Abstract
Purpose
The cortical high-flow sign with the non-enhancing area was reportedly found to be more frequent with oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q codeleted (ODG IDHm-codel) than with IDH-wildtype or astrocytoma, IDH-mutant on arterial spin labeling (ASL) in diffuse gliomas. This study aimed to compare the identification rate of the cortical high-flow sign on ASL in patients with ODG IDHm-codel to that on dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion-weighted imaging (DSC-PWI).
Methods
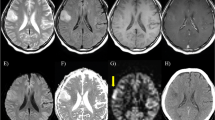
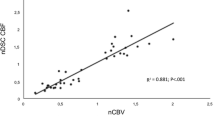
Participants consisted of 32 adult ODG IDHm-codel patients with pathologically confirmed. Subtraction images were generated from paired control and label images on ASL. For DSC, dynamic T2*-weighted perfusion weighted images were obtained after pre-bolus of gadolinium-based contrast agent. Regional cerebral blood flow/volume maps were generated based on the concentration–time curve and arterial input function. Tumor-affecting cortices without contrast enhancement on conventional MR imaging were targeted. The identification rate of the cortical high-flow sign was compared between ASL and DSC using the Pearson’s Chi-Square test.
Results
Frequency of the cortical high-flow sign was significantly higher on ASL (18/32, 56.3%; p < 0.001) than on DSC (5/32, 15.6%). All cases with the positive cortical high-flow sign on DSC were identified on ASL.
Conclusion
ASL effectively identifies the cortical high-flow sign in ODG IDHm-codel, surpassing DSC in identification rates.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASL:
-
Arterial spin labeling
- DSC:
-
Dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced
- IDH :
-
isocitrate dehydrogenase
- ODG IDHm-codel :
-
Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PWI:
-
Perfusion-weighted imaging
References
Yamashita K, Togao O, Kikuchi K et al (2023) Cortical high-flow sign on arterial spin labeling: a novel biomarker for IDH-mutation and 1p/19q-codeletion status in diffuse gliomas without intense contrast enhancement. Neuroradiology 65:1415–1418
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (2021) World Health Organization classification of tumours of the central nervous system, 5th edn. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Van den Bent MJ, Reni M, Gatta G, Vecht C (2008) Oligodendroglioma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 66:262–272
Weber MA, Zoubaa S, Schlieter M et al (2006) Diagnostic performance of spectroscopic and perfusion MRI for distinction of brain tumors. Neurology 66:1899–1906
Noguchi T, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A et al (2008) Perfusion imaging of brain tumors using arterial spin-labeling: correlation with histopathologic vascular density. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:688–693
Yamashita K, Hiwatashi A, Togao O et al (2016) MR Imaging-Based Analysis of Glioblastoma Multiforme: Estimation of IDH1 Mutation Status. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:58–65
Law M, Yang S, Babb JS et al (2004) Comparison of cerebral blood volume and vascular permeability from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging with glioma grade. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:746–755
Boxerman JL, Quarles CC, Hu LS et al (2020) Consensus recommendations for a dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI protocol for use in high-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol 22:1262–1275
Järnum H, Steffensen EG, Knutsson L et al (2009) Perfusion MRI of brain tumours: a comparative study of pseudo-continuous arterial spin labelling and dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging. Neuroradiology 52:307–317
Xu Q, Liu Q, Ge H et al (2017) Tumor recurrence versus treatment effects in glioma: A comparative study of three dimensional pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e9332
Lavrova A, Teunissen WHT, Warnert EAH, van den Bent M, Smits M (2022) Diagnostic Accuracy of Arterial Spin Labeling in Comparison With Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced Perfusion for Brain Tumor Surveillance at 3T MRI. Front Oncol 12:849657
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Koeller KK, Rushing EJ (2005) From the archives of the AFIP: Oligodendroglioma and its variants: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 25:1669–1688
Smits M (2016) Imaging of oligodendroglioma. Br J Radiol 89:20150857
Latysheva A, Emblem KE, Brandal P et al (2019) Dynamic susceptibility contrast and diffusion MR imaging identify oligodendroglioma as defined by the 2016 WHO classification for brain tumors: histogram analysis approach. Neuroradiology 61:545–555
Qi Y, Roper M (2021) Control of low flow regions in the cortical vasculature determines optimal arterio-venous ratios. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118:e2021840118
Chang EF, Potts MB, Keles GE et al (2008) Seizure characteristics and control following resection in 332 patients with low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg 108:227–235
Smits A, Duffau H (2011) Seizures and the natural history of World Health Organization Grade II gliomas: a review. Neurosurgery 68:1326–1333
Kerkhof M, Benit C, Duran-Pena A, Vecht CJ (2015) Seizures in oligodendroglial tumors. CNS. Oncol 4:347–356
Frayne R, Goodyear BG, Dickhoff P, Lauzon ML, Sevick RJ (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging at 3.0 Tesla: challenges and advantages in clinical neurological imaging. Invest Radiol 38:385–402
Funding
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant number 22K07657.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K Yamashita, OT, KK, DK, YS, YF, K Yoshimoto, and KI: Nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the institutional review board of our hospital (Kyushu University Institutional Review Board for Clinical Research).
Informed consent
Informed consent was waived because this study was retrospective nature.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, K., Togao, O., Kikuchi, K. et al. The cortical high-flow sign of oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted: comparison between arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility contrast methods. Neuroradiology 66, 187–192 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03267-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03267-x