Abstract
Purpose
To confirm the hypothesis that brain white matter damage is involved in the pathogenesis and disease progression of Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)-associated neurodegenerative disease (ND), we aimed to analyze pediatric patients with LCH using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI).
Methods
We enrolled 33 patients with LCH and obtained 33 DTI datasets. Using DTI-based tractography, fractional anisotropy (FA), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), axial diffusivity (AD), and radial diffusivity (RD) were measured in the cerebral and cerebellar white matter tracts. The participants were divided into three groups—non-ND, ND without clinical symptoms (r-ND), and ND with clinical symptoms (c-ND)—according to their clinical status during the examination with DTI. We compared the DTI parameters in white matter tracts were compared among the three groups.
Results
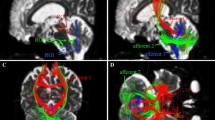
In the order of non-ND, r-ND, and c-ND groups, the FA in superior cerebellar peduncle (SCP) and middle cerebellar peduncle (MCP) significantly decreased, the ADC, AD, and RD of MCP, and the RD of SCP were significantly elevated (FA-SCP; p < 0.001, FA-MCP; p = 0.026, ADC-MCP; p < 0.001, AD-MCP; p = 0.002, RD-MCP; p = 0.003, and RD-SCP; p = 0.018). Furthermore, in the simple linear regression analysis, the FA, ADC, AD, and RD values in the MCP and the FA value in the SCP were significantly influenced by the presence of neurological symptoms and ND findings on MRI (all p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In LCH-ND, we identified microstructural damage in the SCP and MCP. DTI parameters in these tracts may help monitor LCH-ND; therefore, future studies are required to validate these results in a large cohort.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The clinical information and DTI parameters for each patient that led to the results presented in this study can be downloaded from the Harvard Database Repository at https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/URF4IU.
References
Morimoto A, Oh Y, Shioda Y, Kudo K, Imamura T (2014) Recent advances in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr Int 56(4):451–461
Rigaud C, Barkaoui MA, Thomas C, Bertrand Y, Lambilliotte A, Miron J, Aladjidi N, Plat G, Jeziorski E, Galambrun C, Mansuy L, Lutz P, Deville A, Armari-Alla C, Reguerre Y, Fraitag S, Coulomb A, Gandemer V, Leboulanger N, Moshous D, Hoang-Xuan K, Tazi A, Heritier S, Emile JF, Donadieu J (2016) Langerhans cell histiocytosis: therapeutic strategy and outcome in a 30-year nationwide cohort of 1478 patients under 18 years of age. Br J Haematol 174(6):887–898
Sakamoto K, Morimoto A, Shioda Y, Imamura T, Imashuku S, Japan LCHSG (2021) Long-term complications in uniformly treated paediatric Langerhans histiocytosis patients disclosed by 12 years of follow-up of the JLSG-96/02 studies. Br J Haematol 192(3):615–620
Grois N, Potschger U, Prosch H, Minkov M, Arico M, Braier J, Henter JI, Janka-Schaub G, Ladisch S, Ritter J, Steiner M, Unger E, Gadner H, Dalhx LI, Committee IIS (2006) Risk factors for diabetes insipidus in langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 46(2):228–233
Donadieu J, Rolon MA, Thomas C, Brugieres L, Plantaz D, Emile JF, Frappaz D, David M, Brauner R, Genereau T, Debray D, Cabrol S, Barthez MA, Hoang-Xuan K, Polak M, French LCHSG (2004) Endocrine involvement in pediatric-onset Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis: a population-based study. J Pediatr 144(3):344–350
Heritier S, Barkaoui MA, Miron J, Thomas C, Moshous D, Lambilliotte A, Mazingue F, Kebaili K, Jeziorski E, Plat G, Aladjidi N, Pacquement H, Galambrun C, Brugieres L, Leverger G, Mansuy L, Paillard C, Deville A, Pagnier A, Lutun A, Gillibert-Yvert M, Stephan JL, Cohen-Aubart F, Haroche J, Pellier I, Millot F, Gandemer V, Martin-Duverneuil N, Taly V, Helias-Rodzewicz Z, Emile JF, Hoang-Xuan K, Idbaih A, Donadieu J (2018) Incidence and risk factors for clinical neurodegenerative Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a longitudinal cohort study. Br J Haematol 183(4):608–617
Haupt R, Minkov M, Astigarraga I, Schafer E, Nanduri V, Jubran R, Egeler RM, Janka G, Micic D, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Van Gool S, Visser J, Weitzman S, Donadieu J, Euro Histio N (2013) Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH): guidelines for diagnosis, clinical work-up, and treatment for patients till the age of 18 years. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(2):175–184
