Abstract
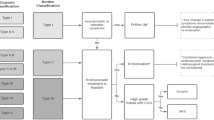
Intracranial pial and dural arteriovenous shunts may exist at different sites in the same patient. The etiology, natural history and treatment of these associated conditions have not been completely determined. We reviewed the records of 765 cases of pial arteriovenous malformation and 137 dural arteriovenous fistulae and malformations. We selected eight patients with both pial and dural arteriovenous shunts, separate anatomically, with distinct feeding arteries and draining veins, representing 1 % of pial and 17 % of dural shunts. Presentation was related to the dural lesion in 5 cases (62.5 %) and to the pial malformation in three (37.5 %). Treatment of these lesions should be considered separately based on their angioarchitecture and natural history.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 January 2001/Accepted: 10 January 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilela, P., terBrugge, K. & Willinsky, R. Association of distinct intracranial pial and dural arteriovenous shunts. Neuroradiology 43, 770–777 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340100571
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340100571