):100–113
Fernández L, Heredia N, Grande L, Gómez G, Rimola A, Marco A, Gelpí E, Roselló-Catafau J, Peralta C (2002) Preconditioning protects liver and lung damage in rat liver transplantation: role of xanthine/xanthine oxidase. Hepatology 36(3):562–572
Souza Filho MV, Loiola RT, Rocha EL, Simão AF, Gomes AS, Souza MH, Ribeiro RA (2009) Hind limb ischemic preconditioning induces an anti-inflammatory response by remote organs in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res 42(10):921–929
Addison PD, Neligan PC, Ashrafpour H, Khan A, Zhong A, Moses M, Forrest CR, Pang CY (2003) Noninvasive remote ischemic preconditioning for global protection of skeletal muscle against infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285(4):H1435–H1443
Matsumura H, Yoshizawa N, Vedder NB, Watanabe K (2001) Preconditioning of the distal portion of a rat random-pattern skin flap. Br J Plast Surg 54(1):58–61
Yamashita N, Hoshida S, Nishida M et al (1997) Time course of tolerance to ischemia-reperfusion injury and induction of heat shock protein 72 by heat stress in the rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 29(7):1815–1821
Cleveland JC Jr, Meldrum DR, Rowland RT, Banerjee A, Harken AH (1997) Preconditioning and hypothermic cardioplegia protect human heart equally against ischemia. Ann Thorac Surg 63(1):147–152
Riepe MW, Esclaire F, Kasischke K et al (1997) Increased hypoxic tolerance by chemical inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation: “chemical preconditioning”. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17(3):257–264
Friehs I, Moran AM, Stamm C et al (2004) Promoting angiogenesis protects severely hypertrophied hearts from ischemic injury. Ann Thorac Surg 77(6):2004–2010
Harder Y, Amon M, Laschke MW et al (2008) An old dream revitalised: preconditioning strategies to protect surgical flaps from critical ischaemia and ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61(5):503–511
Kiumehr S, Demehri S, Rabbani S, Amanpour S, Mohagheghi MA, Dehpour AR (2005) Preconditioning of the rat random-pattern skin flap: modulation by opioids. Br J Plast Surg 58(1):58–64
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponte de Souza Filho, M.V., Loiola, R.T., Rocha, E.L. et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning improves the survival of rat random-pattern skin flaps. Eur J Plast Surg 33, 147–152 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-010-0402-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-010-0402-z