Abstract
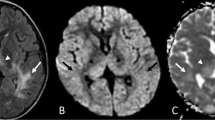
Our purpose was to investigate the role of diffusion imaging (DI) in central nervous system (CNS) infections in pediatric patients. It was anticipated that DI would be more sensitive than conventional MRI in the detection of the infarctive complications of infection, and possibly, in the detection of the infectious process as well. Seventeen pediatric patients, eight having meningitis,, five with herpes encephalitis, three with brain abscess or cerebritis and one with sepsis, were evaluated at 1.5-T with DI. All herpes patients had positive DI at the site of herpetic involvement, and two had the addition of watershed infarctions. DI demonstrated more lesions in three of the four cases of herpetic encephalitis. Half the meningitis cases had watershed infarction where DI was better and half had vasculitic infarctions in which DI was equal to or better than conventional MRI. Diffusion imaging was more sensitive than conventional MRI alone in detection of changes due to infections and ischemic lesions, but did not differentiate between them by DI or apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), although anatomic distribution of lesions proved useful.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, J., Zimmerman, R., Haselgrove, J. et al. Diffusion imaging in pediatric central nervous system infections. Neuroradiology 43, 1031–1039 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340100625
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340100625