Wnorowski M, Prosch H, Prayer D, Janssen G, Gadner H, Grois N (2008) Pattern and course of neurodegeneration in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr 153(1):127–132
Porto L, Schoning S, Hattingen E, Sorensen J, Jurcoane A, Lehrnbecher T (2015) Central nervous system imaging in childhood Langerhans cell histiocytosis - a reference center analysis. Radiol Oncol 49(3):242–249
Prosch H, Grois N, Wnorowski M, Steiner M, Prayer D (2007) Long-term MR imaging course of neurodegenerative Langerhans cell histiocytosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(6):1022–1028
Filippi M, Agosta F (2016) Diffusion tensor imaging and functional MRI. Handb Clin Neurol 136:1065–1087
Douglas PK, Gutman B, Anderson A, Larios C, Lawrence KE, Narr K, Sengupta B, Cooray G, Douglas DB, Thompson PM, McGough JJ, Bookheimer SY (2018) Hemispheric brain asymmetry differences in youths with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuroimage Clin 18:744–752
Yu Q, Peng Y, Kang H, Peng Q, Ouyang M, Slinger M, Hu D, Shou H, Fang F, Huang H (2020) Differential white matter maturation from birth to 8 years of age. Cereb Cortex 30(4):2673–2689
Hasegawa T, Yamada K, Morimoto M, Morioka S, Tozawa T, Isoda K, Murakami A, Chiyonobu T, Tokuda S, Nishimura A, Nishimura T, Hosoi H (2011) Development of corpus callosum in preterm infants is affected by the prematurity: in vivo assessment of diffusion tensor imaging at term-equivalent age. Pediatr Res 69(3):249–254
Morita T, Morimoto M, Yamada K, Hasegawa T, Morioka S, Kidowaki S, Moroto M, Yamashita S, Maeda H, Chiyonobu T, Tokuda S, Hosoi H (2015) Low-grade intraventricular hemorrhage disrupts cerebellar white matter in preterm infants: evidence from diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroradiology 57(5):507–514
Kara B, Albayram S, Çelik A, Yildirim S, Onat L (2011) DTI findings of brainstem involvement in Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. Clin Neuroradiol 21(1):23–26
Tobyne SM, Ochoa WB, Bireley JD, Smith VM, Geurts JJ, Schmahmann JD, Klawiter EC (2018) Cognitive impairment and the regional distribution of cerebellar lesions in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 24(13):1687–1695
Hannoun S, Kocevar G, Durand-Dubief F, Stamile C, Naji A, Cotton F, Cavallari M, Guttmann CRG, Sappey-Marinier D (2018) Evidence of axonal damage in cerebellar peduncles without T2-lesions in multiple sclerosis. Eur J Radiol 108:114–119
Chen YJ, Nabavizadeh SA, Vossough A, Kumar S, Loevner LA, Mohan S (2017) Wallerian Degeneration beyond the corticospinal tracts: conventional and advanced MRI findings. J Neuroimaging 27(3):272–280
Liang Z, Zeng J, Zhang C, Liu S, Ling X, Xu A, Ling L, Wang F, Pei Z (2008) Longitudinal investigations on the anterograde and retrograde degeneration in the pyramidal tract following pontine infarction with diffusion tensor imaging. Cerebrovasc Dis 25(3):209–216
Khong PL, Zhou LJ, Ooi GC, Chung BH, Cheung RT, Wong VC (2004) The evaluation of Wallerian degeneration in chronic paediatric middle cerebral artery infarction using diffusion tensor MR imaging. Cerebrovasc Dis 18(3):240–247
Qin W, Zhang M, Piao Y, Guo D, Zhu Z, Tian X, Li K, Yu C (2012) Wallerian degeneration in central nervous system: dynamic associations between diffusion indices and their underlying pathology. PLoS ONE 7(7):e41441
Thomalla G, Glauche V, Koch MA, Beaulieu C, Weiller C, Rother J (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging detects early Wallerian degeneration of the pyramidal tract after ischemic stroke. Neuroimage 22(4):1767–1774
Liang Z, Zeng J, Zhang C, Liu S, Ling X, Wang F, Ling L, Hou Q, Xing S, Pei Z (2009) Progression of pathological changes in the middle cerebellar peduncle by diffusion tensor imaging correlates with lesser motor gains after pontine infarction. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 23(7):692–698
Lin X, Tench CR, Morgan PS, Niepel G, Constantinescu CS (2005) ‘Importance sampling’ in MS: use of diffusion tensor tractography to quantify pathology related to specific impairment. J Neurol Sci 237(1–2):13–19
Goldberg-Zimring D, Mewes AU, Maddah M, Warfield SK (2005) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimaging 15(4 Suppl):68S-81S
Markvardsen LH, Vaeggemose M, Ringgaard S, Andersen H (2016) Diffusion tensor imaging can be used to detect lesions in peripheral nerves in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy treated with subcutaneous immunoglobulin. Neuroradiology 58(8):745–752
Winklewski PJ, Sabisz A, Naumczyk P, Jodzio K, Szurowska E, Szarmach A (2018) Understanding the physiopathology behind axial and radial diffusivity changes-what do we know? Front Neurol 9:92
