Abstract
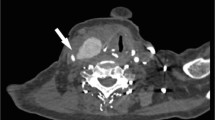
Traumatic internal carotid dissection occurs frequently in motor vehicle accidents, typically extracranially, close to the skull base. Dissection may lead to stenosis or occlusion of the vessel, possibly with a pseudoaneurysm, symptoms ranging from neck pain to neurological deficits. In symptomatic patients and in cases of pseudoaneurysm, when conservative medical treatment fails, surgery or endovascular treatment are indicated. We report a post-traumatic dissecting aneurysm of the extracranial internal carotid artery successfully treated with stenting via a transfemoral approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 November 1998 Accepted: 5 December 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simionato, F., Righi, C. & Scotti, G. Post-traumatic dissecting aneurysm of extracranial internal carotid artery: endovascular treatment with stenting. Neuroradiology 41, 543–547 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050801
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050801