Cohen Aubart F, Idbaih A, Emile JF, Amoura Z, Abdel-Wahab O, Durham BH, Haroche J, Diamond EL (2021) Histiocytosis and the nervous system: from diagnosis to targeted therapies. Neuro Oncol 23(9):1433–1446
McClain KL, Picarsic J, Chakraborty R, Zinn D, Lin H, Abhyankar H, Scull B, Shih A, Lim KPH, Eckstein O, Lubega J, Peters TL, Olea W, Burke T, Ahmed N, Hicks MJ, Tran B, Jones J, Dauser R, Jeng M, Baiocchi R, Schiff D, Goldman S, Heym KM, Wilson H, Carcamo B, Kumar A, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Whipple NS, Campbell P, Murdoch G, Kofler J, Heales S, Malone M, Woltjer R, Quinn JF, Orchard P, Kruer MC, Jaffe R, Manz MG, Lira SA, Parsons DW, Merad M, Man TK, Allen CE (2018) CNS Langerhans cell histiocytosis: common hematopoietic origin for LCH-associated neurodegeneration and mass lesions. Cancer 124(12):2607–2620
Ribeiro MJ, Idbaih A, Thomas C, Remy P, Martin-Duverneuil N, Samson Y, Donadieu J, Hoang-Xuan K (2008) 18F-FDG PET in neurodegenerative Langerhans cell histiocytosis : results and potential interest for an early diagnosis of the disease. J Neurol 255(4):575–580
Sieni E, Barba C, Mortilla M, Savelli S, Grisotto L, Di Giacomo G, Romano K, Fonda C, Biggeri A, Guerrini R, Arico M (2015) Early diagnosis and monitoring of neurodegenerative Langerhans cell histiocytosis. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0131635
Yeh EA, Greenberg J, Abla O, Longoni G, Diamond E, Hermiston M, Tran B, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Allen CE, McClain KL, North American Consortium for Histiocytosis (2018) Evaluation and treatment of Langerhans cell histiocytosis patients with central nervous system abnormalities: current views and new vistas. Pediatr Blood Cancer 65(1):e26784
Baker WJ, Royer GL Jr, Weiss RB (1991) Cytarabine and neurologic toxicity. J Clin Oncol 9(4):679–693
Winkelman MD, Hines JD (1983) Cerebellar degeneration caused by high-dose cytosine arabinoside: a clinicopathological study. Ann Neurol 14(5):520–527
Lebel C, Gee M, Camicioli R, Wieler M, Martin W, Beaulieu C (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter tract evolution over the lifespan. Neuroimage 60(1):340–352
Cancelliere A, Mangano FT, Air EL, Jones BV, Altaye M, Rajagopal A, Holland SK, Hertzler DA 2nd, Yuan W (2013) DTI values in key white matter tracts from infancy through adolescence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34(7):1443–1449
Hermoye L, Saint-Martin C, Cosnard G, Lee SK, Kim J, Nassogne MC, Menten R, Clapuyt P, Donohue PK, Hua K, Wakana S, Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2006) Pediatric diffusion tensor imaging: normal database and observation of the white matter maturation in early childhood. Neuroimage 29(2):493–504
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the study participants and their families. We thank Koji Sakai at the Department of Radiology, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, for advice and guidance on the use of the Trackvis and Diffusion toolkit software and Kengo Yoshii at the Department of Genomic Medical Sciences, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, for statistical advice. We would like to thank Editage (http://www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
This study was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (Grant/Award Number: JP20ck0106605h0001), the research fund of NPO Heart Link working project (Niigata, Japan), and Takeda Science Foundation (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TH, KS, YS, SS, TI, AM, and TI devised this study design. KS and YS contributed to the acquisition of clinical information and YT contributed to the acquisition and interpretation MRI. KS and YS acquired fundings. TI analyzed and interpreted the MRI and diffusion tensor image data and wrote the paper. All coauthors discussed the relationship between the clinical information and the analyzed data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Review Committees of the Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine and the National Center for Child Health and Development (ERB-C-1312).
Consent statement
The attending physician obtained written informed consent from the patients or their parents.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Imai, T., Sakamoto, K., Hasegawa, T. et al. Cerebellar peduncle damage in Langerhans cell histiocytosis-associated neurodegenerative disease revealed by diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroradiology 66, 43–54 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03249-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-023-03249-z